The Paleogene Period is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period 66 Ma to the beginning of the Neogene Period 23.03 Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "Pe" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps.
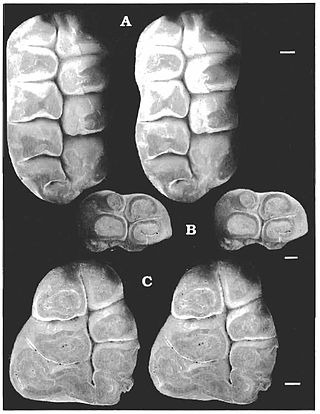
Catopsalis is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of North America. This animal was a relatively large member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. Most multituberculates were much smaller.
Neoplagiaulax is a mammal genus from the Paleocene of Europe and North America. In the case of the latter continent, there may possibly be some slightly earlier, Upper Cretaceous material too. It existed in the age immediately following the extinction of the last dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata, lying within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
Mesodma is an extinct genus of mammal, a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta, family Neoplagiaulacidae. It lived during the upper Cretaceous and Paleocene Periods of what is now North America. The earliest definitive record is from the late Santonian stage strata of the Straight Cliffs Formation. A single premolar tooth from the lower Cenomanian stage strata of the Cedar Mountain Formation has been tentatively assigned to this genus based on its similarity, but its describers noted that it is unlikely that Mesodma lived during that time.
Mimetodon is a small mammal from the Paleocene of North America and perhaps Europe. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
Xyronomys is an extinct genus of small mammals from the Paleocene of North America, with two described species. The genus lies within the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
Microcosmodon is a mammal genus from the Paleocene of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata, and lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Microcosmodontidae. The genus Microcosmodon was named by G.L. Jepsen in 1930.

The Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum (PETM), alternatively ”Eocene thermal maximum 1 (ETM1)“ and formerly known as the "Initial Eocene" or “Late Paleocene thermal maximum", was a geologically brief time interval characterized by a 5–8 °C global average temperature rise and massive input of carbon into the ocean and atmosphere. The event began, now formally codified, at the precise time boundary between the Paleocene and Eocene geological epochs. The exact age and duration of the PETM remain uncertain, but it occurred around 55.8 million years ago (Ma) and lasted about 200 thousand years (Ka).

Simoedosaurus is an extinct reptile known from the Paleocene of North America, Europe and western Asia, and a member of the Choristodera, a group of aquatic reptiles that lived in the Northern Hemisphere from the Jurassic to the early Cenozoic.
Pantodonta is an extinct suborder of eutherian mammals. These herbivorous mammals were one of the first groups of large mammals to evolve after the end of the Cretaceous. The last pantodonts died out at the end of the Eocene.

Teilhardina was an early marmoset-like primate that lived in Europe, North America and Asia during the Early Eocene epoch, about 56-47 million years ago. The paleontologist George Gaylord Simpson is credited with naming it after the French paleontologist, Jesuit and philosopher Teilhard de Chardin.

The Fort Union Formation is a geologic unit containing sandstones, shales, and coal beds in Wyoming, Montana, and parts of adjacent states. In the Powder River Basin, it contains important economic deposits of coal, uranium, and coalbed methane.

Bothremydidae is an extinct family of side-necked turtles (Pleurodira) known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic. They are closely related to Podocnemididae, and are amongst the most widely distributed pleurodire groups, with their fossils having been found in Africa, India, the Middle East, Europe, North America and South America. Bothremydids were aquatic turtles with a high morphological diversity, indicative of generalist, molluscivorous, piscivorous and possibly herbivorous grazing diets, with some probably capable of suction feeding. Unlike modern pleurodires, which are exclusively freshwater, bothremydids inhabited freshwater, marine and coastal environments. Their marine habits allowed bothremydids to disperse across oceanic barriers into Europe and North America during the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). The youngest records of the group are indeterminate remains from Saudi Arabia and Oman, dating to the Miocene.

Cernay-lès-Reims is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France.

The Paleocene, or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek παλαιός palaiós meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch, translating to "the old part of the Eocene".
Compsemys is an extinct genus of prehistoric turtles from the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America and possibly Europe. The type species C. victa, first described by Joseph Leidy from the Hell Creek Formation in Montana in 1856, and another probable species C. russelli, described in 2012, from Paleocene deposits in France. Its affinites have long been uncertain, but it has recently been considered to be the most basal member of Paracryptodira, despite the clade first appearing in the Late Jurassic, and is sometimes included in its own family, Compsemydidae. A revision in 2020 found Compsemydidae to be more expansive, also containing Riodevemys and Selenemys from the Late Jurassic of Europe, and Peltochelys from the Early Cretaceous of Europe.

Triisodon is a genus of extinct mesonychian mammal that existed during the Early Paleocene of New Mexico, North America, from about 63.5-62.0 Ma. The genus was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1881 as a member of the Acreodi, a now invalid taxon that encompassed creodonts, mesonychians and certain arctocyonians. Cope described the type specimen of T. quivirensis as "about the size of a wolf." A smaller species, T. crassicuspis, has also been identified from the same region. Since material from this genus is incomplete, the exact size of adults and whether they showed sexual dimorphism or regional variations in size is unknown.

Macrobaenidae is an extinct family of turtles, known from the Early Cretaceous to Paleogene of Laurasia. Their relationships to other turtles and whether they form a monophlyletic group are controversial. They are typically interpreted as stem or crown group cryptodires, but some more recent analyses have found them to lie outside crown group Testudines. Macrobaenids can be distinguished from other testudinatans by the presence of a carotid fenestra, cruciform plastron with strap-like epiplastra, and a lack of extragulars.

Tytthaena is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Tytthaeninae within extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived in North America from the late Paleocene to early Eocene.

Protictis is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America from early Paleocene to middle Eocene.