Related Research Articles

Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste, together with monitoring and regulation of the waste management process and waste-related laws, technologies, and economic mechanisms.

Extended producer responsibility (EPR) is a strategy to add all of the estimated environmental costs associated with a product throughout the product life cycle to the market price of that product, contemporarily mainly applied in the field of waste management. Such societal costs are typically externalities to market mechanisms, with a common example being the impact of cars.

Zero waste, or waste minimization, is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages redesigning Natural resource resource life cycles so that all products are repurposed and/or reused. The goal of the movement is to avoid sending trash to landfills, incinerators, oceans, or any other part of the environment. Currently 9% of global Plastic recycling plastic is recycled. In a zero waste system, all materials are reused until the optimum level of consumption is reached.
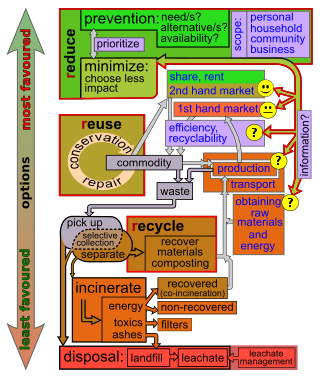
Waste (management) hierarchy is a tool used in the evaluation of processes that protect the environment alongside resource and energy consumption from most favourable to least favourable actions. The hierarchy establishes preferred program priorities based on sustainability. To be sustainable, waste management cannot be solved only with technical end-of-pipe solutions and an integrated approach is necessary.

A plastic bag, poly bag, or pouch is a type of container made of thin, flexible, plastic film, nonwoven fabric, or plastic textile. Plastic bags are used for containing and transporting goods such as foods, produce, powders, ice, magazines, chemicals, and waste. It is a common form of packaging.

Pollution prevention (P2) is a strategy for reducing the amount of waste created and released into the environment, particularly by industrial facilities, agriculture, or consumers. Many large corporations view P2 as a method of improving the efficiency and profitability of production processes through waste reduction and technology advancements. Legislative bodies have enacted P2 measures, such as the Pollution Prevention Act of 1990 and the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 in the United States Congress.
An environmental management system (EMS) is "a system which integrates policy, procedures and processes for training of personnel, monitoring, summarizing, and reporting of specialized environmental performance information to internal and external stakeholders of a firm".

Waste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainable society. Waste minimisation involves redesigning products and processes and/or changing societal patterns of consumption and production.
Cleaner production is a preventive, company-specific environmental protection initiative. It is intended to minimize waste and emissions and maximize product output. By analysing the flow of materials and energy in a company, one tries to identify options to minimize waste and emissions out of industrial processes through source reduction strategies. Improvements of organisation and technology help to reduce or suggest better choices in use of materials and energy, and to avoid waste, waste water generation, and gaseous emissions, and also waste heat and noise.
Precycling is the practice of reducing waste by attempting to avoid buying items which will generate waste into home or business. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also cites that precycling is the preferred method of integrated solid waste management because it cuts waste at its source and therefore trash is eliminated before it is created. According to the EPA, precycling is also characterized as a decision-making process on the behalf of the consumer because it involves making informed judgments regarding a product's waste implications. The implications that are taken into consideration by the consumer include: whether a product is reusable, durable, or repairable; made from renewable or non-renewable resources; over-packaged; and whether or not the container is reusable.

Sustainable Development Strategy for organizations in Canada is about the Government of Canada finding ways to develop social, financial, and environmental resources that meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs in Canada. A Sustainable Development Strategy for the organization needs to be developed that establishes the Sustainable Development goals and objectives set by the Auditor General Act of Canada and provides the written policies and procedures to achieve them. Sustainable Development is based on responsible decision-making, which considers not only the economic benefits of development, but also the short-term and long-term, Canadian environment and environmental impacts.
Design for the environment (DfE) is a design approach to reduce the overall human health and environmental impact of a product, process or service, where impacts are considered across its life cycle. Different software tools have been developed to assist designers in finding optimized products or processes/services. DfE is also the original name of a United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program, created in 1992, that works to prevent pollution, and the risk pollution presents to humans and the environment. The program provides information regarding safer chemical formulations for cleaning and other products. EPA renamed its program "Safer Choice" in 2015.
The End of Life Vehicles Directive is a Directive of the European Union addressing the end of life for automotive products. Every year, motor vehicles which have reached the end of their useful lives create between 8 and 9 million tonnes of waste in the European Union. In 1997, the European Commission adopted a Proposal for a Directive to tackle this problem.

Sustainable packaging is packaging materials and methods that result in improved sustainability. This involves increased use of life cycle inventory (LCI) and life cycle assessment (LCA) to help guide the use of packaging which reduces the environmental impact and ecological footprint. It includes a look at the whole of the supply chain: from basic function, to marketing, and then through to end of life (LCA) and rebirth. Additionally, an eco-cost to value ratio can be useful The goals are to improve the long term viability and quality of life for humans and the longevity of natural ecosystems. Sustainable packaging must meet the functional and economic needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainability is not necessarily an end state but is a continuing process of improvement.

Sustainable engineering is the process of designing or operating systems such that they use energy and resources sustainably, in other words, at a rate that does not compromise the natural environment, or the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Solid waste policy in the United States is aimed at developing and implementing proper mechanisms to effectively manage solid waste. For solid waste policy to be effective, inputs should come from stakeholders, including citizens, businesses, community-based organizations, non-governmental organizations, government agencies, universities, and other research organizations. These inputs form the basis of policy frameworks that influence solid waste management decisions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates household, industrial, manufacturing, and commercial solid and hazardous wastes under the 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). Effective solid waste management is a cooperative effort involving federal, state, regional, and local entities. Thus, the RCRA's Solid Waste program section D encourages the environmental departments of each state to develop comprehensive plans to manage nonhazardous industrial and municipal solid waste.
The City of Oakland, California, adopted a Zero Waste Strategic Plan in 2006, detailing a road map for the city to follow toward the implementation of a Zero Waste System by 2020. As stated in a City Resolution, introduced by then Mayor Jerry Brown, Zero Waste principles:
Sustainable distribution refers to any means of transportation / hauling of goods between vendor and purchaser with lowest possible impact on the ecological and social environment, and includes the whole distribution process from storage, order processing and picking, packaging, improved vehicle loadings, delivery to the customer or purchaser and taking back packaging.

Packaging waste, the part of the waste that consists of packaging and packaging material, is a major part of the total global waste, and the major part of the packaging waste consists of single-use plastic food packaging, a hallmark of throwaway culture. Notable examples for which the need for regulation was recognized early, are "containers of liquids for human consumption", i.e. plastic bottles and the like. In Europe, the Germans top the list of packaging waste producers with more than 220 kilos of packaging per capita.

Overpackaging is the use of excess packaging. The Institute of Packaging Professionals defines overpackaging as “a condition where the methods and materials used to package an item exceed the requirements for adequate containment, protection, transport, and sale”
References
- ↑ "Guidelines on Source Reduction" (PDF). National Center for Vector Borne Diseases Control (NCVBDC).
- ↑ "Source Reduction". Northern Nevada Public Health. 15 August 2023. Retrieved 2024-03-08.
- ↑ Zabaniotou, A; Kassidi (August 2003). "Life cycle assessment applied to egg packaging made from polystyrene and recycled paper". Journal of Cleaner Production. 11 (5): 549–559. doi:10.1016/S0959-6526(02)00076-8.
- ↑ Franklin (April 2004). "Life Cycle Inventory of Packaging Options for Shipment of Retail Mail-Order Soft Goods" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 17, 2008. Retrieved December 15, 2008.
