
Poa pratensis, commonly known as Kentucky bluegrass, smooth meadow-grass, or common meadow-grass, is a perennial species of grass native to practically all of Europe, North Asia and the mountains of Algeria and Morocco. It is a common and incredibly popular lawn grass in North America with the species being spread over all of the cool, humid parts of the United States, despite the fact that it is not native to North America. The Spanish Empire brought the seeds of Kentucky bluegrass to the New World in mixtures with other grasses. In its native range, Poa pratensis forms a valuable pasture plant, characteristic of well-drained, fertile soil. It is also used for making lawns in parks and gardens and has established itself as a common invasive weed across cool moist temperate climates like the Pacific Northwest and the Northeastern United States. When found on native grasslands in Canada, for example, it is considered an unwelcome exotic plant, and is indicative of a disturbed and degraded landscape.
Leptosphaeria pratensis is a plant pathogen. It causes stagonospora root rot.
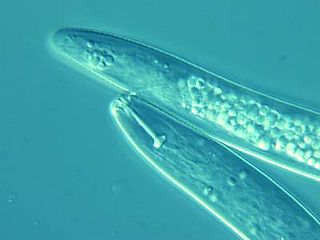
Pratylenchus coffeae is a plant-pathogenic nematode infecting several hosts including potato, banana, sweet potato, strawberry, Persian violet, peanut and citrus.
Pratylenchus goodeyi is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting bananas. It is native to the mountainous regions of Africa. There it is considered the second most devastating nematode after R. similis, especially under poor management.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.

Pratylenchus penetrans is a species of nematode in the genus Pratylenchus, the lesion nematodes. It occurs in temperate regions worldwide, regions between the subtropics and the polar circles. It is an animal that inhabits the roots of a wide variety of plants and results in necrotic lesions on the roots. Symptoms of P. penetrans make it hard to distinguish from other plant pathogens; only an assay of soil can conclusively diagnose a nematode problem in the field. P. penetrans is physically very similar to other nematode species, but is characterized by its highly distinctive mouthpiece. P. penetrans uses its highly modified mouth organs to rupture the outer surface of subterranean plant root structures. It will then enter into the root interior and feed on the plant tissue inside. P. penetrans is considered to be a crop parasite and farmers will often treat their soil with various pesticides in an attempt to eliminate the damage caused by an infestation. In doing this, farmers will also eliminate many of the beneficial soil fauna, which will lead to an overall degradation of soil quality in the future. Alternative, more environmentally sustainable methods to control P. penetrans populations may be possible in certain regions.

Pratylenchus neglectus is a plant-pathogenic nematode infecting potato, alfalfa and mint.
Pratylenchus vulnus is a species of plant pathogenic nematode best known for infecting Persian walnut. It is also known to infest potatoes, apricots, peaches and nectarines, holiday cacti, grape and citruses.
Pratylenchus scribneri is a plant pathogenic nematode. It is one of the major plant-parasitic nematodes infecting potatoes.
Thorne's meadow nematode is a plant pathogenic nematode.
Pratylenchus crenatus is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting potatoes.
Pratylenchus flakkensis is a plant pathogenic nematode.
Pratylenchus fallax is a plant pathogenic nematode.
Pratylenchus hexincisus is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting sunflowers.

Pratylenchus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as lesion nematodes. They are parasitic on plants and are responsible for root lesion disease on many taxa of host plants in temperate regions around the world. Lesion nematodes are migratory endoparasites that feed and reproduce in the root and move around, unlike the cyst or root-knot nematodes, which may stay in one place. They usually only feed on the cortex of the root. Species are distinguished primarily by the morphology of the stylets.

Succisa pratensis, also known as devil's-bit or devil's-bit scabious, is a flowering plant in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae. It differs from other similar species in that it has four-lobed flowers, whereas small scabious and field scabious have five lobes and hence it has been placed in a separate genus in the same family. It also grows on damper ground.
P. pratensis may refer to:

Poa compressa, the Canada bluegrass or flattened meadow-grass, is a perennial flattened meadow grass, similar to common meadow-grass, Poa pratensis. It is native to Europe but it can be found nearly worldwide as an introduced species. It grows in old wall tops, pavement cracks, dry stony grassland, and many types of wild habitat. It has a flattened stem, 23–30 cm tall, a close one sided panicle of grey green, with purple florets.

Helictochloa pratensis, known as meadow oat-grass, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the grass family Poaceae, found in temperate parts of Europe and Asia. Its culms are erect and 30–85 cm long; leaves are mostly basal. It is restricted to shallow, calcareous soils such as those formed on chalk and limestone substrates.
Pratylenchus alleni is a migratory endoparasitic nematode, living inside of plant roots and feeding on parenchyma cells in the root cortex. P. alleni is an obligate biotroph, meaning it must have a living host in order to survive. Due to their incredibly broad host range, Pratylenchus species fall third in total economic impact, finishing just behind cyst nematodes and root knot nematodes (Meloidogyne). In Canada, it was isolated for the first time in 2011 in a soybean field.







