Cantabria is an autonomous community and province in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a comunidad histórica, a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east by the Basque autonomous community, on the south by Castile and León, on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea, which forms part of the Bay of Biscay.

The Province of Burgos is a province of northern Spain, in the northeastern part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is bordered by the provinces of Palencia, Cantabria, Vizcaya, Álava, La Rioja, Soria, Segovia, and Valladolid. Burgos is the province of Spain that has borders with most provinces. Its capital is the city of Burgos.

Ferdinand IV of Castile called the Summoned, was King of Castile and León from 1295 until his death.

Alfonso of León, Lord of Molina was an infante (prince) of León and Castile, the son of King Alfonso IX of León and his second wife Queen Berengaria of Castile. He was the brother of King Ferdinand III of Castile and León, and father of Queen Maria of Molina, wife of King Sancho IV. He became Lord of Molina and Mesa after his first marriage to Mafalda González de Lara, the heiress of those lands.

The Battle of Santander was fought in the War in the North campaign of the Spanish Civil War during the summer of 1937. Santander's fall on 26 August assured the Nationalist conquest of the province of Santander, now Cantabria. The battle devastated the Republic's "Army of the North"; 60,000 soldiers were captured by the Nationalists.
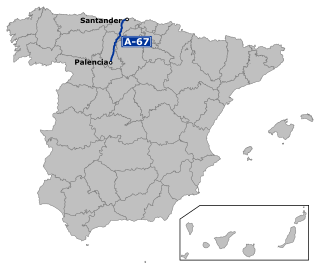
The Autovía A-67 is a highway in north west Spain. It connects the Cantabrian Atlantic Coast at Santander to Palencia. It follows the route of the N-611.

Campoo is a comarca (district) of Cantabria (Spain) located in the High Ebro. With an area of slightly more than 1,000 km2, it includes the municipalities of Hermandad de Campoo de Suso, Campoo de Enmedio, Campoo de Yuso, Valdeolea, Valdeprado del Río, Valderredible, Reinosa, Las Rozas de Valdearroyo, Santiurde de Reinosa, Pesquera, and San Miguel de Aguayo. The local inhabitants are called Campurrians . Its highest elevation is the Cuchillón peak, and the lowest is Pesquera, with the capital, Reinosa at 850 m.

The N-623 is a highway in northern Spain. It connects Burgos with Santander.

The Ebro is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows 930 kilometres (580 mi), almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a delta in the Terres de l'Ebre region, in southern Catalonia. In the Iberian peninsula, it ranks second in length after the Tagus and second in discharge volume, and drainage basin, after the Douro. It is the longest river entirely within Spain; the other two mentioned flow into Portugal. It is also the second-longest river in the Mediterranean basin, after the Nile.

Pedro Fernández de Castro "the Castilian" was a Castilian nobleman, son of Fernando Rodríguez de Castro and Estefanía Alfonso la Desdichada. He inherited the Infantazgo of León from his parents and was mayordomo mayor of Fernando II and his son Alfonso IX of León.

Agoncillo is a town and municipality in La Rioja province in northern Spain.

Alfonsode Aragon y Escobar (1417–1495), Duke of Villahermosa, Count of Ribagorza and Cortes and Grand Master of the Order of Calatrava, was an illegitimate son of John II of Aragon and one of his mistresses, Leonor de Escobar, daughter of Alfonso Rodríguez de Escobar.

Pedro Ruiz de Villegas y Cevallos II was a Spanish noble baron in the service of the Kingdom of Castile and a member of the Order of Santiago. He was the head of the House of Villegas and a descendant of the houses of Cevallos and of Lucio. As the majorat of his own heraldic crest, he received titles over Villegas, Manquillos, Castillo Pedroso, Moñux, Pedrosa del Páramo, Manciles, Valdegómez and the palace of Sasamón. For his service in the First Castilian Civil War, and his role in the destruction of the Blanche of Bourbon league he received the castle of Caracena, and was named high adelantado of Castile in 1354. A year later, Peter of Castile would execute him in the village of Medina del Campo.
Alfonso Fernández el Niño was a Spanish nobleman, the illegitimate son of King Alfonso X of Castile and Elvira Rodríguez de Villada. He was the lord of Molina and Mesa through his marriage to Blanca Alfonso de Molina, daughter of the infante Alfonso of Molina and niece of King Alfonso IX of León.
Violant of Castile was infanta of Castile and Lady of Biscay on her marriage to Diego López V de Haro. She was the daughter of Alfonso X of Castile, and Violant of Aragon.

Berengaria of Castile, Infanta of Castile and Lady of Guadalajara in her own right. She was the eldest child of King Alfonso X of Castile and Violante of Aragon. She was probably named after her paternal great-grandmother, Queen Berengaria of Castile.

Francisco de Paula de Ceballos and Vargas was a Spanish Lieutenant General who acted as captain general in Catalonia and Cuba. He was also Senator for life as Senator, representing Santander Province.

The Hermandad of the Cuatro Villas de la Costa de la Mar, also cited under the name Cuatro Villas de la Costa de Cantabria, was a medieval and modern administrative entity that grouped the coastal cities of the north of the kingdom of Castile, all of them part of present-day Cantabria; namely, from west to east: San Vicente de la Barquera, Santander, Laredo, and Castro-Urdiales. At the end of the 15th century, it became part of the corregimiento of the Cuatro Villas along with other territories in the north of the Iberian Peninsula. In 1514 the province was renamed the corregimiento de las Tres Villas de la Costa, by separation from the town of San Vicente, which rejoined in 1521. Towns twinned since the 13th century, its foundation as a corregimiento dates back to the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, around 1496, surviving until its inclusion in the province of Cantabria in 1778.

The Híjar river or The Híjar is a river in northern Spain whose waters give rise to the Ebro River. This was accredited as early as 1862 by Pedro Antonio de Mesa in the first known hydrogeographic survey. This river runs more than 20 km from the headwaters of the Campoo Valley, and then part of its flow filters and makes a short subway journey of 800 m, resurfacing along with 4 other springs in the town of Fontibre, then receiving the name of "Ebro". The flow of the Hijar River that is not submerged continues along the surface in an easterly direction and joins the Ebro at Reinosa, a few kilometers downstream. This fact was scientifically demonstrated by technicians from the Geological and Mining Institute of Spain in 1987, after pouring fluorescein into the river, and observing that the same flow filtered by the Híjar was the one that came out dyed in the Fontibre spring.
The Sonsierra de Navarra or simply Sonsierra is a Spanish geographical region that extends through the south of the province of Álava, north of La Rioja and southwest of Navarra. Currently most of the territory that comprised that region is known as Rioja Alavesa, although this has lost, by its current administrative delimitation, other municipalities that historically and geographically formed a whole one with the current wine region.