An international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and nonproprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs are intended to make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.

Etoperidone, associated with several brand names, is an atypical antidepressant which was developed in the 1970s and either is no longer marketed or was never marketed. It is a phenylpiperazine related to trazodone and nefazodone in chemical structure and is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) similarly to them.

Tropisetron is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist used mainly as an antiemetic to treat nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, although it has been used experimentally as an analgesic in cases of fibromyalgia.

Arfendazam (INN) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. Arfendazam is a 1,5-benzodiazepine, with the nitrogen atoms located at positions 1 and 5 of the diazepine ring, and so is most closely related to other 1,5-benzodiazepines such as clobazam.

Nelivaptan (INN) is a selective, orally active, non-peptide vasopressin receptor antagonist selective for the V1B subtype. The drug had entered clinical trials for treatment of anxiety and depression. In July 2008, Sanofi-Aventis announced that further development of this drug had been halted.

Bradanicline is a drug which was being developed by Targacept that acts as a partial agonist at the α7 subtype of the neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It showed cognitive enhancing effects in animal studies, and was being developed through a collaboration between Targacept and AstraZeneca as a potential treatment for schizophrenia and attention deficit disorder. Phase I clinical trials were completed successfully, and it was in phase II trials.
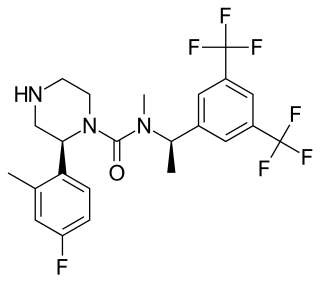
Vestipitant (INN) is a drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. It is under development as a potential antiemetic and anxiolytic drug, and as a treatment for tinnitus and insomnia.

Acefylline (INN), also known as acetyloxytheophylline, is a stimulant drug of the xanthine chemical class. It acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. It is combined with diphenhydramine in the pharmaceutical preparation etanautine to help offset diphenhydramine induced drowsiness.

Ezlopitant (INN, code name CJ-11,974) is an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic and antinociceptive effects. Pfizer was developing ezlopitant for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome but it appears to have been discontinued.

Capeserod (INN; development code SL65.0155) is a selective 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist with Ki = 0.6 nM and IA = 40–50% (relative to serotonin). It potently enhances cognition, learning, and memory, and also possesses antidepressant effects. Capeserod was in phase II clinical trials around 2004–2006 for the treatment of memory deficits and dementia but no new information has surfaced since and it appears to have been abandoned.
Lavoltidine (INN, USAN, BAN; previously known as loxtidine, code name AH-23,844) is a highly potent and selective H2 receptor antagonist which was under development by Glaxo Wellcome (now GlaxoSmithKline) as a treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease but was discontinued due to the discovery that it produced gastric carcinoid tumors in rodents.

Elinogrel (INN, USAN) was an experimental antiplatelet drug acting as a P2Y12 inhibitor. Similarly to ticagrelor and in contrast to clopidogrel, elinogrel was a reversible inhibitor that acted fast and short (for about 12 hours), and it was not a prodrug but pharmacologically active itself. The substance was used in form of its potassium salt, intravenously for acute treatment and orally for long-term treatment. Development was terminated in 2012.

Becampanel (INN) (code name AMP397) is a quinoxalinedione derivative drug which acts as a competitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor (IC50 = 11 nM). It was investigated as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of epilepsy by Novartis, and was also looked at as a potential treatment for neuropathic pain and cerebral ischemia, but never completed clinical trials.

Encenicline is a selective partial agonist of the α7 nicotinic receptor. It was in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, but failed to meet the study endpoints in 2016.

Serlopitant (INN, codenamed VPD-737) is a drug which acts as an NK1 receptor antagonist. It was assessed in clinical trials for the treatment of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder, but while it was superior to placebo it provided no advantage over existing approved drugs, and was not approved for further development for this indication. Serlopitant is now undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of chronic pruritus (itch)
Vobarilizumab is a humanized bispecific nanobody designed for the treatment of inflammatory autoimmune diseases.

Lanepitant (INN, code name LY303870) is a drug developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, and was one of the first compounds developed that act at this target. It was under development as a potential analgesic drug, but despite promising results in initial animal studies, human clinical trials against migraine, arthritis and diabetic neuropathy all failed to show sufficient efficacy to support further development, with the drug being only marginally more effective than placebo and inferior to older comparison drugs such as naproxen. Failure of analgesic action was thought to be due to poor penetration of the blood–brain barrier in humans, but research has continued into potential applications in the treatment of other disorders with a peripheral site of action, such as corneal neovascularization.
Nemolizumab is an experimental drug for the treatment of itching in people with atopic dermatitis. It is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the interleukin-31 receptor A. Results of a Phase II clinical trial were published in March 2017.
Rosmantuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer.














