
The Australian bonito, horse mackerel or little bonito, Sarda australis is a ray-finned fish of the family Scombridae and is found in eastern Australia and New Zealand. They swim at depths reaching depths of approximately 30 m (98 ft), in open water. Its length is commonly at around 40–45 centimetres (16–18 in) fork length and 1.8–2.3 kilograms (4.0–5.1 lb) weight. Its maximum length and weight are about 100 centimetres (39 in) and 9.4 kilograms (21 lb), respectively.

Pacific bonito, Sarda lineolata, is a marine species of bonito that is a game fighter but not highly thought of as a food fish. While it has been considered to be a subspecies of Sarda chiliensis, recent treatments recognize it as a species, S. lineolata.
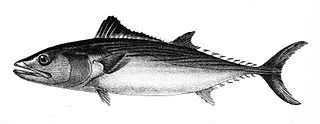
Sarda chiliensis, the eastern Pacific bonito, is a marine species of bonito. It ranges from Ecuador to Chile. Sarda lineolata, which ranges from Alaska to Mexico was formerly considered a subspecies, as Sarda chiliensis lineolata, but this treatment renders the species geographically disjunct.

The Atlantic bonito is a large mackerel-like fish of the family Scombridae. It is common in shallow waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea, where it is an important commercial and game fish.

Cubiceps caeruleus, the blue fathead or cubehead, is a species of driftfish native to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. It is a pelagic fish that can be found at depths of from 20 to 250 metres. It mostly feeds on salps. This species can reach a length of 25.6 centimetres (10.1 in) TL.

The bullet tuna is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found circumglobally in tropical oceans, including the Mediterranean Sea, in open surface waters to depths of 50 m (164 ft). The population of bullet tuna in the Eastern Pacific was classified as a subspecies of A. rochei, A. rochei eudorax, but some authorities regard this as a valid species Auxis eudorax. Its maximum length is 50 centimetres (20 in).

The slender sole is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms near rocky areas at depths of between 25 and 800 metres. Its native habitat is the eastern Pacific coast, from the mouth of the Alsek River in Alaska in the north to Isla Cedros in Baja California, Mexico in the south. It can reach up to 35 centimetres (14 in) in length.

Thunnus tonggol is a species of tuna of tropical Indo-West Pacific waters.

Sarda is a genus of medium-sized, predatory ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae, and belonging to the tribe Sardini, more commonly called the bonito tribe. There are four species which comprise the genus Sarda. One of those species, the Pacific bonito, is further divided into two subspecies.

The leaping bonito is a species of saltwater finfish from the Scombridae (Mackerel) family. Scombridae includes such tribes as the mackerels, tunas, and bonitos – of the latter of which, the Sardini tribe, this fish is a member. It is the only member of the genus Cybiosarda, which is therefore called a monotypic taxon. Since the bonitos and tunas are close relatives, this fish has variously been referred to by such other common names as Australian tuna, striped bonito, and Watson's bonito.
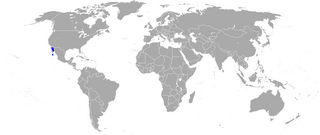
The ocellated turbot is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of between 1 and 140 metres. Its native habitat is the subtropical waters of the eastern Pacific, specifically southern Baja California and the upper Gulf of California ; it is the only member of the genus to prefer subtropical waters. It can grow up to 24 centimetres (9.4 in) in length.

The spotted turbot is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of between 1 and 50 metres. Its native habitat is the subtropical waters of the eastern Pacific, from Morro Bay in California to southern Baja California in Mexico. It can grow up to 30 centimetres (12 in) in length.

The hornyhead turbot is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on soft sand and mud bottoms at depths of between 9 and 200 metres. Its native habitat is the subtropical waters of the eastern Pacific, from Point Reyes in California to Magdalena Bay in Baja California, and the northern and central eastern parts of the Gulf of California. It can grow up to 37 centimetres (15 in) in length.

The willowy flounder is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of between 100 and 200 metres. Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the Western Pacific, from Southern Hokkaido in Japan to the Gulf of Bohai, the East China Sea and Taiwan. It can grow up to 30 centimetres (12 in) in length. It is sometimes classified in the monotypic genus Tanakius.

The stone flounder is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on sandy and muddy bottoms in coastal areas at depths of up to 150 metres (500 ft). Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the north-western Pacific, from Japan to the Kuril Islands, Sakhalin, Korea, northern China and Taiwan. It is oceanodromous and is found in salt, brackish and fresh waters. It can grow up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in length, and may reach 12 years of age. It was formerly classified in the now defunct genus Kareius.
Nesiarchus nasutus, the Black gemfish, is a species of snake mackerel found in tropical and subtropical waters in most parts of the world, though not in east Pacific and north Indian waters. It occurs at depths of from 200 to 1,200 metres though they make diel vertical migrations from benthopelagic to mesopelagic depths at night. This species can reach a length of 130 centimetres (51 in) SL though most do not exceed 80 centimetres (31 in) SL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. This species is currently the only known member of its genus, Nesiarchus.

Orcynopsis unicolor, the plain bonito, is a species of ray-finned, bony fish in the bonito tribe of the mackerel family (Scombridae). It occurs in the eastern Atlantic from southern Norway, where it is a vagrant, to Senegal, although it is not found in the seas around the Macaronesian Islands. It is also found in the Mediterranean Sea and extends to the Black Sea.
Perissias taeniopterus, the striped-fin flounder, is a species of lefteye flounder native to the eastern Pacific Ocean along the coast of Central America from Mexico to Panama. It is found at depths of from 46 to 157 metres. This species grows to a length of 11 centimetres (4.3 in) TL. This species is the only known member of its genus.

Pseudaesopia japonica, the wavyband sole or Seto sole, is a species of sole native to the western Pacific Ocean, where found over sandy mud bottoms. This species is the only known member of its genus. This species grows to a length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in) SL.
Diplospinus multistriatus, the Striped escolar, is a species of snake mackerel of cosmopolitan distribution at depths of from 50 to 1,000 metres. This species grows to a length of 33 centimetres (13 in) SL though most do not exceed 20 centimetres (7.9 in) SL. This species is important as a food fish to local populations. This species is the only known member of its genus.

















