
Alphonsus is an ancient impact crater on the Moon that dates from the pre-Nectarian era. It is located on the lunar highlands on the eastern end of Mare Nubium, west of the Imbrian Highlands, and slightly overlaps the crater Ptolemaeus to the north. To the southwest is the smaller Alpetragius. The crater name was approved by the IAU in 1935.

Shackleton is an impact crater that lies at the lunar south pole. The peaks along the crater's rim are exposed to almost continual sunlight, while the interior is perpetually in shadow. The low-temperature interior of this crater functions as a cold trap that may capture and freeze volatiles shed during comet impacts on the Moon. Measurements by the Lunar Prospector spacecraft showed higher than normal amounts of hydrogen within the crater, which may indicate the presence of water ice. The crater is named after Antarctic explorer Ernest Shackleton.

Cleopatra is an impact crater on Venus, in Maxwell Montes. Cleopatra is a double-ring impact basin about 100 kilometers (62 mi) in diameter and 2.5 kilometers (1.6 mi) deep. A steep-walled, winding channel a few kilometers wide breaks through the rough terrain surrounding the crater rim. A large amount of lava originating in Cleopatra flowed through this channel and filled valleys in Fortuna Tessera. Cleopatra is superimposed on the structures of Maxwell Montes and appears to be undeformed, indicating that Cleopatra is relatively young. The crater is named after Egyptian queen Cleopatra VII.

Mead is an impact crater on Venus named in honor of the cultural anthropologist Margaret Mead.

The Tolstoj quadrangle in the equatorial region of Mercury runs from 144 to 216° longitude and -25 to 25° latitude. It was provisionally called "Tir", but renamed after Leo Tolstoy by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Also called Phaethontias.

The Beethoven quadrangle is located in the equatorial region of Mercury, in the center of the area imaged by Mariner 10. Most pictures of the quadrangle were obtained at high sun angles as the Mariner 10 spacecraft receded from the planet. Geologic map units are described and classified on the basis of morphology, texture, and albedo, and they are assigned relative ages based on stratigraphic relations and on visual comparisons of the density of superposed craters. Crater ages are established by relative freshness of appearance, as indicated by topographic sharpness of their rim crests and degree of preservation of interior and exterior features such as crater floors, walls, and ejecta aprons. Generally, topography appears highly subdued because of the sun angle, and boundaries between map units are not clearly defined.

Barton crater is a 54-km (32-mi) diameter crater on Venus. It is the size at which craters on Venus begin to possess peak rings instead of a single central peak. The floor of Barton crater is flat and radar-dark, indicating possible infilling by lava flows sometime following the impact. Barton's central peak-ring is discontinuous and appears to have been disrupted or separated during or following the cratering process. The crater was named in 1991 after Clara Barton, the founder of the American Red Cross.

Mozart is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976 after Austrian composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.
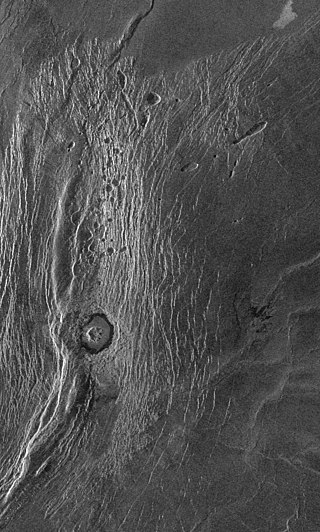
Wanda is a crater in the Akna Montes on Venus first mapped first by the Soviet Venera 15/16 mission in 1984. It was formed by the impact of an asteroid. The crater has a rugged central peak and a smooth radar-dark floor, probably volcanic material. The crater does not appear to be much deformed by later crustal movement that uplifted the mountains and crumpled the plains. Material from the adjacent mountain ridge to the west, however, appears to have collapsed into the crater. Small pits seen to the north of the crater may be volcanic collapse pits a few kilometers across.

Eminescu is a peak ring crater on Mercury 125 kilometers (78 mi) in diameter. Since there are very few later craters superposed on it, Eminescu appears to be a young crater formed around one billion years ago. It has a transitional morphology between larger more complex impact basins like Raditladi and smaller simpler central peak craters.
The Oxia Palus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Oxia Palus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-11.
The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. It is also referred to as MC-20 . The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle covers the area from 315° to 360° west longitude and 0° to 30° degrees south latitude on Mars. It contains Schiaparelli, a large, easily visible crater that sits close to the equator. The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle contains parts of Noachis Terra and Terra Sabaea.

Zumba is a very young crater on Mars, located in the Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle at 28.68 South and 133.18 West. It measures approximately 2.93 kilometres (1.82 mi) in diameter and was named after the town of Zumba in Ecuador. The name was adopted by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 2006.

Ritchey is a crater on Mars, located in the Coprates quadrangle at 28.8° South and 51° West. It measures 79 kilometers in diameter and was named after George W. Ritchey, an American astronomer (1864–1945). Ritchey lies south of Valles Marineris and north of Argyre Planitia, a large impact crater. There is strong evidence that it was once a lake.

Moody is an impact crater on Mercury.

Amaral is a crater on the planet Mercury. With its smooth floor, surrounding ejecta, and small secondary craters, it appears noticeably younger than the heavily cratered surface around it. Along with a smooth crater floor, Amaral also has a central peak. Bright material on this peak is of particular interest as it appears to have an unusual color. In color-enhanced images, the central peak of Amaral appears as a bright blue color in striking contrast to the otherwise orange tones of surface material nearby. The different color of the central peak likely indicates rocks with different chemical composition from those on the neighboring surface.

Raditladi is a large impact crater on Mercury with a diameter of 263 km. Inside its peak ring there is a system of concentric extensional troughs (graben), which are rare surface features on Mercury. The floor of Raditladi is partially covered by relatively light smooth plains, which are thought to be a product of the effusive volcanism. The troughs may also have resulted from volcanic processes under the floor of Raditladi. The basin is relatively young, probably younger than one billion years, with only a few small impact craters on its floor and with well-preserved basin walls and peak-ring structure. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.

Burton is an impact crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. It is 123.0 km in diameter and was named after British astronomer Charles E. Burton; the name was approved in 1973.

Occator is an impact crater located on Ceres, the largest object in the main asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, that contains "Spot 5", the brightest of the bright spots observed by the Dawn spacecraft. It was known as "Region A" in ground-based images taken by the W. M. Keck Observatory on Mauna Kea.

Baltisk is a crater in the Argyre quadrangle of Mars. It was named after a town in Russia in 1976. Baltisk is located on the western edge of the Argyre impact basin.




















