Parnall was a British aircraft manufacturer that evolved from a wood-working company before the First World War to a significant designer of military and civil aircraft into the 1940s. It was based in the west of England and was originally known as George Parnall & Co. Ltd.

Handley Page Limited was a British aerospace manufacturer. Founded by Frederick Handley Page in 1909, it was the United Kingdom's first publicly traded aircraft manufacturing company. It went into voluntary liquidation and ceased to exist in 1970. The company, based at Radlett Aerodrome in Hertfordshire, was noted for its pioneering role in aviation history and for producing heavy bombers and large airliners.
Short Brothers plc, usually referred to as Shorts or Short, is an aerospace company based in Belfast, Northern Ireland. Shorts was founded in 1908 in London, and was the first company in the world to make production aeroplanes. It was particularly notable for its flying boat designs manufactured into the 1950s.

The Mitsubishi F1M is a Japanese reconnaissance floatplane of World War II. It was the last biplane type of the Imperial Japanese Navy, with 944 built between 1936 and 1944. The Navy designation was "Type Zero Observation Seaplane" (零式水上観測機).

Aichi Kokuki KK was a Japanese aerospace manufacturer which produced several designs for the Imperial Japanese Navy. After the war, the company was reorganized as Aichi Machine Industry Co., Ltd (愛知機械工業) where they made small kei cars until 1966 when they were integrated into Nissan and developed the Nissan Sunny and Nissan Vanette.

The Blackburn Shark was a carrier-borne torpedo bomber designed and built by the British aviation manufacturer Blackburn Aircraft. It was originally known as the Blackburn T.S.R., standing for "torpedo-spotter-reconnaissance", in reference to its intended roles. The Shark was the last of Blackburn's biplane torpedo bombers.

Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal had many names, each depending on the period of its existence, and the circumstances at that time. Many of the names were acronyms that were derived from its military name or designation, which changed from time to time. The arsenal was sometimes known as "Kūgi-shō". The name Yokosuka prevailed however, even though it referred to the Arsenal's location at Yokosuka, Japan.
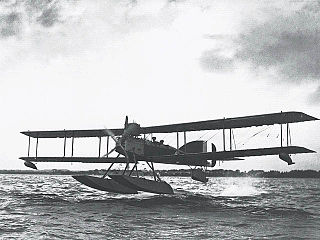
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It was first flown in 1915 and remained in service until after the armistice in 1918. A Short 184 was the first aircraft to sink a ship using a torpedo, and another was the only British aircraft to take part in the Battle of Jutland.

The Short Bomber was a British two-seat long-range reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying aircraft designed by Short Brothers as a land-based development of the very successful Short Type 184.

The Short Sturgeon was a planned British carrier-borne reconnaissance bomber whose development began during Second World War with the S.6/43 requirement for a high-performance torpedo bomber, which was later refined into the S.11/43 requirement which was won by the Sturgeon. With the end of the war in the Pacific production of the aircraft carriers from which the Sturgeon was intended to operate was suspended and the original reconnaissance bomber specification was cancelled.

The Latécoère 298 was a French seaplane that served during World War II. It was designed primarily as a torpedo bomber, but served also as a dive bomber against land and naval targets, and as a maritime reconnaissance aircraft. Of a sturdy and reliable construction and possessing good manoeuvrability, it was France's most successful military seaplane, and served throughout the war in various guises.

The Raid on Cuxhaven was a British ship-based air-raid on the Imperial German Navy at Cuxhaven mounted on Christmas Day, 1914.
The Short Admiralty Type 74 was a single-engined biplane tractor seaplane with non-folding wings, which saw service with the Royal Naval Air Service during the First World War.

The Short Type 827 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance floatplane. It was also known as the Short Admiralty Type 827.

The Short Type 166 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying folder seaplane, designed by Short Brothers.

The Short Type 320, also known as the Short Admiralty Type 320, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying "folder" seaplane of the First World War.
The Short N.2B was a prototype British patrol seaplane of the First World War, designed and built by Short Brothers. A single-engined biplane intended to replace Short's successful Type 184, only two were built, the Fairey III being preferred.
The Short S.6 Sturgeon was a prototype single-engined biplane naval reconnaissance aircraft, built to an Air Ministry specification but mostly intended as a demonstrator of the corrosion resistance of duralumin aircraft structures. Two were made.

The Short S.41 was a British single-engined biplane built for the Royal Navy in 1912. Capable of being operated either on wheels or floats, it was successful enough for a further two similar aircraft to be built, with the type remaining in use until the early years of the First World War.

The Short Admiralty Type 81 was a series of British two-seat floatplanes built prior to the First World War, and used by the Royal Naval Air Service in the early years of the war. They were powered by 160 hp (120 kW) Gnome Lambda-Lambda 14 cylinder two-row rotary engines and had folding wings to aid storage on ship, hence the popular name Short Folder, shared with a number of other seaplanes made by Short Brothers.















