
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett.

Aldabra is the world's second-largest coral atoll. It is situated in the Aldabra Group of islands in the Indian Ocean that are part of the Outer Islands of the Seychelles, with a distance of 1,120 km (700 mi) southwest of the capital, Victoria, on Mahé Island.

The Aldabra giant tortoise, from the islands of the Aldabra Atoll in the Seychelles, is one of the largest tortoises in the world. Historically, giant tortoises were found on many of the western Indian Ocean islands, as well as Madagascar, and the fossil record indicates giant tortoises once occurred on every continent and many islands with the exception of Australia and Antarctica. Many of the Indian Ocean species were thought to be driven to extinction by over-exploitation by European sailors, and they were all seemingly extinct by 1840 with the exception of the Aldabran giant tortoise on the island atoll of Aldabra. Although some remnant individuals of A. g. hololissa and A. g. arnoldi may remain in captivity, in recent times, these have all been reduced as subspecies of A. gigantea.

Pennisetum is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family, native to tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. They are known commonly as fountaingrasses. Pennisetum is considered a synonym of Cenchrus in Kew's Plants of the World Online.
Wielandia is a genus of flowering plant, of the family Phyllanthaceae first described as a genus in 1858. The plants are native to Kenya, Madagascar, and to various other islands in the Indian Ocean.

Dactyloctenium is a genus of Asian, African, and Australian plants in the grass family. A common name for the plants is crowfoot grasses.

Lepturus is a genus of plants in the grass family, native to Asia, Africa, Australia, and various islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Eleusine is a genus of Asian, African, and South American plants in the grass family, sometimes called by the common name goosegrass. One species (Eleusine indica), is a widespread weed in many places. Another species Eleusine coracana, is finger millet, cultivated as a cereal grain in India and parts of Africa.
Acrachne is a genus of Asian, African, and Australian plants in the grass family. Species in the genus are commonly known as goosegrass.

Apluda is a genus of plants in the grass family native to Asia and to various islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Centotheca is a genus of African, Asian, and Pacific Island plants in the grass family.
Daknopholis is a genus of African and Indian Ocean plants in the grass family. The only known species is Daknopholis boivinii, native to Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, Aldabra and Madagascar.

Stenotaphrum is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family.

Thuarea is a genus of plants in the grass family, native to Asia, Africa, Australia, and various islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Oxyrhachis is a genus of African plants in the grass family. The only known species is Oxyrhachis gracillima, native to Sierra Leone, Nigeria, Cameroon, Tanzania, Madagascar, KwaZulu-Natal, Cape Province.

Enteropogon is a genus of tropical and subtropical plants in the grass family. It is widespread across many parts of Asia, Africa, Australia, the Americas, and various islands.
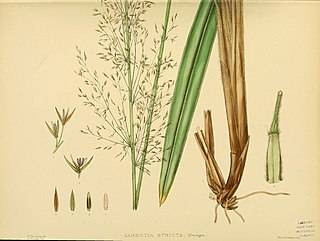
Garnotia is a genus of Asian, Australian, and tropical island plants in the grass family. Several of the species are native to Sri Lanka and southern India.
Halopyrum is a genus of Asian and African plants in the grass family. The only known species is Halopyrum mucronatum, native to the Indian Subcontinent, Iran, the Arabian Peninsula, Socotra, Madagascar, and eastern + northeastern Africa.
Leptaspis is a genus of Paleotropical plants in the grass family, native to Africa, southern Asia, northern Australia, and a few islands of the western Pacific.

The flora of Madagascar consists of more than 12,000 species of plants, as well as a poorly known number of fungi and algae. Around 83% of Madagascar's vascular plants are found only on the island. These endemics include five plant families, 85% of the over 900 orchid species, around 200 species of palms, and such emblematic species as the traveller's tree, six species of baobab and the Madagascar periwinkle. The high degree of endemism is due to Madagascar's long isolation following its separation from the African and Indian landmasses in the Mesozoic, 150–160 and 84–91 million years ago, respectively. However, few plant lineages remain from the ancient Gondwanan flora; most extant plant groups immigrated via across-ocean dispersal well after continental break-up.














