
An impact crater is a depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

Meitner is a multiring impact crater on Venus. This crater was named in 1979 after the female Austrian-Swedish physicist, Lise Meitner, in her honour.

Cleopatra is an impact crater on Venus, in Maxwell Montes. Cleopatra is a double-ring impact basin about 100 kilometers (62 mi) in diameter and 2.5 kilometers (1.6 mi) deep. A steep-walled, winding channel a few kilometers wide breaks through the rough terrain surrounding the crater rim. A large amount of lava originating in Cleopatra flowed through this channel and filled valleys in Fortuna Tessera. Cleopatra is superimposed on the structures of Maxwell Montes and appears to be undeformed, indicating that Cleopatra is relatively young. The crater is named after Egyptian queen Cleopatra VII.

Yablochkina is an impact crater on Venus. It was named in 1985 after Soviet actress Aleksandra Yablochkina.

Mead is an impact crater on Venus named in honor of the cultural anthropologist Margaret Mead.

Golubkina is a crater on Venus. It was named in 1985 after the Soviet sculptor Anna Golubkina.
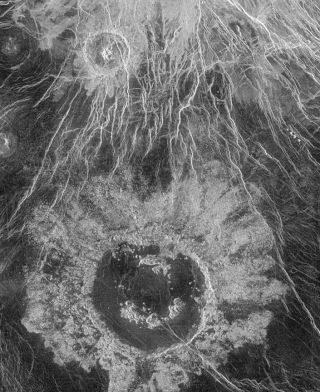
Wheatley is a crater on Venus at latitude 16.6, longitude 268 in Asteria Regio. It was named in 1994 after Phillis Wheatley, the first black writer of note in America (1753–1784).

Mona Lisa is a crater on Venus at latitude 25.55, longitude 25.1. It was named in 1991 after Lisa Giacondo, Leonardo da Vinci's model for the painting Mona Lisa.

Mozart is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976 after Austrian composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.

Isabella is the second largest impact crater on Venus. The feature was named in 1994, in honor of the 15th Century queen of Spain, Isabella I of Castile. Located at 30 degrees south latitude, 204 degrees east longitude, the crater has two extensive flow-like structures extending to the south and to the southeast. The end of the southern flow partially surrounds a pre-existing 40-kilometer (25 mi) circular volcanic shield. The southeastern flow shows a complex pattern of channels and flow lobes, and is overlain at its southeastern tip by deposits from a later 20-kilometer (12 mi) diameter impact crater, Cohn.

Buck is a crater in the Navka region of Venus. It has the terraced walls, flat radar-dark floor, and central peak that are characteristic of craters classified as "complex". The central peak on its floor is unusually large. Flow-like deposits extend beyond the limits of the coarser rim deposits on its west and southwest. Like about half of the craters mapped by Magellan to date, it is surrounded by a local, radar-dark halo.

Eminescu is a peak ring crater on Mercury 125 kilometers (78 mi) in diameter. Since there are very few later craters superposed on it, Eminescu appears to be a young crater formed around one billion years ago. It has a transitional morphology between larger more complex impact basins like Raditladi and smaller simpler central peak craters.

Verdi is an impact crater on the planet Mercury. It was named after Italian Romantic composer Giuseppe Verdi (1813–1901) in 1979, as recognized by the International Astronomical Union. The crater's extensive ejecta blanket and secondary crater field are superposed on plains materials and older craters.

Moody is an impact crater on Mercury.

Complex craters are a type of large impact crater morphology. Complex craters are classified into two groups: central-peak craters and peak-ring craters. Peak-ring craters have diameters that are larger in than central-peak craters and have a ring of raised massifs which are roughly half the rim-to-rim diameter, instead of a central peak.

Scarlatti is a pit-floored crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1974 by the Mariner 10 spacecraft. It has a prominent peak ring, and it is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. The crater floor is covered by the smooth plains material. The crater displays an arcuate collapse feature along the northeastern peak ring. The size of the pit, which was first noticed in MESSENGER images obtained in January 2008, is 38 × 12 km. Such a feature may have resulted from collapse of a magma chamber underlying the central peak ring complex of the crater. The collapse feature is an analog of Earth's volcanic calderas. Scarlatti is thought to have the same age as the Caloris basin.

Rachmaninoff is an impact crater on Mercury. This basin, first imaged in its entirety during MESSENGER's third Mercury flyby, was quickly identified as a feature of high scientific interest, because of its fresh appearance, its distinctively colored interior plains, and the extensional troughs on its floor. The morphology of Rachmaninoff is similar to that of Raditladi, which is one of the youngest impact basins on Mercury. The age of Raditladi is estimated at one billion years. Rachmaninoff appears to be only slightly older.
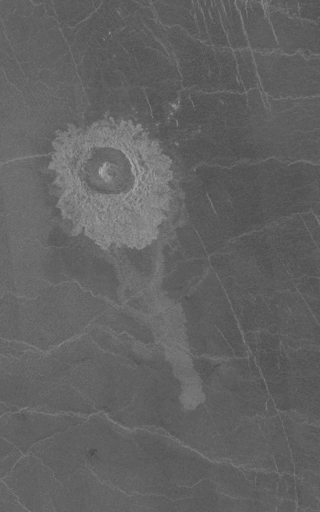
Ariadne is a crater on Venus. Its central peak serves as the prime meridian of the planet, a status formerly held by Eve Crater until relocated.

A multi-ringed basin is not a simple bowl-shaped crater, or a peak ring crater, but one containing multiple concentric topographic rings; a multi-ringed basin could be described as a massive impact crater, surrounded by circular chains of mountains resembling rings on a bull's-eye. A multi-ringed basin may have an area of many thousands of square kilometres.

A peak ring crater is a type of complex crater, which is different from a multi-ringed basin or central-peak crater. A central peak is not seen; instead, a roughly circular ring or plateau, possibly discontinuous, surrounds the crater's center, with the crater rim still farther out from the center.




















