
A boot is a type of footwear. Most boots mainly cover the foot and the ankle, while some also cover some part of the lower calf. Some boots extend up the leg, sometimes as far as the knee or even the hip. Most boots have a heel that is clearly distinguishable from the rest of the sole, even if the two are made of one piece. Traditionally made of leather or rubber, modern boots are made from a variety of materials.

A riding boot is a boot made to be used for horse riding. The classic boot comes high enough up the leg to prevent the leathers of the saddle from pinching the leg of the rider, has a sturdy toe to protect the rider's foot when on the ground and has a distinct heel to prevent the foot from sliding through the stirrup. The sole is smooth or lightly textured to avoid being caught on the tread of the stirrup in the event of a fall.

Chaps are sturdy coverings for the legs consisting of leggings and a belt. They are buckled on over pants with the chaps' integrated belt, but unlike trousers, they have no seat and are not joined at the crotch. They are designed to provide protection for the legs and are usually made of leather or a leather-like material. Their name is a shortened version of the Spanish word chaparajos. Chaparajos were named after the chaparral, from which they were designed to protect the legs while riding on horseback. Like much of western American horse culture, the origin of chaparajos was in the south of Spain, from which it then passed on to the part of New Spain that later became Mexico, and has been assimilated into cowboy culture of the American West. They are a protective garment to be used when riding a horse through brushy terrain. In the modern world, they are worn for both practical work purposes and for exhibition or show use. Chaps have also been adopted for use on motorcycles, particularly by cruiser-style motorcycle riders.

An orthopedic cast, or simply cast, is a shell, frequently made from plaster or fiberglass, that encases a limb to stabilize and hold anatomical structures—most often a broken bone, in place until healing is confirmed. It is similar in function to a splint.

Motorcycle boots are associated with motorcycle riders and range from above ankle to below knee boots. They have an outside of a typical boot but a low heel to control the motorcycle. To improve motorcycle safety, motorcycle boots are generally made from a thick, heavy leather and may include energy absorbing and load spreading padding, metal, plastic and/or composite materials to protect the motorcycle rider's feet, ankles and legs in an accident. For use in wet weather, some boots have a waterproof membrane lining such as Gore-Tex or SympaTex.

Breeches are an article of clothing covering the body from the waist down, with separate coverings for each leg, usually stopping just below the knee, though in some cases reaching to the ankles. Formerly a standard item of Western men's clothing, they had fallen out of use by the mid-19th century in favour of trousers.
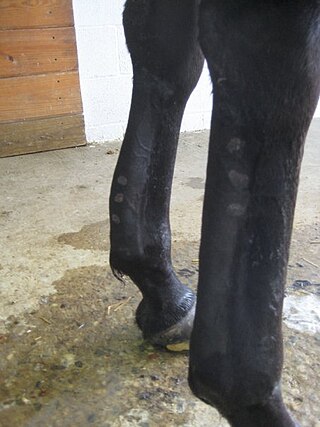
Tendinitis/tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon, often involving torn collagen fibers. A bowed tendon is a horseman's term for a tendon after a horse has sustained an injury that causes swelling in one or more tendons creating a "bowed" appearance.

Equine conformation evaluates a horse's bone structure, musculature, and its body proportions in relation to each other. Undesirable conformation can limit the ability to perform a specific task. Although there are several faults with universal disadvantages, a horse's conformation is usually judged by what its intended use may be. Thus "form to function" is one of the first set of traits considered in judging conformation. A horse with poor form for a Grand Prix show jumper could have excellent conformation for a World Champion cutting horse, or to be a champion draft horse. Every horse has good and bad points of its conformation and many horses excel even with conformation faults.

Polo wraps or exercise bandages are bandage-style leg protectors for horses. Made of fleece or elastic material, they are wound around a horse's legs from the fetlock to the knee or hock. They can be quite stretchy compared to other bandaging materials, and are used mainly for protection during ridden work, longeing, and turnout. They are often used as an alternative to boots.

Gaiters are garments worn over the shoe and bottom of the pant or trouser leg and used primarily as personal protective equipment, in particular against snakebite; similar garments used primarily for display are spats.

Bell boots, or overreach boots, are a type of protective boot worn by a horse. They encircle the horse's ankle, and protect the back of the lower front leg—the pastern and heels—from being struck by the toe of the rear hoof.

A stable bandage, or standing bandage/wrap, is a type of wrap used on the lower legs of a horse. A stable bandage runs from just below the knee or hock, to the bottom of the fetlock joint, and protects the cannon bone, tendons of the lower leg, and fetlock joint.

There are many aspects to horse management. Horses, ponies, mules, donkeys and other domesticated equids require attention from humans for optimal health and long life.

Jodhpurs, in their modern form, are tight-fitting trousers to the ankle, where they end in a snug cuff, and are worn primarily for horse riding. The term is also used as slang for a type of short riding boot, also called a paddock boot or a jodhpur boot, because they are worn with jodhpurs. According to Tara Mayer, "Jodhpurs … exemplify the material and cultural exchanges between Britain and its Indian colony in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries."

Leg wraps and boots are used for the protection of the lower legs of horses during training, shipping, and exercise, as well as for therapeutic and medical purposes to provide support or cover for injuries.

Splint boots or brushing boots are used to protect a horse's legs during exercise, protecting the lower leg from injury that may occur if one leg or hoof strikes the opposite leg. The boots generally cover the leg from below the knee to below the fetlock. Shorter boots are called fetlock boots.

A fashion boot is a boot worn for reasons of style or fashion. The term is usually applied to women's boots. Fashion boots come in a wide variety of styles, from ankle to thigh-length, and are used for casual, formal, and business attire. Although boots were a popular style of women's footwear in the 19th century, they were not recognized as a high fashion item until the 1960s. They became widely popular in the 1970s and have remained a staple of women's winter wardrobes since then.

Cowboy boots are a specific style of riding boot, historically worn by cowboys. They have a high heel that is traditionally made of stacked leather, rounded to pointed toe, high shaft, and, traditionally, no lacing. Cowboy boots are normally made from cowhide leather, which may be decoratively hand-tooled, but are also sometimes made from "exotic" skins like alligator, snake, ostrich, lizard, eel, elephant, stingray, elk, buffalo, and so on.

Over-the-knee boots, OTK boots, are long boots that fully or partly cover the knee. Originally created as a man's riding boot in the 15th century, in the latter part of the 20th century, the style was redefined as a fashion boot for women. Over-the-knee boots are also used as a work boot in circumstances requiring additional protection for the legs.

The limbs of the horse are structures made of dozens of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the weight of the equine body. They include two apparatuses: the suspensory apparatus, which carries much of the weight, prevents overextension of the joint and absorbs shock, and the stay apparatus, which locks major joints in the limbs, allowing horses to remain standing while relaxed or asleep. The limbs play a major part in the movement of the horse, with the legs performing the functions of absorbing impact, bearing weight, and providing thrust. In general, the majority of the weight is borne by the front legs, while the rear legs provide propulsion. The hooves are also important structures, providing support, traction and shock absorption, and containing structures that provide blood flow through the lower leg. As the horse developed as a cursorial animal, with a primary defense mechanism of running over hard ground, its legs evolved to the long, sturdy, light-weight, one-toed form seen today.



















