| Pritchardia forbesiana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Arecales |
| Family: | Arecaceae |
| Tribe: | Trachycarpeae |
| Genus: | Pritchardia |
| Species: | P. forbesiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Pritchardia forbesiana | |
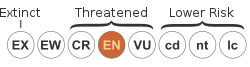
Pritchardia forbesiana, the Mt. Eke pritchardia, [2] is a species of palm tree. It is endemic to the island of Maui in Hawaii. It grows in forests. Populations are recovering since the removal of destructive feral pigs. [1]