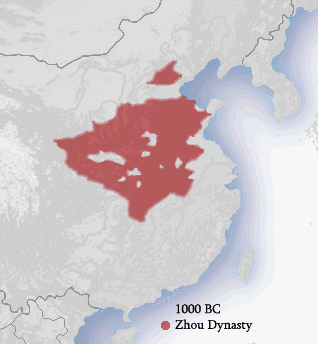
The Zhou dynasty was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of ancient China by the royal house, surnamed Ji, lasted from 1046 until 771 BC for a period known as the Western Zhou, and the political sphere of influence it created continued well into the Eastern Zhou period for another 500 years. The establishment date of 1046 BC is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC.

The Shang dynasty, also known as the Yin dynasty, was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the Book of Documents, Bamboo Annals and Records of the Grand Historian. Modern scholarship dates the dynasty between the 16th to 11th centuries BC, with more agreement surrounding the end date than beginning date.

A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 1950–1880 BCE and are depicted on cylinder seals from Central Anatolia in Kültepe dated to c. 1900 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel.

Chariot racing was one of the most popular ancient Greek, Roman, and Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from a very early time. With the institution of formal races and permanent racetracks, chariot racing was adopted by many Greek states and their religious festivals. Horses and chariots were very costly. Their ownership was a preserve of the wealthiest aristocrats, whose reputations and status benefitted from offering such extravagant, exciting displays. Their successes could be further broadcast and celebrated through commissioned odes and other poetry.

Yinxu is the site of one of the ancient and major historical capitals of China. It is the source of the archeological discovery of oracle bones and oracle bone script, which resulted in the identification of the earliest known Chinese writing. The archeological remnants known as Yinxu represent the ancient city of Yin, the last capital of China's Shang dynasty which existed through eight generations for 255 years, and through the reign of 12 kings. Yinxu was discovered, or rediscovered, in 1899. It is now one of China's oldest and largest archeological sites, and was selected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006. Yinxu is located in northernmost Henan province near the modern city of Anyang, and near the Hebei and Shanxi province borders. Public access to the site is permitted.

The Charioteer of Delphi, also known as Heniokhos, is a statue surviving from Ancient Greece, and an example of ancient bronze sculpture. The life-size (1.8m) statue of a chariot driver was found in 1896 at the Sanctuary of Apollo in Delphi. It is now in the Delphi Archaeological Museum.
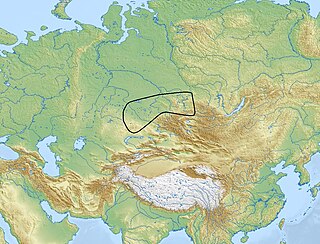
The Karasuk culture describes a group of late Bronze Age societies who ranged from the Aral Sea to the upper Yenisei in the east and south to the Altai Mountains and the Tian Shan in ca. 1500–800 BC.
The Afanasievo culture, or Afanasevo culture, is an early archaeological culture of south Siberia, occupying the Minusinsk Basin and the Altai Mountains during the eneolithic era, c. 3300 to 2500 BCE. It is named after a nearby mountain, Gora Afanasieva in what is now Bogradsky District, Khakassia, Russia, first excavated by archaeologist Sergei Teploukhov in 1920-1929. Afanasievo burials have been found as far as Shatar Chuluu in central Mongolia, confirming a further expansion about 1,500 km beyond the Altai mountains. The Afanasievo culture is now considered as an integral part of the Prehistory of Western and Central Mongolia.

The first evidence of humans using vehicle in warfare are Sumerian depictions of four-wheeled wagons pulled by semi-domesticated onagers. These war wagons were slow and cumbersome, but provided a protected elevated platform for javelineers and slingers. First depictions of war chariots come from Indo-European burials in the Ural steppes dated to around 2000 BC and became widespread around Eurasia by 500 BC. Chariots with spoke-wheels pulled by horses were lightweight and fast which made it feasible to outrun light infantry and wagons. Although horses have been ridden as from at least the 4th millennium BC they were most likely largely relegated to transporting warriors, who fought on foot. Until the invention and widespread adoption of the saddle and stirrup chariots remained the primary form of cavalry, as they offered a controllable and reliable platform from which fighters could rapidly manoeuvre around the battlefield and engage with projectile and melee weapons, dismount and fight on foot or climb on to make a swift retreat.

Western riding is considered a style of horse riding which has evolved from the ranching and welfare traditions which were brought to the Americas by the Spanish Conquistadors, as well as both equipment and riding style which evolved to meet the working needs of the cowboy in the American West. At the time, American cowboys had to work long hours in the saddle and often over rough terrain, sometimes having to rope a cattle using a lariat, also known as a lasso. Because of the necessity to control the horse with one hand and use a lariat with the other, western horses were trained to neck rein, that is, to change direction with light pressure of a rein against the horse's neck. Horses were also trained to exercise a certain degree of independence in using their natural instincts to follow the movements of a cow, thus a riding style developed that emphasized a deep, secure seat, and training methods encouraged a horse to be responsive on very light rein contact.

Deer stones, sometimes called the Deer stone-khirigsuur complex (DSKC) in reference to neighbouring khirigsuur tombs, are ancient megaliths carved with symbols found largely in Siberia and Mongolia. The name comes from their carved depictions of flying deer. The "Deer stones culture" relates to the lives and technologies of the late Bronze Age peoples associated with the deer stones complexes, as informed by archaeological finds, genetics and the content of deer stones art.

The Ordos culture was a material culture occupying a region centered on the Ordos Loop during the Bronze and early Iron Age from c. 800 BCE to 150 BCE. The Ordos culture is known for significant finds of Scythian art and may represent the easternmost extension of Indo-European Eurasian nomads, such as the Saka, or may be linkable to Palaeo-Siberians or Yeniseians. Under the Qin and Han dynasties, the area came under the control of contemporaneous Chinese states.
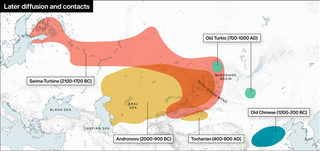
The Seima-Turbino culture, also Seima-Turbinsky culture or Seima-Turbino phenomenon, is a pattern of burial sites with similar bronze artifacts. Seima-Turbino is attested across northern Eurasia, particularly Siberia and Central Asia, maybe from Fennoscandia to Mongolia, Northeast China, Russian Far East, Korea, and Japan. The homeland is considered to be the Altai Mountains. These findings have suggested a common point of cultural origin, possession of advanced metal working technology, and unexplained rapid migration. The buried were nomadic warriors and metal-workers, traveling on horseback or two-wheeled carts.

The Xianyun was an ancient nomadic tribe that invaded the Zhou dynasty. This Chinese exonym is written with xian獫 or 玁 "long-snouted dog", and this "dog" radical 犭 is commonly used in graphic pejorative characters. "Xianyun" was the preferred designation for northern tribes during the Zhou dynasty, earlier designations being the Xunyu, Guifang, and later ones being the Xiongnu, during the Han dynasty.

Guifang was an ancient ethnonym for a northern people that fought against the Shang Dynasty. Chinese historical tradition used various names, at different periods, for northern tribes such as Guifang, Rong, Di, Xunyu, Xianyun, or Xiongnu peoples. This Chinese exonym combines gui and fang, a suffix referring to "non-Shang or enemy countries that existed in and beyond the borders of the Shang polity."
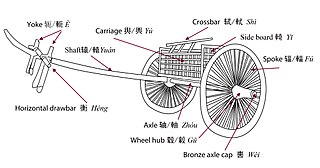
The ancient Chinese chariot was used as an attack and pursuit vehicle on the open fields and plains of ancient China from around 1200 BCE. Chariots also allowed military commanders a mobile platform from which to control troops while providing archers and soldiers armed with dagger-axes increased mobility. They reached a peak of importance during the Spring and Autumn period, but were largely superseded by cavalry during the Han dynasty.
Sun Yang (traditional Chinese: 孫陽; simplified Chinese: 孙阳; pinyin: Sūn Yáng; Wade–Giles: Sun1 Yang2), better known by the honorific name Bole or Bo Le (Po-le; traditional Chinese: 伯樂; simplified Chinese: 伯乐; pinyin: Bólè; Wade–Giles: Po2-le4) was a horse tamer in Spring and Autumn period, a retainer for the Duke Mu of Qin (r. 659-621 BCE), and a famous judge of horses. Bole was the legendary inventor of equine physiognomy ("judging a horse's qualities from appearance").

The Eastern Zhou is a period of Chinese history, approximately the second half of the Zhou dynasty, following the Western Zhou period. Characterised by weak central government, it is subdivided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn, during which the ancient aristocracy still held power in a large number of separate polities, and the Warring States, which saw the consolidation of territory into a few domains and the dominance of other social classes. "Eastern" refers to the geographic situation of the royal capital, near present-day Luoyang.

The Ulaanzuukh culture, also Ulaanzuukh-Tevsh culture, is an archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age eastern Mongolia. It likely preceded and was the origin of the Slab-grave culture.
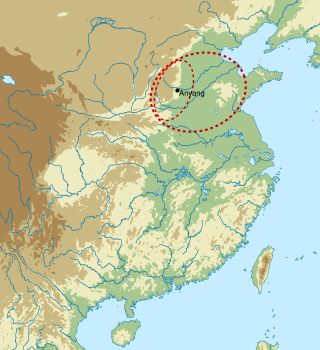
The Late Shang, also known as the Anyang period, is the earliest known literate civilization in China, spanning the reigns of the last nine kings of the Shang dynasty, beginning with Wu Ding in the second half of 13th century BC and ending with the overthrow of the Shang by the Zhou in the mid-11th century BC. The state is known from artifacts recovered from its capital at a site near Anyang now known as Yinxu and other sites across the North China Plain. One of the richest finds was the Tomb of Fu Hao at Yinxu, thought to belong to a consort of Wu Ding mentioned in Shang inscriptions.