
Aa is a genus of plants of the family Orchidaceae.

Brassia is a genus of orchids classified in the subtribe Oncidiinae. It is native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and northern South America, with one species extending into Florida.

Barkeria, abbreviated Bark in horticultural trade, is a genus of orchids. It consists of about 17 currently recognized species native to Mexico and Central America. This genus was once considered part of Epidendrum. Type species is Barkeria elegans; this is now considered a synonym of B. uniflora yet retains its status as type per ICN.

Kraenzlinella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae, first described as a genus in 1903. It is native to S Mexico, Central America, and South America.
- Kraenzlinella anfracta(Luer) Luer - Tolima region in Colombia
- Kraenzlinella echinocarpa(C.Schweinf.) Luer - Peru, Ecuador
- Kraenzlinella erinacea(Rchb.f.) Solano - Oaxaca, Chiapas, Central America, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia
- Kraenzlinella gigantea(Lindl.) Luer - Peru
- Kraenzlinella hintonii(L.O.Williams) Solano - Guerrero
- Kraenzlinella lappago(Luer) Luer - El Oro + Napo Provinces in Ecuador
- Kraenzlinella phrynoglossa(Luer & Hirtz) Luer - Azuay Province in Ecuador
- Kraenzlinella rinkeiLuer - Costa Rica
- Kraenzlinella sigmoidea(Ames & C.Schweinf.) Luer - Costa Rica
- Kraenzlinella tunguraguae(F.Lehm. & Kraenzl.) Kuntze ex Engl. & Prantl - Colombia, Ecuador, Peru
- Kraenzlinella platyrachis(Rolfe) Rolfe = Specklinia pfavii(Rchb.f.) Pupulin & Karremans
- Kraenzlinella shuarii(Luer) Luer = Echinosepala shuarii(Luer) Luer
- Kraenzlinella smaragdina(Luer) Luer = Anathallis smaragdina(Luer) Pridgeon & M.W.Chase

Ponthieva is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), commonly known as the shadow witch. They are named after Henry de Ponthieu, an English merchant of Huguenot ancestry who sent West Indian plant collections to Sir Joseph Banks in 1778.

Stenia is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae). It was established by John Lindley in 1837. These epiphytic plants occur in warm, humid habitats of Trinidad and the Amazonian slope of the northern Andean region in South America.

Paphinia, abbreviated in horticultural trade Pna, is a genus of orchids, composed of an estimated 16 species from Central America, northern South America and Trinidad. These species are medium-sized epiphytes with small ovoid pseudobulbs and 2 or more leaves. The generic name comes from the Greek Paphia, the name of Aphrodite of Cyprus. Most authorities consider the genus rare.

Huntleya is a small orchid genus native to South America, Central America and Trinidad.

Cycnoches, abbreviated as Cyc. in the horticultural trade, is a genus of 34 currently accepted species of orchids native to South America, Central America and southern Mexico. Also called "swan orchids", they are epiphytes found in lowland and pre-montane forests.

Rodriguezia, abbreviated Rdza. in the horticultural trade, is a genus of orchids. It consists of 49 known species, native to tropical America from southern Mexico and the Windward Islands south to Argentina, with many of the species endemic to Brazil.

Teuscheria is a genus of orchids native to southern Mexico, Central America and northern South America. The genus is named for Henry Teuscher, an award-winning landscape artist and horticulturalist.

Ornithocephalus is a genus of orchids comprising more than 50 known species widespread in South America, Central America, Southern Mexico, Trinidad and the Windward Islands.

Lueddemannia is a genus of orchids found from Venezuela to Peru. Three species are currently recognized as of June 2014:

Polycycnis, abbreviated in horticultural trade as Pcn, is a genus of orchid, comprising 17 species found in Central America, and northern South America.

Stanhopea gibbosa is a species of orchids from Colombia and West Ecuador. The name was often misapplied for a species from Costa Rica and Panama which was later described as Stanhopea confusa. Stanhopea carchiensis and Stanhopea impressa are synonyms of Stanhopea gibbosa.
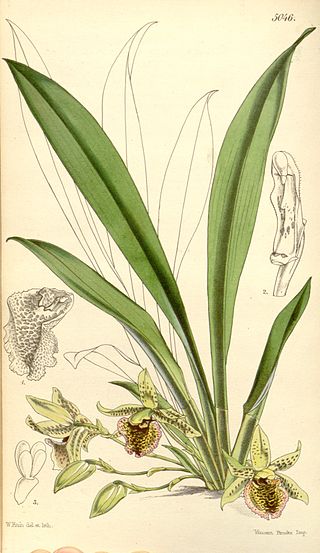
Kefersteinia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has about 40-50 species, widespread across much of Latin America. The genus was named for Keferstein of Kröllwitz, an orchidologist.

Sarcoglottis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is widespread across much of Latin America from Mexico to Argentina, with one species extending northward into Trinidad and the Windward Islands.






























