
The rails, or Rallidae, are a large cosmopolitan family of small- to medium-sized, ground-living birds. The family exhibits considerable diversity and includes the crakes, coots, and gallinules. Many species are associated with wetlands, although the family is found in every terrestrial habitat except dry deserts, polar regions, and alpine areas above the snow line. Members of the Rallidae occur on every continent except Antarctica. Numerous island species are known. The most common rail habitats are marshland and dense forest. They are especially fond of dense vegetation.

Tringa is a genus of waders, containing the shanks and tattlers. The genus name Tringa is the New Latin name given to the green sandpiper by the Italian naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi in 1599. They are mainly freshwater birds, often with brightly coloured legs as reflected in the English names of six species, as well as the specific names of two of these and the green sandpiper. They are typically associated with northern hemisphere temperate regions for breeding. Some of this group—notably the green sandpiper—nest in trees, using the old nests of other birds, usually thrushes.

The Decapoda or decapods are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossil decapod is the Devonian Palaeopalaemon.

The Stenopodidea or boxer shrimps are a small group of decapod crustaceans. Often confused with Caridea shrimp or Dendrobranchiata prawns, they are neither, belonging to their own group.

The Glypheoidea, is a group of lobster-like decapod crustaceans which forms an important part of fossil faunas, such as the Solnhofen limestone. These fossils included taxa such as Glyphea, and Mecochirus, mostly with elongated chelipeds. This group of decapods is a good example of a living fossil, or a lazarus taxon, since until their discovery in the 1970s, the group was considered to have become extinct in the Eocene. The superfamily Glypheoidea comprises five families. The two extant species, Neoglyphea inopinata and Laurentaeglyphea neocaledonica, are both in the Glypheidae.

Telmatobius is a genus of frogs native to the Andean highlands in South America, where they are found in Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, northwestern Argentina and northern Chile. It is the only genus in the family Telmatobiidae. Some sources recognize Batrachophrynus as a valid genus distinct from Telmatobius.

Reef lobsters, Enoplometopus, are a genus of small lobsters that live on reefs in the Indo-Pacific, Caribbean and warmer parts of the Atlantic Ocean.

Embrithopoda ("heavy-footed") is an order of extinct mammals known from Asia, Africa and Eastern Europe. Most of the embrithopod genera are known exclusively from jaws and teeth dated from the late Paleocene to the late Eocene; however, the order is best known from its terminal member, the elephantine Arsinoitherium.

Pararhabdodon is a genus of tsintaosaurin hadrosaurid dinosaur, from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Group of Spain. The first remains were discovered from the Sant Romà d’Abella fossil locality and assigned to the genus Rhabdodon, and later named as the distinct species Pararhabdodon isonensis in 1993. Known material includes assorted postcranial remains, mostly vertebrae, as well as maxillae from the skull. Specimens from other sites, including remains from France, a maxilla previously considered the distinct taxon Koutalisaurus kohlerorum, an additional maxilla from another locality, the material assigned to the genera Blasisaurus and Arenysaurus, and the extensive Basturs Poble bonebed have been considered at different times to belong to the species, but all of these assignments have more recently been questioned. It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known from the fossil record that went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Retroplumidae is a family of heterotrematan crabs, placed in their own (monotypic) superfamily, Retroplumoidea.

Thalassina is a genus of mud lobsters found in the mangrove swamps of the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean. Its nocturnal burrowing is important for the recycling of nutrients in the mangrove ecosystem, although it is sometimes considered a pest of fish and prawn farms.

Agathaeromys is an extinct genus of oryzomyine rodents from the Pleistocene of Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles. Two species are known, which differ in size and some details of tooth morphology. The larger A. donovani, the type species, is known from hundreds of teeth, found in four localities that are probably 900,000 to 540,000 years old. A. praeuniversitatis, the smaller species, is known from 35 teeth found in a single fossil site, which is probably 540,000 to 230,000 years old.

The Galatheoidea are a superfamily of decapod crustaceans comprising the porcelain crabs and some squat lobsters. Squat lobsters within the three families of the superfamily Chirostyloidea are not closely related to the squat lobsters within the Galatheoidea. The fossil record of the superfamily extends back to the Middle Jurassic genus Palaeomunidopsis.

Campylonotoidea is a superfamily of shrimp, containing the two families Campylonotidae and Bathypalaemonellidae. Fenner A. Chace considered it to be the sister group to the much larger superfamily Palaemonoidea, with which it shares the absence of endopods on the pereiopods, and the fact that the first pereiopod is thinner than the second. Using molecular phylogenetics, Bracken et al. proposed that Campylonotoidea may be closer to Atyoidea. There are sixteen described species in 3 genera; no fossils are known.

Neoglyphea inopinata is a species of glypheoid lobster, a group thought long extinct before Neoglyphea was discovered. It is a lobster-like animal, up to around 15 centimetres (5.9 in) in length, although without claws. It is only known from 17 specimens, caught at two sites – one at the entrance to Manila Bay in the Philippines, and one in the Timor Sea, north of Australia. Due to the small number of specimens available, little is known about the species, but it appears to live up to five years, with a short larval phase. A second species, previously included in Neoglyphea, is now placed in a separate genus, Laurentaeglyphea.
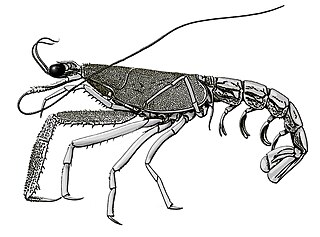
Laurentaeglyphea neocaledonica is a species of glypheoid lobster, and the only species in the genus Laurentaeglyphea. It is known from a single specimen collected on a guyot in the Coral Sea between Australia and New Caledonia. It is thought to be an active predator with colour vision, unlike its nearest living relative, Neoglyphea inopinata.
Michèle de Saint Laurent was a French carcinologist. She spent most of her career at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris, working on the systematics of decapod crustaceans; her major contributions were to hermit crabs and Thalassinidea, and she also co-described Neoglyphea, a living fossil discovered in 1975.

Goulmimichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pachyrhizodontidae. The genus, first described by Cavin in 1995, is known from various Turonian age formations. The type species G. arambourgi from the Akrabou Formation in the El Rachidia Province of Morocco, and other fossils described are G. gasparini of the La Frontera Formation, Colombia, and G. roberti from the Agua Nueva Formation of Mexico.
Canaanimico is an extinct genus of medium-sized New World monkeys from the Late Oligocene fossiliferous fluvio-lacustrine Chambira Formation of the Ucayali Basin in Amazonian Peru. The genus was described by Marivaux et al. in 2016 and the type species is C. amazonensis.

















