
The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was one of the largest aircraft in the world. There were two main variants, the Handley Page O/100 (H.P.11) and the Handley Page O/400 (H.P.12).

The Fairey Aviation Company Fairey III was a family of British reconnaissance biplanes that enjoyed a very long production and service history in both landplane and seaplane variants. First flying on 14 September 1917, examples were still in use during the Second World War.

The Blackburn Shark was a carrier-borne torpedo bomber designed and built by the British aviation manufacturer Blackburn Aircraft. It was originally known as the Blackburn T.S.R., standing for "torpedo-spotter-reconnaissance", in reference to its intended roles. The Shark was the last of Blackburn's biplane torpedo bombers.
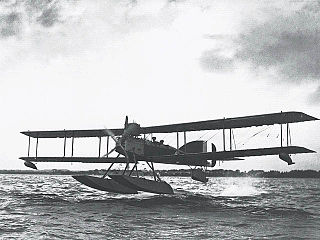
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It was first flown in 1915 and remained in service until after the armistice in 1918. A Short 184 was the first aircraft to sink a ship using a torpedo, and another was the only British aircraft to take part in the Battle of Jutland.

The Avro 549 Aldershot was a British single-engined heavy bomber aircraft built by Avro.

The Handley Page H.P.24 Hyderabad was a twin-engine biplane heavy bomber designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Handley Page. It holds the distinction of being the last wooden heavy bomber to be operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF).
The Wight Seaplane was a British twin-float seaplane produced by J Samuel White & Company Limited. It was also known as the Admiralty Type 840.

The Wight Converted Seaplane was a British twin-float patrol seaplane produced by John Samuel White & Company Limited.
The Short Admiralty Type 74 was a single-engined biplane tractor seaplane with non-folding wings, which saw service with the Royal Naval Air Service during the First World War.

The Short S.8/8 Rangoon was a 1930s British three-engined biplane flying boat, designed and built by Short Brothers for the Royal Air Force.
The Sopwith Admiralty Type 807 was a 1910s British biplane seaplane designed and built for the Admiralty by the Sopwith Aviation Company.

The Short Type 827 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance floatplane. It was also known as the Short Admiralty Type 827.

The Short Type 166 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying folder seaplane, designed by Short Brothers.
The Sopwith B.1 was an experimental British bomber aircraft of the First World War. A single-seat, single-engined biplane, the B.1 was built by the Sopwith Aviation Company for the Royal Navy. Although only two were built, one was used for bombing raids over France.

The Short Type 320, also known as the Short Admiralty Type 320, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying "folder" seaplane of the First World War.
The Short N.2B was a prototype British patrol seaplane of the First World War, designed and built by Short Brothers. A single-engined biplane intended to replace Short's successful Type 184, only two were built, the Fairey III being preferred.

The Short S.41 was a British single-engined biplane built for the Royal Navy in 1912. Capable of being operated either on wheels or floats, it was successful enough for a further two similar aircraft to be built, with the type remaining in use until the early years of the First World War.
The Short S.45 — also known as the Short T.5 after its naval serial number — was a training biplane built for Britain's Royal Navy by Short Brothers in 1912. It was the forerunner of another three identical aircraft delivered to the Royal Navy and Royal Flying Corps during 1912 and 1913. The Royal Naval Air Service was still operating the type when World War I broke out in 1914.

The Short Admiralty Type 81 was a series of British two-seat floatplanes built prior to the First World War, and used by the Royal Naval Air Service in the early years of the war. They were powered by 160 hp (120 kW) Gnome Lambda-Lambda 14 cylinder two-row rotary engines and had folding wings to aid storage on ship, hence the popular name Short Folder, shared with a number of other seaplanes made by Short Brothers.
The Sunbeam Bomber was a prototype single-engined, single seat bomber aircraft of the First World War. Only one example flew as the type proved to be unsuccessful and was abandoned.














