
Threadfins are silvery grey perciform fish of the family Polynemidae. Found in tropical to subtropical waters throughout the world, the threadfin family contains eight genera and about 40 species. An unrelated species sometimes known by the name threadfin, Alectis indicus, is properly the Indian threadfish.

The Atlantic threadfin is a species of ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae native to subtropical and temperate waters of the western Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.

The yellow grouper, also known as the banded grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in eastern Asian waters of the Western Pacific Ocean. Its natural habitats are shallow seas and rocky reefs.

Eleutheronema tetradactylum, the fourfinger threadfin, known as ranwas in India is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which occurs in the Indian and western Pacific Ocean.

Nemipterus virgatus, the golden threadfin bream or yellowlipped threadfin bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nemipteridae, the threadfin breams. This species is found in the Western Pacific Ocean.

The giant African threadfin is a species of ray-finned fish from the threadfin family Polynemidae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Africa.

The king threadfin, also known as the blind salmon, blink tassel-fish, burnett salmon, gold threadfin, king salmon, kingfish, Sheridan threadfin, striped tassel fish, or threadfin salmon, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is found in southern New Guinea and northern Australia.

The Indian threadfin is a species of marine ray-finned fish from the family Polynemidae, the threadfins. It is a coastal species from south-east Asia which has been recorded in Papua New Guinea.

Polynemus multifilis, the elegant paradise fish is a species of ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is found in rivers in southeast Asia.
Polynemus aquilonaris, commonly known as the northern paradise fish, is a fish of the threadfin family Polynemidae. It is native to the large rivers of mainland Southeast Asia.

Polydactylus sextarius, the blackspot threadfin, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is native to the western Pacific and eastern Indian Oceans.

Polydactylus plebeius, the striped threadfin, also known as the common threadfin, Northern threadfin or puttynose, is a species of marine fish native to the Indo-Pacific.

Nemipterus peronii, the notchedfin threadfin bream, notchedfin butterfly breamrosy threadfin bream or Peron's threadfin bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to family Nemipteridae, the threadfin breams. This species occurs in the Indo-West Pacific region.
Nemipterus isacanthus, the teardrop threadfin bream or twinlined threadfin bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nemipteridae, the threadfin and whiptail breams. This fish is found in the western Pacific Ocean.
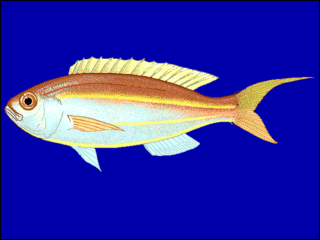
The yellowbelly threadfin bream is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nemipteridae, the threadfin and whiptail breams. This fish is found in the western Pacific Ocean.
The dwarf paradise fish, also known as the streamer threadfin or streamered tasselfish, is a species of ray-finned fish from a family Polynemidae, the threadfins. It is the only species in the genus Parapolynemus and it is found in Australia and New Guinea.

The paradise threadfin is a species of catadromous ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is found in south and southeast Asia in freshwater rivers where it is a valued food fish.

Filimanus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, threadfins from the family Polynemidae.

The lesser African threadfin is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae which is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the western coast of Africa.

The royal threadfin is a species of ray-finned fish, a threadfin from the family Polynemidae, the threadfins. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean along the western coast of Africa.















