
Trillium is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. Trillium species are native to temperate regions of North America and Asia, with the greatest diversity of species found in the southern Appalachian Mountains in the southeastern United States.

Pinus ponderosa, commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine, is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the most widely distributed pine species in North America.

Nolina is a genus of tropical xerophytic flowering plants, with the principal distribution being in Mexico and extending into the southern United States. They are large, dioecious plants.

Clintonia is a genus of flowering plants in the lily family Liliaceae. Plants of the genus are distributed across the temperate regions of North America and eastern Asia, in the mesic understory of deciduous or coniferous forests. The genus, first described by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1818, was named for DeWitt Clinton (1769–1828), a naturalist and politician from the U.S. state of New York. For this reason, plants of the genus are commonly known as Clinton's lily. The common name bluebead refer to the distinctive fruit of members of the genus. Since fruit color varies somewhat across species, the common name bead lily is used as well.

The Coronado Islands are a group of islands located 13 km (8 mi) off the northwest coast of the Mexican state of Baja California. Battered by the wind and waves, the rocky islands are mostly uninhabited except for a small military detachment and a lighthouse keeper. Despite their barren appearance, they serve as a refuge for seabirds and support a sizable number of plants, including 6 endemic taxa found only on the islands. The waters around the islands support a considerable amount of diverse marine life.
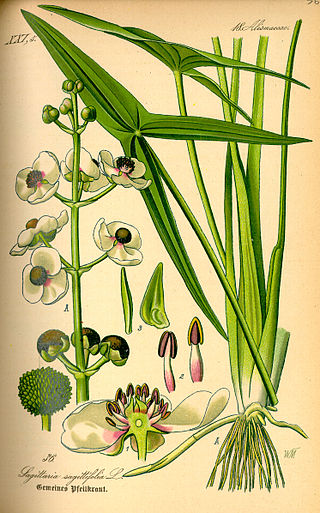
Sagittaria is a genus of about 30 species of aquatic plants whose members go by a variety of common names, including arrowhead, duck potato, swamp potato, tule potato, and wapato. Most are native to South, Central, and North America, but there are also some from Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Adenostoma fasciculatum, commonly known as chamise or greasewood, is a flowering plant native to California and Baja California. This shrub is one of the most widespread plants of the California chaparral ecoregion. Chamise produces a specialized lignotuber underground and at the base of the stem, known as a burl, that allow it to resprout after fire has off burned its stems. It is noted for its greasy, resinous foliage, and its status as one of California's most iconic chaparral shrubs.

Bouteloua is a genus of plants in the grass family. Members of the genus are commonly known as grama grass.

Allium cernuum, known as nodding onion or lady's leek, is a perennial plant in the genus Allium. It grows in open areas in North America.

Muhlenbergia is a genus of plants in the grass family.

Ornithostaphylos is a monotypic plant genus which contains the single species Ornithostaphylos oppositifolia, commonly known as the Baja California birdbush or Baja California manzanita. A large, evergreen shrub in the heather family, this species is near-endemic to northwestern Baja California, with a small population just north of the border in San Ysidro, California. It produces a much-branched inflorescence of white, urn-shaped flowers, and has leathery leaves that appear opposite or in whorls. These characteristics separate it from its close relatives in the region, which include manzanitas (Arctostaphylos), summer holly (Comarostaphylis) and mission manzanita (Xylococcus).

Euphorbia misera is a semi-succulent shrub in the genus Euphorbia commonly known as the cliff spurge or coast spurge. A drought-deciduous shrub, it is typically found as a gnarled, straggly plant occupying seashore bluffs, hills and deserts. Like other members of its genus, it has a milky sap, which can be found exuding out of the light gray bark when damaged. The alternately-arranged leaves are round and folded in the middle, with small hairs on them. The "flowers" can be found blooming year-round, and are colored maroon or yellow in the center with 5 white to light-yellow petal-like appendages attached outside. This species is native to the Baja California peninsula and Sonora in Mexico, and the coast of southern California in the United States, where it is a rare species. It is threatened in some localities by the development of its coastal habitat, which tends to be prime locations for high-end residential and commercial developments.

Pseudognaphalium californicum is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by several common names, including ladies' tobacco, California rabbit tobacco, California cudweed, and California everlasting.

Artemisia ludoviciana is a North American species of flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae, known by several common names, including silver wormwood, western mugwort, Louisiana wormwood, white sagebrush, lobed cud-weed, prairie sage, and gray sagewort.

Oxalis albicans, commonly known as radishroot woodsorrel, is North American species of perennial herbs in the woodsorrel family. It is widespread in Mexico and the southwestern United States.

Brickellia grandiflora, known by the common name tasselflower brickellbush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.

Salvia brandegeei is a perennial evergreen shrub in the mint family known by the common names Santa Rosa Island sage or Brandegee's sage. It is a fragrant plant characterized by lavender flowers and dark green leaves. For many years, it was thought to be native only to Santa Rosa Island, one of the Channel Islands of California, until it was discovered along the coast of Baja California. It is threatened by development and mining along the mainland portions of its range, but otherwise has a stable population on Santa Rosa Island.

Pseudognaphalium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as cudweeds or rabbit tobacco. They are widespread in tropical and temperate regions of many countries.

Silene scouleri is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common names simple campion and Scouler's catchfly.

Heterotheca villosa, commonly known as the hairy goldenaster, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae found in central and western North America.





















