Herstory is a term for history written from a feminist perspective and emphasizing the role of women, or told from a woman's point of view. It originated as an alteration of the word "history", as part of a feminist critique of conventional historiography, which in their opinion is traditionally written as "his story", i.e., from the male point of view. The term is a neologism since the word "history"—from the Ancient Greek word ἱστορία, or more directly from its Latin derivate historia, meaning "knowledge obtained by inquiry"— is etymologically unrelated to the possessive pronoun his.
Misandry is the hatred of, contempt for, or prejudice against men. Through a series of books published in the 2000s and 2010s, religion scholars Paul Nathanson and Katherine Young argue that misandry is commonly seen in North America in the demonization of men as a result of women exercising power through feminism. Nathanson and Young give as examples many cultural tropes that diminish men.
Individualist feminism is a libertarian feminist tradition that emphasizes individualism, personal autonomy, choice, consent, freedom from state-sanctioned discrimination against women, and equality under the law. It also opposes what is considered political or gender feminism.

Christina Marie Hoff Sommers is an American author and philosopher. Specializing in ethics, she is a resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute. Sommers is known for her critique of contemporary feminism. Her work includes the books Who Stole Feminism? (1994) and The War Against Boys (2000). She also hosts a video blog called The Factual Feminist.
The term postfeminism is used to describe reactions against contradictions and absences in feminism, especially second-wave feminism and third-wave feminism. The term postfeminism is sometimes confused with subsequent feminisms such as fourth-wave feminism and xenofeminism.
The Independent Women's Forum (IWF) is a conservative American non-profit organization focused on economic policy issues of concern to women. IWF was founded by activist Rosalie Silberman to promote a "conservative alternative to feminist tenets" following the controversial Supreme Court nomination of Clarence Thomas in 1992. IWF's sister organization is the Independent Women's Voice (IWV), a 501(c)(4) organization.
Victim feminism is a term used by some liberal and libertarian feminists in the 1990s to contrast their conceptions of feminism with other feminists who they view as reinforcing the idea that women are weak or lacking in agency, and therefore need to be protected.
Lad culture was a media-driven, principally British and Irish subculture of the 1990s and early 2000s. The image of the "lad"—or "new lad"—was that of a generally middle class figure espousing attitudes typically attributed to the working classes. The subculture involved heterosexual young men assuming an anti-intellectual position, shunning cultural pursuits and sensitivity in favour of drinking, sport, sex and sexism. Lad culture was diverse and popular involving literature, magazines, film, music and television, with ironic humour being a defining trope. Principally understood at the time as a male backlash against feminism and the pro-feminist "new man", the discourse around the new lad represented some of the earliest mass public discussion of how heterosexual masculinity is constructed.
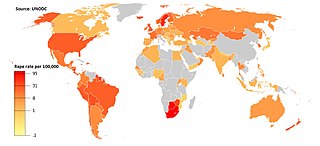
Rape culture is a setting, studied by several sociological theories, in which rape is pervasive and normalized due to societal attitudes about gender and sexuality. Behaviors commonly associated with rape culture include victim blaming, slut-shaming, sexual objectification, trivializing rape, denial of widespread rape, refusing to acknowledge the harm caused by sexual violence, or some combination of these. It has been used to describe and explain behavior within social groups, including prison rape and in conflict areas where war rape is used as psychological warfare. Entire societies have been alleged to be rape cultures. It is associated with rape fantasy and rape pornography.

The Beauty Myth: How Images of Beauty Are Used Against Women is a nonfiction book by Naomi Wolf, originally published in 1990 by Chatto & Windus in the UK and William Morrow & Co (1991) in the United States. It was republished in 2002 by HarperPerennial with a new introduction.
Antifeminism, also spelled anti-feminism, is opposition to some or all forms of feminism. In the late 19th century and early 20th century, antifeminists opposed particular policy proposals for women's rights, such as the right to vote, educational opportunities, property rights, and access to birth control. In the mid and late 20th century, antifeminists often opposed the abortion-rights movement and, in the United States, the Equal Rights Amendment.

In a Different Voice: Psychological Theory and Women's Development is a book on gender studies by American professor Carol Gilligan, published in 1982, which Harvard University Press calls "the little book that started a revolution".

Sexual Politics is the debut book by American writer and activist Kate Millett, based on her PhD dissertation. It was published in 1970 by Doubleday. It is regarded as a classic of feminism and one of radical feminism's key texts. Sexual Politics analyses the subjugation of women in prominent art and literature in the 20th century, specifically looking at the ubiquity of male domination in culture.

The Network of enlightened Women (NeW) is an organization for culturally conservative women at American universities. Started as a book club at the University of Virginia in 2004, NeW seeks to cultivate "a community of conservative women and expands intellectual diversity on college campuses through its focus on education."

The Morning After: Sex, Fear and Feminism on Campus is a 1993 book about date rape by author and journalist Katie Roiphe. Her first book, it was reprinted with a new introduction in 1994. Part of the book had previously been published as an essay, "The Rape Crisis, or 'Is Dating Dangerous?'" in the New York Times Magazine.

The Myth of Male Power: Why Men are the Disposable Sex is a 1993 book by Warren Farrell, in which the author argues that the widespread perception of men having inordinate social and economic power is false, and that men are systematically disadvantaged in many ways.
Gynocentrism is a dominant or exclusive focus on women in theory or practice. Anything can be gynocentric when it is considered exclusively with a female point of view in mind.
Neil Alexander Lyndon is a British journalist and writer. He has written for The Sunday Times, The Times, The Independent, the Evening Standard the Daily Mail and the Telegraph

Who Stole Feminism? How Women Have Betrayed Women is a 1994 book about American feminism by Christina Hoff Sommers, a writer who was at that time a philosophy professor at Clark University. Sommers argues that there is a split between equity feminism and what she terms "gender feminism". Sommers contends that equity feminists seek equal legal rights for women and men, while gender feminists seek to counteract historical inequalities based on gender. Sommers argues that gender feminists have made false claims about issues such as anorexia and domestic battery and exerted a harmful influence on American college campuses. Who Stole Feminism? received wide attention for its attack on American feminism, and it was given highly polarized reviews divided between conservative and liberal commentators. Some reviewers praised the book, while others found it flawed.
Feminist activism in hip hop is a feminist movement based by hip hop artists. The activism movement involves doing work in graffiti, break dancing, and hip hop music. Hip hop has a history of being a genre that sexually objectifies and disrespects women ranging from the usage of video vixens to explicit rap lyrics. Within the subcultures of graffiti and breakdancing, sexism is more evident through the lack of representation of women participants. In a genre notorious for its sexualization of women, feminist groups and individual artists who identify as feminists have sought to change the perception and commodification of women in hip hop. This is also rooted in cultural implications of misogyny in rap music.









