
Peary Land is a peninsula in northern Greenland, extending into the Arctic Ocean. It reaches from Victoria Fjord in the west to Independence Fjord in the south and southeast, and to the Arctic Ocean in the north, with Cape Morris Jesup, the northernmost point of Greenland's mainland, and Cape Bridgman in the northeast.

Frederick E. Hyde Fjord is a fjord in Peary Land, far northern Greenland.

The Stauning Alps are a large system of mountain ranges in Scoresby Land, King Christian X Land, northeastern Greenland. Administratively the Stauning Alps are part of the Northeast Greenland National Park zone.
Henson Glacier, is one of the major glaciers in northern Greenland.

Sands Fjord is a fjord in Peary Land, northern Greenland. To the north, the fjord opens into the Lincoln Sea of the Arctic Ocean. Administratively, it belongs to the Northeast Greenland National Park.
Nordkrone is a mountainous area in Peary Land, Northern Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.
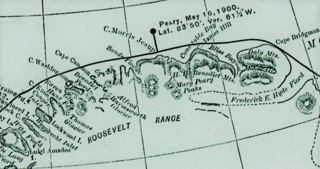
Helvetia Tinde is the highest mountain in the Roosevelt Range, Northern Greenland. It is also the highest mountain of the northernmost mountain range on Earth.

Frigg Fjord is a fjord in Peary Land, far northern Greenland.

The H. H. Benedict Range or H. H. Benedict Mountains is a mountain range in Peary Land, Northern Greenland. Administratively this range is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.
The Daly Range or Daly Mountains is a mountain range in Peary Land, Northern Greenland. Administratively this range is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Sif Glacier, is a glacier in northern Greenland. Administratively it belongs to the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Johannes V. Jensen Land is an area in Peary Land, Northern Greenland. Administratively it lies in the Northeast Greenland National Park zone. The area is remote and currently uninhabited.

Navarana Fjord is a fjord in Peary Land, far northern Greenland. It is named after an Inuit woman.

Nansen Land is a peninsula in far northwestern Greenland. It is a part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

The Mary Peary Peaks are a mountain in the Roosevelt Range, Peary Land, Northern Greenland. Administratively they belong to the Northeast Greenland National Park.
Polkorridoren, formerly known as Nordpassagen, is a mountain pass in Peary Land, Greenland. Administratively, it is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Roosevelt Land is a peninsula in far northern Greenland. It is a part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Gertrud Rask Land is an area in Peary Land, North Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

Herluf Trolle Land is an area in Peary Land, North Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.










