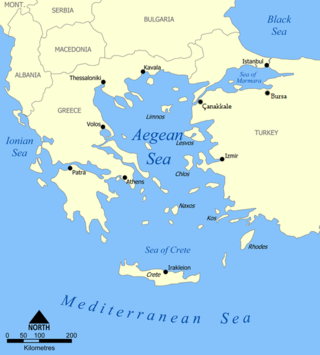
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 km2 (83,000 sq mi). In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

Hydra, or Ydra or Idra, and in antiquity Hydrea, is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece, located in the Aegean Sea between the Myrtoan Sea and the Argolic Gulf. It is separated from the Peloponnese by a narrow strip of water. In ancient times, the island was known as Hydrea, a reference to the natural springs on the island.

Salamis or Salamina is the largest Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about two kilometres from the coast of Piraeus and about 16 km west of central Athens. The chief city, Salamina, lies in the west-facing core of the crescent on Salamis Bay, which opens into the Saronic Gulf. On the eastern side of the island is its main port, Paloukia, the second largest port in Greece in terms of size, after the port of Piraeus.

The Saronic Gulf or Gulf of Aegina in Greece is formed between the peninsulas of Attica and Argolis and forms part of the Aegean Sea. It defines the eastern side of the isthmus of Corinth, being the eastern terminus of the Corinth Canal, which cuts across the isthmus. The Saronic Islands in the gulf have played a pivotal role in the history of Greece, with the largest, Salamis being the location of a significant naval battle in the Greco-Persian wars. The Megara Gulf makes up the northern end of the Saronic Gulf.

Poros is a small Greek island-pair in the southern part of the Saronic Gulf, about 58 km south of the port of Piraeus and separated from the Peloponnese by a 200 m (656 ft) wide sea channel, with the town of Galatas on the mainland across the strait. Its surface area is about 31 square kilometres (12 sq mi) and it has 3,261 inhabitants (2021). The ancient name of Poros was Pogon. Like other ports in the Saronic, it is a popular weekend destination for Athenian travellers.

The (Northern) Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea, in the Aegean Sea. They consist of 24 islands, four of which are permanently inhabited: Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros. They may also be referred to as the Thessalian Sporades.

Perama is a coastal town and a suburb of Piraeus and belongs to the Piraeus regional unit. It lies on the southwest edge of the Aegaleo mountains, on the Saronic Gulf coast. It is 8 km northwest of Piraeus, and 14 km west of the city of Athens. The municipality has an area of 14.729 km2. It forms the western terminus of the Port of Piraeus, and there is also a passenger port that provides ferry services to Salamis Island.

Dokos is a small Greek island of the Argo-Saronic Gulf, adjacent to Hydra, and separated from the Peloponnese by a narrow strait called, on some maps, "the Hydra Gulf." It is part of the municipality of Ýdra (Hydra) in Islands regional unit and reported a population of 18 persons at the 2011 census. The island is populated only by some Orthodox monks and perennial sheep herders. The island is rocky, reaching a height of 308 metres (1,010 ft). During ancient times it was called Aperopia (Ἀπεροπία).

The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The Isthmus was known in the ancient world as the landmark separating the Peloponnese from mainland Greece. In the first century AD the geographer Strabo noted a stele on the Isthmus of Corinth, which bore two inscriptions. One towards the East, i.e. towards Megara, reading: "Here is not Peloponnesus, but Ionia" and the one towards the West, i.e. towards the Peloponnese: "Here is Peloponnesus, not Ionia" ; Plutarch ascribed the erection of the stele to the Attic hero Theseus, on his way to Athens.

National Road 70 is a single carriageway road in southern Greece. It connects Corinth with Argos, via Epidavros and Nafplio. It is situated in the regional units Corinthia and Argolis, in the Peloponnese peninsula. The total length is 96 kilometres (60 mi).

Methana is a town and a former municipality on the Peloponnese peninsula, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia-Methana, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 50.161 km2.

Kineta is a beach town in West Attica, Greece. Since 2017 it is a separate community of the municipality Megara.

Piraeus Prefecture was one of the prefectures of Greece. Created in 1964 as a separate Prefecture (Νομός) and after the dissolution of the prefecture in 1972 was one of the 4 prefectures (Νομαρχίες) of Attica prefecture, and from 1994, part of the Athens-Piraeus super-prefecture (1994–2011). The capital of the prefecture was Piraeus. As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the prefecture was abolished, and its territory was divided into two regional units: Islands and Piraeus.
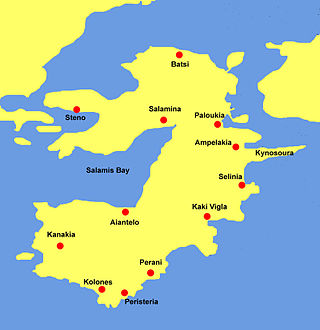
Salamis Bay is a bay on the west coast of Salamis Island, Greece. It connects with the Saronic Gulf to the west. Its maximum length is approximately 9 km from northeast to west. Cape Petriti forms its southwestern end. The main town of the island, Salamina, is on the northeastern end of the bay. The village Aianteio is on its south coast.

Hydra was a Greek destroyer of the Kountouriotis class, which served with the Hellenic Navy during the early stages of the Second World War. It was named after the Saronic Gulf island of Hydra, which played an important role in the Greek War of Independence, and was the fourth ship to bear this name.

The Greek People's Liberation Navy, commonly abbreviated as ELAN (ΕΛΑΝ), was the naval force of the communist-led Greek People's Liberation Army (ELAS) resistance movement during World War II, and later during the Greek Civil War.
The Dokos shipwreck is the oldest underwater shipwreck discovery known to archeologists. The wreck has been dated to the second Proto-Helladic period, 2700–2200 BC.

Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan seas, and to the west by the Ionian Sea which separates Greece from Italy.

The Islands Regional Unit is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Attica. The regional unit covers the Saronic Islands, a small part of the Peloponnese peninsula, and a few islands off the eastern Peloponnese coast.

Agios Georgios or San Tzortzis is a Greek uninhabited island in the entry of Saronic Gulf. It is the largest uninhabited island of the Saronic Islands with an area of 4.3 km2. Administratively, it is part of the municipality of Hydra.