
Quercus stellata, the post oak or iron oak, is a North American species of oak in the white oak section. It is a slow-growing oak that lives in dry areas on the edges of fields, tops of ridges also grows in poor soils, and is resistant to rot, fire, and drought. Interbreeding occurs among white oaks, thus many hybrid species combinations occur.

Quercus gambelii, with the common name Gambel oak, is a deciduous small tree or large shrub that is widespread in the foothills and lower mountains of western North America. It is also regionally called scrub oak, oak brush, and white oak.

Quercus coccinea, the scarlet oak, is a deciduous tree in the red oak section Lobatae of the genus Quercus, in the family Fagaceae.

Quercus ellipsoidalis, the northern pin oak or Hill's oak, is a North American species of oak tree native to the north-central United States and south-central Canada, primarily in the Great Lakes region and the Upper Mississippi Valley. It most commonly occurs on dry, sandy soils.

Quercus acutissima, the sawtooth oak, is an Asian species of oak native to China, Tibet, Korea, Japan, Indochina and the Himalayas. It is widely planted in many lands and has become naturalized in parts of North America.

Quercus phellos, the willow oak, is a North American species of a deciduous tree in the red oak group of oaks. It is native to the south-central and eastern United States.

Quercus imbricaria, the shingle oak, is a deciduous tree in the red oak group of oaks. It is native primarily to the Midwestern and Upper South regions of North America.

Quercus dentata, also called Japanese emperor oak or daimyo oak is a species of oak native to East Asia. The name of the tree is often translated as "sweet oak" in English to distinguish it from Western varieties. It is placed in section Quercus.

Quercus lyrata, the overcup oak, is an oak in the white oak group. The common name, overcup oak, refers to its acorns that are mostly enclosed within the acorn cup. It is native to lowland wetlands in the eastern and south-central United States, in all the coastal states from New Jersey to Texas, inland as far as Oklahoma, Missouri, and Illinois. There are historical reports of it growing in Iowa, but the species appears to have been extirpated there. It is a slow-growing tree that often takes 25 to 30 years to mature. It has an estimated lifespan of 400 years.
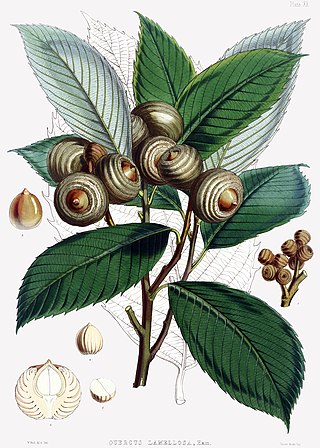
Quercus lamellosa is a species of oak (Quercus) native to the Himalaya and adjoining mountains from Tibet and Nepal east as far as Guangxi and northern Thailand, growing at altitudes of 1300–2500 m. The Lepcha of Sikkim call it book koong. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.

Quercus nigra, the water oak, is an oak in the red oak group, native to the eastern and south-central United States, found in all the coastal states from New Jersey to Texas, and inland as far as Oklahoma, Kentucky, and southern Missouri. It occurs in lowlands and up to 450 meters in elevation.

Quercus myrsinifolia is an Asian species of tree in the beech family Fagaceae. It has several common names, including bamboo-leaf oak, Chinese evergreen oak, and Chinese ring-cupped oak. Its Chinese name is 小叶青冈; pinyin: xiǎo yè qīng gāng, which means little leaf ring-cupped oak, in Japan it is called white oak and in Korea it is known as gasinamu (가시나무). It is native to east central and southeast China, Japan, Korea, Laos, northern Thailand, and Vietnam. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.

Quercus similis, the swamp post oak or bottomland post oak, is an oak species native to the southeastern and south-central United States. The greatest concentration of populations is in Louisiana and Arkansas, Mississippi, and eastern Texas, with isolated population in Missouri, Alabama, and the Coastal Plain of Georgia and South Carolina.

Quercus castanea is a species of oak tree. It is widespread across much of Mexico, from Sonora to Chiapas, and in Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras.

Quercus insignis is a Mesoamerican species of oak in the white oak section, within the beech family. It is native to southern Mexico and Central America, from Veracruz to Panamá.
Quercus augustinii is a rare species of tree in the beech family Fagaceae. It has been found in Vietnam as well as Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan Provinces in southern China. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.
Quercus hypargyrea is an Asian species of tree in the beech family Fagaceae. It is native to south-central and southeast China, in particular the provinces of Anhui, Fujian, Guangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Shaanxi, and Sichuan. It has incorrectly been known as Quercus multinervis, which is properly the name of a fossil species. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.

Quercus rex is an Asian species of tree in the family Fagaceae. It has been found in the seasonal tropical forests of northern Indochina, northeastern India, and also in the province of Yunnan in southwestern China. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.

Quercus schottkyana is an Asian species of tree in the beech family Fagaceae. It has been found in southwestern China. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.
Quercus langbianensis is an uncommon oak tree species in the family Fagaceae. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis, the ring-cupped oaks. These differ from other Quercus groups in that they have acorns with distinctive cups: usually with substantial rings, made-up of scales that have grown together. This species can be found in sub-tropical and tropical seasonal forests of Cambodia, China and Vietnam.



















