The Bodleian Library is the main research library of the University of Oxford, and is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. It derives its name from its founder, Sir Thomas Bodley. With over 13 million printed items, it is the second-largest library in Britain after the British Library. Under the Legal Deposit Libraries Act 2003, it is one of six legal deposit libraries for works published in the United Kingdom, and under Irish law it is entitled to request a copy of each book published in the Republic of Ireland. Known to Oxford scholars as "Bodley" or "the Bod", it operates principally as a reference library and, in general, documents may not be removed from the reading rooms.

The Aztec or Mexica calendar is the calendrical system used by the Aztecs as well as other Pre-Columbian peoples of central Mexico. It is one of the Mesoamerican calendars, sharing the basic structure of calendars from throughout the region.

John Selden was an English jurist, a scholar of England's ancient laws and constitution and scholar of Jewish law. He was known as a polymath; John Milton hailed Selden in 1644 as "the chief of learned men reputed in this land."

The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec codex, believed to have been created around the year 1541. It contains a history of both the Aztec rulers and their conquests as well as a description of the daily life of pre-conquest Aztec society. The codex is written using traditional Aztec pictograms with a translation and explanation of the text provided in Spanish. It is named after Don Antonio de Mendoza (1495-1552), the viceroy of New Spain, who supervised its creation and who was a leading patron of native artists.

Aztec codices are Mesoamerican manuscripts made by the pre-Columbian Aztec, and their Nahuatl-speaking descendants during the colonial period in Mexico.

The Aubin Codex is an 81-leaf Aztec codex written in alphabetic Nahuatl on paper from Europe. Its textual and pictorial contents represent the history of the Aztec peoples who fled Aztlán, lived during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and into the early Spanish colonial period, ending in 1608.

The Codex Magliabechiano is a pictorial Aztec codex created during the mid-16th century, in the early Spanish colonial period. It is representative of a set of codices known collectively as the Magliabechiano Group. The Codex Magliabechiano is based on an earlier unknown codex, which is assumed to have been the prototype for the Magliabechiano Group. It is named after Antonio Magliabechi, a 17th-century Italian manuscript collector, and is held in the Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale, Florence, Italy.

The Codex Borbonicus is an Aztec codex written by Aztec priests shortly before or after the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. It is named after the Palais Bourbon in France and kept at the Bibliothèque de l'Assemblée Nationale in Paris. The codex is an outstanding example of how Aztec manuscript painting is crucial for the understanding of Mexica calendric constructions, deities, and ritual actions.

Codex Boturini, also known as the Tira de la Peregrinación de los Mexica, is an Aztec codex, which depicts the migration of the Azteca, later Mexica, people from Aztlán. Its date of manufacture is unknown, but likely to have occurred before or just after the Conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521). At least two other Aztec codices have been influenced by the content and style of the Boturini Codex. This Codex has become an insignia of Mexica history and pilgrimage and is carved into a stone wall at the entrance of the National Museum of Anthropology and History in Mexico City.
Mesoamerica, along with Mesopotamia and China, is one of three known places in the world where writing is thought to have developed independently. Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are a combination of logographic and syllabic systems. They are often called hieroglyphs due to the iconic shapes of many of the glyphs, a pattern superficially similar to Egyptian hieroglyphs. Fifteen distinct writing systems have been identified in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, many from a single inscription. The limits of archaeological dating methods make it difficult to establish which was the earliest and hence the progenitor from which the others developed. The best documented and deciphered Mesoamerican writing system, and the most widely known, is the classic Maya script. Earlier scripts with poorer and varying levels of decipherment include the Olmec hieroglyphs, the Zapotec script, and the Isthmian script, all of which date back to the 1st millennium BC. An extensive Mesoamerican literature has been conserved, partly in indigenous scripts and partly in postconquest transcriptions in the Latin script.

Mixtec writing originated as a logographic writing system during the Post-Classic period in Mesoamerican history. Records of genealogy, historic events, and myths are found in the pre-Columbian Mixtec codices. The arrival of Europeans in 1520 AD caused changes in form, style, and the function of the Mixtec writings. Today these codices and other Mixtec writings are used as a source of ethnographic, linguistic, and historical information for scholars, and help to preserve the identity of the Mixtec people as migration and globalization introduce new cultural influences.

The Codex Laud, or Laudianus, is a sixteenth-century Mesoamerican codex named for William Laud, an English archbishop who was the former owner. It is from the Borgia Group, and is a pictorial manuscript consisting of 24 leaves from Central Mexico, dating from before the Spanish takeover. It is evidently incomplete.

In art history, a speech scroll is an illustrative device denoting speech, song, or other types of sound.

Antiquities of Mexico is a compilation of facsimile reproductions of Mesoamerican literature such as Maya codices, Mixtec codices, and Aztec codices as well as historical accounts and explorers' descriptions of archaeological ruins. It was assembled and published by Edward King, Lord Kingsborough, in the early decades of the 19th century. While much of the material pertains to pre-Columbian cultures, there are also documents relevant to studies of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. Antiquities of Mexico was produced to make copies of rare manuscripts in European collections available for study by scholars.

The Codex Cospi is a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican pictorial manuscript, included in the Borgia Group. It is currently located in the library of the University of Bologna.
Elizabeth Hill Boone is an American art historian, ethnohistorian and academic, specializing in the study of Latin American art and in particular the early colonial and pre-Columbian art, iconography and pictorial codices associated with the Mixtec, Aztec and other Mesoamerican cultures in the central Mexican region. Her extensive published research covers investigations into the nature of Aztec writing, the symbolism and structure of Aztec art and iconography and the interpretation of Mixtec and Aztec codices.
Yahui is a supernatural figure that takes on various mixtures of animal and human forms within the culture and belief systems of the Mixtec—indigenous Mixtecan-speaking people of La Mixteca in central-southeastern Mexico. It is an important and recurring motif in Mixtec iconography, thought and culture, especially during the pre-Columbian era. As a supernatural figure, the yahui appears in Postclassic Mixtec codices as an entity wearing a serpent or reptilian tail and headdress and the carapace of a turtle.

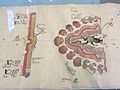
The Codex Bodley is an important pictographic manuscript and example of Mixtec historiography. It was named after the colloquial name of the Bodleian Library, where it has been stored since the 17th century.

The Codex Selden is a Mexican manuscript of Mixtec origin. The codex is an account of the genealogy of the Jaltepec dynasty from the tenth to the 16th century. Codex Selden is possibly a fragment of a much longer improperly stored document. Although it was completed after the arrival of the conquistadors in the Mixtec region, it is considered one of the six pre-Hispanic Mixtec codices that survived the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. The last date mentioned in the Codex is 1556, which can be interpreted as the date when the codex was finished.

Mesoamerican codices are manuscripts that present traits of the Mesoamerican indigenous pictoric tradition, either in content, style, or in regards to their symbolic conventions. The unambiguous presence of Mesoamerican writing systems in some of these documents is also an important, but not defining, characteristic, for Mesoamerican codices can comprise pure pictorials, native cartographies with no traces of glyphs on them, or colonial alphabetic texts with indigenous illustrations. Perhaps the best-known examples among such documents are Aztec codices, Maya codices, and Mixtec codices, but other cultures such as the Tlaxcaltec, the Purépecha, the Otomi, the Zapotecs, and the Cuicatecs, are creators of equally relevant manuscripts. The destruction of Mesoamerican civilizations resulted in only about twenty known pre-Columbian codices surviving to modern times.