Related Research Articles

The Division of Barton is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.

The Division of Dobell is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.

The Division of Macarthur is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.

The Division of Mayo is an Australian electoral division located to the east and south of Adelaide, South Australia. Created in the state redistribution of 3 September 1984, the division is named after Helen Mayo, a social activist and the first woman elected to an Australian University Council. The 9,315 km² rural seat covers an area from the Barossa Valley in the north to Cape Jervis in the south. Taking in the Adelaide Hills, Fleurieu Peninsula and Kangaroo Island regions, its largest population centre is Mount Barker. Its other population centres are Aldgate, Bridgewater, Littlehampton, McLaren Vale, Nairne, Stirling, Strathalbyn and Victor Harbor, and its smaller localities include American River, Ashbourne, Balhannah, Brukunga, Carrickalinga, Charleston, Cherry Gardens, Clarendon, Crafers, Cudlee Creek, Currency Creek, Delamere, Echunga, Forreston, Goolwa, Gumeracha, Hahndorf, Houghton, Inglewood, Kersbrook, Kingscote, Langhorne Creek, Lobethal, Macclesfield, McLaren Flat, Meadows, Middleton, Milang, Mount Compass, Mount Pleasant, Mount Torrens, Mylor, Myponga, Normanville, Norton Summit, Oakbank, Penneshaw, Piccadilly, Port Elliot, Second Valley, Springton, Summertown, Uraidla, Willunga, Woodchester, Woodside, Yankalilla, and parts of Birdwood, Old Noarlunga and Upper Sturt.
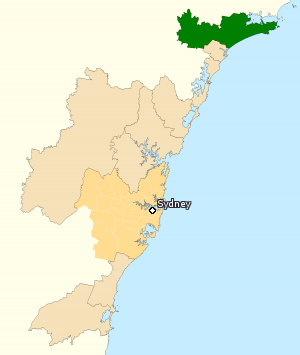
The Division of Paterson is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales. It is located just north of Newcastle, on the coast of the Tasman Sea. The division is named after federation-era poet and author Banjo Paterson and was originally created in 1949 and abolished in 1984. It was recreated after a redistribution in 1992.

An election was held in the Australian state of Queensland on 9 September 2006 to elect the 89 members of the state's Legislative Assembly, after being announced by Premier Peter Beattie on 15 August 2006.
In Australia, a redistribution is the process of redrawing the boundaries of electoral divisions for the House of Representatives arising from changes in population and changes in the number of representatives. There is no redistribution for the Senate as each State constitutes a division, though with multiple members. The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC), an independent statutory authority, oversees the apportionment and redistribution process for federal divisions, taking into account a number of factors. Politicians, political parties and the public may make submissions to the AEC on proposed new boundaries, but any interference with their deliberations is considered a serious offence.

The 2010 Australian federal election was held on Saturday, 21 August 2010 to elect members of the 43rd Parliament of Australia. The incumbent centre-left Australian Labor Party led by Prime Minister Julia Gillard won a second term against the opposition centre-right Liberal Party of Australia led by Opposition Leader Tony Abbott and Coalition partner the National Party of Australia, led by Warren Truss, after Labor formed a minority government with the support of three independent MPs and one Australian Greens MP.

The 2014 South Australian state election elected members to the 53rd Parliament of South Australia on 15 March 2014, to fill all 47 seats in the House of Assembly and 11 of 22 seats in the Legislative Council. The 12-year-incumbent Australian Labor Party (SA) government, led by Premier Jay Weatherill, won its fourth consecutive four-year term in government, a record 16 years of Labor government, defeating the opposition Liberal Party of Australia (SA), led by Opposition Leader Steven Marshall.
The following is a Mackerras pendulum for the 2006 Victorian state election.
The following pendulum is known as the Mackerras pendulum, invented by psephologist Malcolm Mackerras. Designed for the outcome of the 2010 Victorian state election, the pendulum works by lining up all of the seats held in Parliament, according to the percentage point margin on a two candidate preferred basis. The two party result is also known as the swing required for the seat to change hands. Given a uniform swing to the opposition or government parties in an election, the number of seats that change hands can be predicted. Swing is never uniform, but in practice variations of swings usually tend to cancel each other out. "Safe" seats require a swing of over 10 per cent to change, "fairly safe" seats require a swing of between 6 and 10 per cent, while "marginal" seats require a swing of less than 6 per cent.
The following is a pendulum based on the outcome of the 2010 federal election and changes since, including the redistributions of seats in South Australia and Victoria. It is a Mackerras pendulum, invented by psephologist Malcolm Mackerras, which works by lining up all of the seats held in Parliament according to the percentage point margin on a two-candidate-preferred basis. The two-party result is also known as the swing required for the seat to change hands. Given a uniform swing to the opposition or government parties in an election, the number of seats that change hands can be predicted. Swings are never uniform, but in practice variations of swing among the Australian states usually tend to cancel each other out. Seats are arranged in safeness categories according to the Australian Electoral Commission's (AEC) classification of safeness. "Safe" seats require a swing of over 10 per cent to change, "fairly safe" seats require a swing of between 6 and 10 per cent, while "marginal" seats require a swing of less than 6 per cent. The swings for South Australian and Victorian seats are notional, based on calculations by the AEC.
The following is a Mackerras pendulum for the 2002 Victorian state election.
The following is a Mackerras pendulum for the 1992 Victorian state election.
The following is a Mackerras pendulum for the 1996 Victorian state election.
At the 2016 federal election of the 150 House of Representatives seats the Liberal/National Coalition won 76, a one-seat majority, Labor won 69 seats and crossbenchers won the remaining five. A redistribution in 2017/18 changed the representation entitlements. For the next election, the number of seats in the House will increase to 151, South Australia will lose a seat, Victoria and the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) will gain one seat each.
The following pendulum is known as the Mackerras pendulum, invented by psephologist Malcolm Mackerras. Based upon the outcome of the 2007 federal election and changes before the 2010 election, the pendulum works by lining up all of the seats held in Parliament, 83 Labor, 55 Liberal, 9 National, and 3 independent, according to the percentage point margin on a two party preferred basis.
This is a Mackerras pendulum for the 2016 Australian federal election.
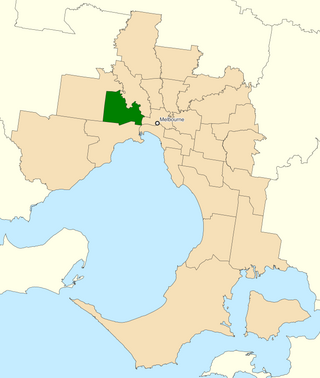
The Division of Fraser is an Australian electoral division in the state of Victoria, which was contested for the first time at the 2019 federal election.
The Mackerras pendulum was devised by the Australian psephologist Malcolm Mackerras as a way of predicting the outcome of an election contested between two major parties in a Westminster style lower house legislature such as the Australian House of Representatives, which is composed of single-member electorates and which uses a preferential voting system such as a Condorcet method or IRV.
References
- ↑ Green, Antony. "2013 Victorian Redistribution: Analysis of New Electoral Boundaries" (PDF). Retrieved 14 October 2014.