
Hellas Planitia is a plain located within the huge, roughly circular impact basin Hellas located in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. Hellas is the fourth- or fifth-largest known impact crater in the Solar System. The basin floor is about 7,152 m (23,465 ft) deep, 3,000 m (9,800 ft) deeper than the Moon's South Pole-Aitken basin, and extends about 2,300 km (1,400 mi) east to west. It is centered at 42.4°S 70.5°E. It features the lowest point on Mars, serves as a known source of global dust storms, and may have contained lakes and glaciers. Hellas Planitia spans the boundary between the Hellas quadrangle and the Noachis quadrangle.

A cryovolcano is a type of volcano that erupts gases and volatile material such as liquid water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. The erupted material is collectively referred to as cryolava; it originates from a reservoir of subsurface cryomagma. Cryovolcanic eruptions can take many forms, such as fissure and curtain eruptions, effusive cryolava flows, and large-scale resurfacing, and can vary greatly in output volumes. Immediately after an eruption, cryolava quickly freezes, constructing geological features and altering the surface.
The Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) is a scientific research institute dedicated to study of the solar system, its formation, evolution, and current state. The Institute is part of the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) and is supported by the Science Mission Directorate of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Located at 3600 Bay Area Boulevard in Houston, Texas, the Institute serves as a scientific forum attracting visiting scientists, postdoctoral fellows, students, and resident experts; supports and serves the research community through newsletters, meetings, and other activities; collects and disseminates planetary data while facilitating the community's access to NASA astromaterials samples and facilities; engages and excites the public about space science; and invests in the development of future generations of scientists. The LPI sponsors and organizes several workshops and conferences throughout the year, including the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) held in March in the Houston area.

Elysium, located in the Elysium and Cebrenia quadrangles, is the second largest volcanic region on Mars, after Tharsis. The region includes the volcanoes Hecates Tholus, Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus. The province is centered roughly on Elysium Mons at 24.7°N 150°E. Elysium Planitia is a broad plain to the south of Elysium, centered at 3.0°N 154.7°E. Another large volcano, Apollinaris Mons, lies south of Elysium Planitia and is not part of the province. Besides having large volcanoes, Elysium has several areas with long trenches, called fossa or fossae (plural) on Mars. They include the Cerberus Fossae, Elysium Fossae, Galaxias Fossae, Hephaestus Fossae, Hyblaeus Fossae, Stygis Fossae and Zephyrus Fossae.
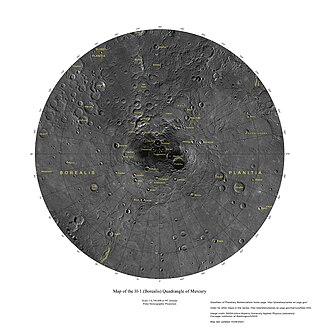
The Borealis quadrangle is a quadrangle on Mercury surrounding the north pole down to 65° latitude. It was mapped in its entirety by the MESSENGER spacecraft, which orbited the planet from 2008 to 2015, excluding areas of permanent shadow near the north pole. Only approximately 25% of the quadrangle was imaged by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during its flybys in 1974 and 1975. The quadrangle is now called H-1.
The Caloris group is a set of geologic units on Mercury. McCauley and others have proposed the name “Caloris Group” to include the mappable units created by the impact that formed the Caloris Basin and have formally named four formations within the group, which were first recognized and named informally by Trask and Guest based on imagery from the Mariner 10 spacecraft that flew by Mercury in 1974 and 1975. The extent of the formations within the group have been expanded and refined based on imagery and other data from the MESSENGER spacecraft which orbited Mercury from 2011 to 2015, and imaged parts of the planet that were in shadow at the time of the Mariner 10 encounters.
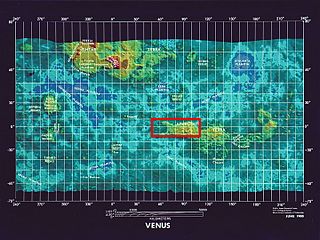
Ovda Regio is a Venusian crustal plateau located near the equator in the western highland region of Aphrodite Terra that stretches from 10°N to 15°S and 50°E to 110°E. Known as the largest crustal plateau in Venus, the regio covers an area of approximately 15,000,000 square kilometres (5,800,000 sq mi) and is bounded by regional plains to the north, Salus Tessera to the west, Thetis Regio to the east, and Kuanja as well as Ix Chel chasmata to the south. The crustal plateau serves as a place to hold the localized tessera terrains in the planet, which makes up roughly 8% of Venus' surface area. The kinematic evolution of crustal plateaus on Venus has been a debated topic in the planetary science community. Understanding its complex evolution is expected to contribute to a better knowledge of the geodynamic history of Venus. It is named after a Marijian forest spirit that can appear as both male and female.
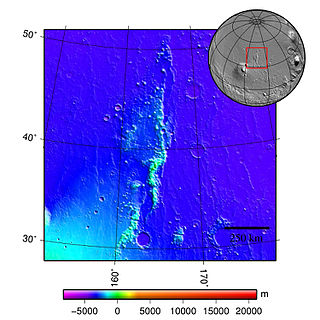
The Phlegra Montes are a system of eroded Hesperian–Noachian-aged massifs and knobby terrain in the mid-latitudes of the northern lowlands of Mars, extending northwards from the Elysium Rise towards Vastitas Borealis for nearly 1,400 km (870 mi). The mountain ranges separate the large plains provinces of Utopia Planitia (west) and Amazonis Planitia (east), and were named in the 1970s after a classical albedo feature. The massif terrains are flanked by numerous parallel wrinkle ridges known as the Phlegra Dorsa.
The Hesperian is a geologic system and time period on the planet Mars characterized by widespread volcanic activity and catastrophic flooding that carved immense outflow channels across the surface. The Hesperian is an intermediate and transitional period of Martian history. During the Hesperian, Mars changed from the wetter and perhaps warmer world of the Noachian to the dry, cold, and dusty planet seen today. The absolute age of the Hesperian Period is uncertain. The beginning of the period followed the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment and probably corresponds to the start of the lunar Late Imbrian period, around 3700 million years ago (Mya). The end of the Hesperian Period is much more uncertain and could range anywhere from 3200 to 2000 Mya, with 3000 Mya being frequently cited. The Hesperian Period is roughly coincident with the Earth's early Archean Eon.

The geological history of Mars follows the physical evolution of Mars as substantiated by observations, indirect and direct measurements, and various inference techniques. Methods dating back to 17th-century techniques developed by Nicholas Steno, including the so-called law of superposition and stratigraphy, used to estimate the geological histories of Earth and the Moon, are being actively applied to the data available from several Martian observational and measurement resources. These include landers, orbiting platforms, Earth-based observations, and Martian meteorites.

The Amazonian is a geologic system and time period on the planet Mars characterized by low rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and by cold, hyperarid conditions broadly similar to those on Mars today. The transition from the preceding Hesperian period is somewhat poorly defined. The Amazonian is thought to have begun around 3 billion years ago, although error bars on this date are extremely large. The period is sometimes subdivided into the Early, Middle, and Late Amazonian. The Amazonian continues to the present day.

Guinevere Planitia is an expansive lowland region of Venus that lies east of Beta Regio and west of Eistla Regio. These low-lying plains, particularly in the western portion, are characterized by apparent volcanic source vents and broad regions of bright, dark, and mottled deposits. They are the only break in an equatorially connected zone of highlands and tectonic zones. The types, numbers, and patterns of mapped tectonic features and small volcanic landforms in the region provide important detail in the interpretation and evolution of venusian landscape.

NASA's Magellan spacecraft mission discovered that Venus has a geologically young surface with a relatively uniform age of 500±200 Ma. The age of Venus was revealed by the observation of over 900 impact craters on the surface of the planet. These impact craters are nearly uniformly distributed over the surface of Venus and less than 10% have been modified by plains of volcanism or deformation. These observations indicate that a catastrophic resurfacing event took place on Venus around 500 Ma, and was followed by a dramatic decline in resurfacing rate. The radar images from the Magellan missions revealed that the terrestrial style of plate tectonics is not active on Venus and the surface currently appears to be immobile.

Devana Chasma is a weak extensional rift zone on Venus, with a length of 4000 km, a width of 150–250 km, and a depth reaching 5 km. Most of the faults are facing north–south. The rift is located in Beta Regio, a 3000 km rise created by volcanic activity. Mantle plumes rising from the bottom are the reason behind the formation of the rift zone. The slow extension rates in the rift may be driven by the same reason.
The Accruva Formation is one of multiple geologic units found on Venus. Abbreviated psh, it is also known as shield plains due to the shield like structures formed in its region. It is characterized by its abundant clusters of small shield dome structures located throughout the unit and lack of pervasive tectonic deformation. The domes that characterize the unit are likely volcanic edifices, the result of multiple small volcanic eruptions over an extended period of time. It formed during the second half of the Guineverian Period, in which vast plains formed globally on Venus. It is one of 14 formations identified by Mikhail A. Ivanov and James W. Head.

A tessera is a region of heavily deformed terrain on Venus, characterized by two or more intersecting tectonic elements, high topography, and subsequent high radar backscatter. Tesserae often represent the oldest material at any given location and are among the most tectonically deformed terrains on Venus's surface. Diverse types of tessera terrain exist. It is not currently clear if this is due to a variety in the interactions of Venus's mantle with regional crustal or lithospheric stresses, or if these diverse terrains represent different locations in the timeline of crustal plateau formation and fall. Multiple models of tessera formation exist and further extensive studies of Venus's surface are necessary to fully understand this complex terrain.

Lada Terra, named for a Slavic goddess of Love, is a major landmass near the south pole of Venus which is centered at 60°S and 20°E and has a diameter of 8,615 kilometres (5,353 mi). It is defined by the International Astronomical Union as one of the three "major landmasses," or terrae, of Venus. The term "landmass" is not analogous to the landmass on Earth, as there are no apparent oceans on Venus. The term here applies to a substantial portion of land that lies above the average planetary radius, and corresponds to highlands.

Ganis Chasma is a group of rift zones on the surface of the planet Venus. Bright spots detected by the Venus Monitoring Camera on the European Space Agency's Venus Express in the area suggest that there may be active volcanism on Venus.

PateraPAT-ər-ə is an irregular crater, or a complex crater with scalloped edges on a celestial body. Paterae can have any origin, although the majority of them were created by volcanism. The term comes from Latin, where it refers to a shallow bowl used in antique cultures.
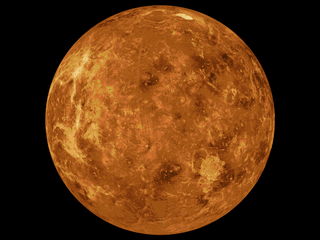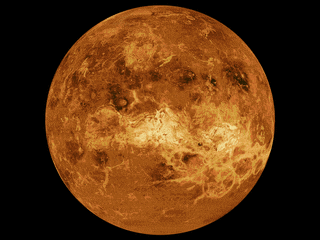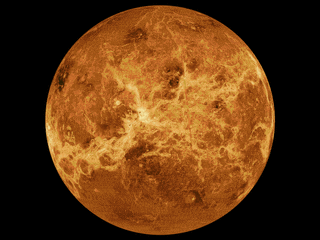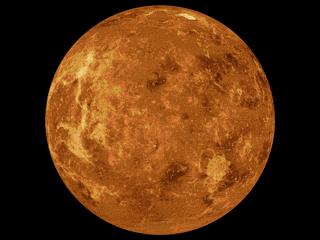
The mapping of Venus refers to the process and results of human description of the geological features of the planet Venus. It involves surface radar images of Venus, construction of geological maps, and the identification of stratigraphic units, volumes of rock with a similar age.

















