
Verticillium is a genus of fungi in the division Ascomycota, and are an anamorphic form of the family Plectosphaerellaceae. The genus used to include diverse groups comprising saprobes and parasites of higher plants, insects, nematodes, mollusc eggs, and other fungi, thus the genus used to have a wide-ranging group of taxa characterised by simple but ill-defined characters. The genus, currently thought to contain 51 species, may be broadly divided into three ecologically based groups - mycopathogens, entomopathogens, and plant pathogens and related saprotrophs. However, the genus has undergone recent revision into which most entomopathogenic and mycopathogenic isolates fall into a new group called Lecanicillium.

The Clavicipitaceae are a family of fungi within the order Hypocreales. A 2008 estimate placed 43 genera in the family, but a study in 2020 has increased this number to 50.

Stachybotrys is a genus of molds, hyphomycetes or asexually reproducing, filamentous fungi, now placed in the family Stachybotryaceae. The genus was erected by August Carl Joseph Corda in 1837. Historically, it was considered closely related to the genus Memnoniella, because the spores are produced in slimy heads rather than in dry chains. Recently, the synonymy of the two genera is generally accepted. Most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution and contained about 50 species in 2008. There are 88 records of Stachybotrys on Species Fungorum, of which 33 species have DNA sequence data in GenBank. Species in the genus are commonly found in soil, plant litter and air and a few species have been found from damp paper, cotton, linen, cellulose-based building materials water-damaged indoor buildings, and air ducts from both aquatic and terrestrial habitats.

Geotrichum candidum is a fungus which is a member of the human microbiome, notably associated with skin, sputum, and faeces where it occurs in 25–30% of specimens. It is common in soil and has been isolated from soil collected around the world, in all continents.
Caprettia is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Monoblastiaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Augusto Chaves Batista and Heraldo da Silva Maia in 1965, with Caprettia amazonensis assigned as the type species.
Lyromma is a genus of foliicolous (leaf-dwelling) lichens, and the sole member of Lyrommataceae, a family in the order Chaetothyriales. The genus was circumscribed in 1965 by Brazilian mycologists Augusto Chaves Batista and Heraldo da Silva Maia, with Lyromma nectandrae assigned as the type species. The family was proposed by Robert Lücking in 2008. Characteristics of the genus include the spherical to short barrel-shaped perithecia and elongated barrel-shaped pycnidia, and smooth thalli of rounded patches formed by its symbiotic relationship with green algae from the genus Phycopeltis.
Yamamotoa is a genus of fungi in the Asterinaceae family. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class is unknown, and it has not yet been placed with certainty into any order.

Lecanicillium lecanii is now an approved name of an entomopathogenic fungus species, that was previously widely known as Verticillium lecanii (Zimmerman) Viegas), but is now understood to be an anamorphic form in the Cordyceps group of genera in the Clavicipitaceae. Isolates formerly classified as V. lecanii could be L. attenuatum, L. lecanii, L. longisporum, L. muscarium or L. nodulosum. For example, several recent papers, such as Kouvelis et al. who carried out mitochondrial DNA studies, refer to the name L. muscarium.
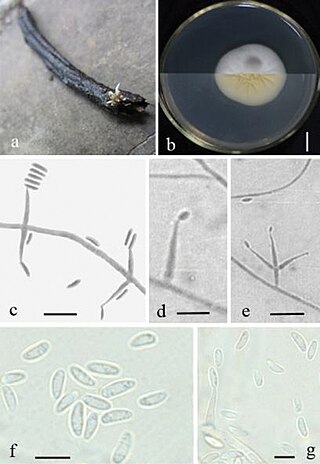
Lecanicillium is a genus of fungi in the order Hypocreales and is described as anamorphic Cordycipitaceae; 21 species are currently described. Some of these entomopathogenic fungus species were previously widely known as Verticillium lecanii (Zimmerman) Viegas. This genus was first named and introduced by Rasoul Zare (IRIPP) and Walter Gams (CBS).
Emericella is a former genus of fungi.
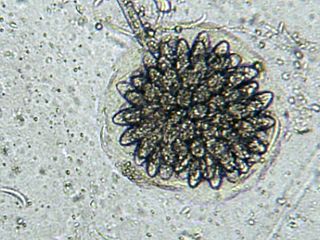
Rhopalomyces elegans is a common species of zygomycete fungus, and the type species of the genus Rhopalomyces. Widely distributed, it is found in soil, rotting plant material, and animal dung. It is a facultative parasite of nematode eggs.

The Cordycipitaceae are a family of parasitic fungi in the Ascomycota, class Sordariomycetes and order Hypocreales. The family was first published in 1969 by mycologist Hanns Kreisel, but the naming was invalid according to the code of International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. It was validly published in 2007.
Wardomyces is a genus of seven species of mould fungi in the family Microascaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1923 by Frederick Tom Brooks and Clifford Gerald Hansford. The generic name honours Harry Marshall Ward, Professor of Botany at Cambridge University. The type species, Wardomyces anomalus, was originally found as a mould growing on rabbit meat kept in cold storage. The most recent addition to the genus is W. moseri, described by Walter Gams in 1995. Found in Colombia, it was discovered growing on a dead petiole of moriche palm.

Glomerellales is an order of ascomycetous fungi within the subclass Hypocreomycetidae (Sordariomycetes). The order includes saprobes, endophytes and pathogens on plants, animals and other fungi with representatives found all over the world in varying habitats.
Harzia acremonioides is a species of seed-borne fungus that occurs in the soil. It has been categorized in the Ceratostomataceae family and under the genus Harzia. The genus Harzia contained up to three accepted species: H. acremonioides, H. verrucose, and H. velatea in 1974. Within the genus Harzia, H. acremonioides is one of the most common species that can be found in all climate regions around the world.
Oidiodendron cereale is a species of ascomycetes fungi in the order Helotiales. This fungus is found globally in temperate climates where average summer temperatures are below 25 °C, but there have been scattered reports from tropical and subtropical environments. It is predominantly found in soil, but little is known regarding their ecological roles in nature. However, an enzymatic study from Agriculture Canada showed that O. cereale can break down a variety of plant, fungal, and animal based substrates found in soil, which may have beneficial effects for plants. On rare occasions, this fungus is found on human skin and hair. There has been one reported case of O. cereale infection in 1969, causing Neurodermitis Nuchae.
Harzia is a genus of seed-borne fungus that occurs in the soil. It has been categorized in the Ceratostomataceae family. The genus Harzia originally contained three accepted species: Harzia acremonioides, Harzia verrucose, and Harzia velatea. Within the genus Harzia, Harzia acremonioides is one of the most common species that can be found in all climate regions around the world.
Gibellulopsis is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Plectosphaerellaceae.
Oidiodendron is a genus of fungi in the family Myxotrichaceae. It has 26 species. The genus was circumscribed by Norwegian forester Håkon Robak in 1932, with Oidiodendron fuscum assigned as the type species. The species is now known as Oidiodendron tenuissimum.
Strongwellsea is a genus of fungi within the order Entomophthorales of the Zygomycota. They are known to infect insects. Infected adult dipteran hosts develop a large hole in their abdomens, through which conidia (spores) are then actively discharged while the hosts are still alive.








