
The lungs are the most important organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. The pleurae, which are thin, smooth, and moist, serve to reduce friction between the lungs and chest wall during breathing, allowing for easy and effortless movements of the lungs.

A gill is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia is the zoologists' name for gills.

The respiratory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals, the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles, these are called alveoli, and in birds, they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds, the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.

The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth without having to expend energy in swimming. Also, the dorsal position of the swim bladder means that the expansion of the bladder moves the center of mass downwards, allowing it to act as a stabilizing agent in some species. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonating chamber, to produce or receive sound.

The bowfin is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "primitive fish" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus Amia, along with Amia ocellicauda, the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei.

A rete mirabile is a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other, found in some vertebrates, mainly warm-blooded ones. The rete mirabile utilizes countercurrent blood flow within the net to act as a countercurrent exchanger. It exchanges heat, ions, or gases between vessel walls so that the two bloodstreams within the rete maintain a gradient with respect to temperature, or concentration of gases or solutes. This term was coined by Galen.

Fish anatomy is the study of the form or morphology of fish. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in living fish.

Actinopteri is the sister group of Cladistia (bichirs) in the class Actinopterygii.

Aquatic respiration is the process whereby an aquatic organism exchanges respiratory gases with water, obtaining oxygen from oxygen dissolved in water and excreting carbon dioxide and some other metabolic waste products into the water.

Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment.

Ostariophysi is the second-largest superorder of fish. Members of this superorder are called ostariophysians. This diverse group contains 10,758 species, about 28% of known fish species in the world and 68% of freshwater species, and are present on all continents except Antarctica. They have a number of common characteristics such as an alarm substance and a Weberian apparatus. Members of this group include fish important to people for food, sport, the aquarium industry, and research.

Amphibious fish are fish that are able to leave water for extended periods of time. About 11 distantly related genera of fish are considered amphibious. This suggests that many fish genera independently evolved amphibious traits, a process known as convergent evolution. These fish use a range of terrestrial locomotory modes, such as lateral undulation, tripod-like walking, and jumping. Many of these locomotory modes incorporate multiple combinations of pectoral-, pelvic-, and tail-fin movement.

The ninespine stickleback, also called the ten-spined stickleback, is a freshwater species of fish in the family Gasterosteidae that inhabits temperate waters. It is widely but locally distributed throughout Eurasia and North America. Despite its name, the number of spines can vary from 8 to 12.
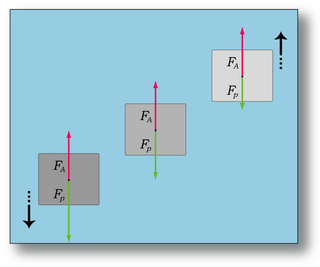
Neutral buoyancy occurs when an object's average density is equal to the density of the fluid in which it is immersed, resulting in the buoyant force balancing the force of gravity that would otherwise cause the object to sink or rise. An object that has neutral buoyancy will neither sink nor rise.

The sand grey mullet is a species of mullet found in coastal marine waters of Australia.

Swim bladder disease, also called swim bladder disorder or flipover, is a common ailment in aquarium fish. The swim bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of a fish to control its buoyancy, and thus to stay at the current water depth without having to waste energy in swimming. A fish with swim bladder disorder can float nose down tail up, or can float to the top or sink to the bottom of the aquarium.
The Root effect is a physiological phenomenon that occurs in fish hemoglobin, named after its discoverer R. W. Root. It is the phenomenon where an increased proton or carbon dioxide concentration (lower pH) lowers hemoglobin's affinity and carrying capacity for oxygen. The Root effect is to be distinguished from the Bohr effect where only the affinity to oxygen is reduced. Hemoglobins showing the Root effect show a loss of cooperativity at low pH. This results in the Hb-O2 dissociation curve being shifted downward and not just to the right. At low pH, hemoglobins showing the Root effect don't become fully oxygenated even at oxygen tensions up to 20kPa. This effect allows hemoglobin in fish with swim bladders to unload oxygen into the swim bladder against a high oxygen gradient. The effect is also noted in the choroid rete, the network of blood vessels which carries oxygen to the retina. In the absence of the Root effect, retia will result in the diffusion of some oxygen directly from the arterial blood to the venous blood, making such systems less effective for the concentration of oxygen. It has also been hypothesized that the loss of affinity is used to provide more oxygen to red muscle during acidotic stress.
Physoclisti are, collectively, fishes that lack a connection between the gas bladder and the alimentary canal, with the bladder serving only as a buoyancy organ.

Fish physiology is the scientific study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. It can be contrasted with fish anatomy, which is the study of the form or morphology of fishes. In practice, fish anatomy and physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the later dealing with how those components function together in the living fish. For this, at first we need to know about their intestinal morphology.

The evolution of tetrapods began about 400 million years ago in the Devonian Period with the earliest tetrapods evolved from lobe-finned fishes. Tetrapods are categorized as animals in the biological superclass Tetrapoda, which includes all living and extinct amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. While most species today are terrestrial, little evidence supports the idea that any of the earliest tetrapods could move about on land, as their limbs could not have held their midsections off the ground and the known trackways do not indicate they dragged their bellies around. Presumably, the tracks were made by animals walking along the bottoms of shallow bodies of water. The specific aquatic ancestors of the tetrapods, and the process by which land colonization occurred, remain unclear. They are areas of active research and debate among palaeontologists at present.



















