Short Brothers plc, usually referred to as Shorts or Short, is an aerospace company based in Belfast, Northern Ireland. Shorts was founded in 1908 in London, and was the first company in the world to make production aeroplanes. It was particularly notable for its flying boat designs manufactured into the 1950s.

The Short Calcutta or S.8 was a civilian biplane airliner flying boat made by Short Brothers.

The Short S.26 G-class was a large transport flying boat designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Short Brothers. It was designed to achieve a non-stop transatlantic capability, increasing the viability of long distant services/duties.
The Short Shetland was intended as a British long-range, four-engined flying boat built by Short Brothers at Rochester, Kent for use in the Second World War. It was designed to meet an Air Ministry requirement for a very-long range reconnaissance flying boat. The design used the company's experience with large scale production of the Short Sunderland. Two prototypes flew, but the end of World War II prevented the Shetland from entering production. It was the first aircraft designed with a 110 volt electrical system.

The Short Mayo Composite was a piggy-back long-range seaplane and flying boat combination produced by Short Brothers to provide a reliable long-range air transport service to North America and, potentially, to other distant places in the British Empire and the Commonwealth.
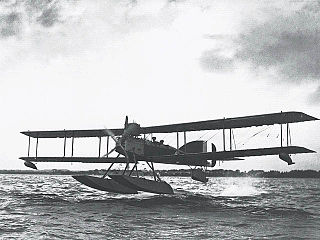
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It was first flown in 1915 and remained in service until after the armistice in 1918. A Short 184 was the first aircraft to sink a ship using a torpedo, and another was the only British aircraft to take part in the Battle of Jutland.

The Short Bomber was a British two-seat long-range reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying aircraft designed by Short Brothers as a land-based development of the very successful Short Type 184.

The Blackburn R.T.1 Kangaroo was a British twin-engine reconnaissance torpedo biplane of the First World War, built by Blackburn Aircraft.

The Short SA.6 Sealand was a light commercial amphibious aircraft designed and produced by Short Brothers. It was sized to accommodate between five and seven passengers as well as to suit the general overseas market in territories with suitable water access and/or runways. It could take off from and land on rivers, lakes and sheltered bays or prepared runways, and could be flown by either a single pilot or a pilot and navigator.

The Short S.17 Kent was a British four-engined 15-seat biplane luxury flying boat airliner, designed and built by Shorts to meet a requirement from Imperial Airways for an aircraft with greater range than the Short Calcutta. The new aircraft was to have sufficient range to fly the stage from Mirabella, Crete, to Alexandria in Egypt without the need for refuelling stops in Italian colonial territory due to a political row which had led the Italian Government to ban British aircraft from its ports.

The Short S.16 Scion and Scion II were 1930s British two-engine, cantilever monoplanes built by Short Brothers and by Pobjoy Airmotors and Aircraft Ltd. in Rochester, Kent between 1933 and 1937. Altogether 22 Scion/Scion II aircraft were built and they provided useful service to operators working from small airstrips/water courses in many parts of the globe, including Europe, the Near and Middle East, Sierra Leone, Papua New Guinea and Australia. Many were impressed into the Royal Air Force during the Second World War, providing pilot ferry services, anti-aircraft co-operation and radar calibration duties. Of the civilian Scions, at least two were still operating in Australia in 1966, one having been re-engined with de Havilland Gipsy Minor engines.
John Lankester Parker OBE FRAeS Hon. MSLAE was Chief Test Pilot for Short Brothers from 1918 until his retirement in 1945. He joined Shorts in 1916 as a part-time test pilot and assistant to then Chief Test Pilot Ronald Kemp, having been recommended for the post by Captain, later Admiral Sir, Murray Sueter, RNAS. By the time he retired he was a director of the company.

Short Folder is a generic name often applied to several different Short Brothers' aircraft types designed and built prior to and during World War I. Short Brothers developed and patented folding wing mechanisms for ship-borne aircraft from 1913; the wings were hinged so that they folded back horizontally alongside the fuselage, reducing the storage space required for stowing them aboard ship.

The Supermarine Sea Eagle was a British, passenger–carrying, amphibious flying boat. It was designed and built by the Supermarine Aviation Works for its subsidiary, the British Marine Air Navigation Co Ltd, to be used on their cross-channel route between Southampton, the Channel Islands and France.

The Short Type 166 was a 1910s British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying folder seaplane, designed by Short Brothers.

The Short Type 320, also known as the Short Admiralty Type 320, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying "folder" seaplane of the First World War.

The Short S.7 Mussel was a single-engined two-seat monoplane built by Short Brothers to test the performance of their duralumin monocoque floats. Two were built.

The Gouge flap, invented by Arthur Gouge of Short Brothers in 1936, allowed the pilot to increase both the wing area and the chord of an aircraft's wing, thereby reducing the stalling speed at a given weight. This provided the benefit of a shorter takeoff distance for a given load, a shorter distance to achieve a given height and a lower takeoff speed. This type of flap, in spite of its use on successful aircraft such as the Short Sunderland and the Short Stirling, was limited to use on aircraft produced by Short Brothers.

The Short S.41 was a British single-engined biplane built for the Royal Navy in 1912. Capable of being operated either on wheels or floats, it was successful enough for a further two similar aircraft to be built, with the type remaining in use until the early years of the First World War.
The Short S.45 — also known as the Short T.5 after its naval serial number — was a training biplane built for Britain's Royal Navy by Short Brothers in 1912. It was the forerunner of another three identical aircraft delivered to the Royal Navy and Royal Flying Corps during 1912 and 1913. The Royal Naval Air Service was still operating the type when World War I broke out in 1914.


















