
Bonitos are a tribe of medium-sized, ray-finned predatory fish in the family Scombridae – a family it shares with the mackerel, tuna, and Spanish mackerel tribes, and also the butterfly kingfish. Also called the tribe Sardini, it consists of eight species across four genera; three of those four genera are monotypic, having a single species each. Bonitos closely resemble the skipjack tuna, which is often called a bonito, especially in Japanese contexts.

The Australian bonito, horse mackerel or little bonito, Sarda australis is a ray-finned fish of the family Scombridae and is found in eastern Australia and New Zealand. They swim at depths reaching depths of approximately 30 m (98 ft), in open water. Its length is commonly at around 40–45 centimetres (16–18 in) fork length and 1.8–2.3 kilograms (4.0–5.1 lb) weight. Its maximum length and weight are about 100 centimetres (39 in) and 9.4 kilograms (21 lb), respectively.
The squaretails are a genus, Tetragonurus, of scombriform ray-finned fishes, the only genus in the family Tetragonuridae.

Pacific bonito, Sarda lineolata, is a marine species of bonito that is a game fighter but not highly thought of as a food fish. While it has been considered to be a subspecies of Sarda chiliensis, recent treatments recognize it as a species, S. lineolata.
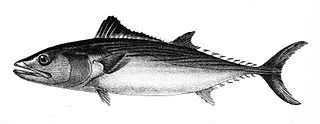
Sarda chiliensis, the eastern Pacific bonito, is a marine species of bonito. It ranges from Ecuador to Chile. Sarda lineolata, which ranges from Alaska to Mexico was formerly considered a subspecies, as Sarda chiliensis lineolata, but this treatment renders the species geographically disjunct.

Scomberomorini is a tribe of ray-finned saltwater bony fishes that is commonly known as the Spanish mackerels, seerfishes or seer fish. This tribe is a subset of the mackerel family (Scombridae) – a family that it shares with three sister tribes, the tunas, mackerels, and bonitos, and the butterfly kingfish. Scomberomorini comprises 21 species across three genera. They are pelagic fish, fast swimmers and predatory in nature, that fight vigorously when caught. They are mainly caught using hooks and lines.

Hippoglossus is a genus of very large righteye flounders. It comprises two species of halibut, with one species native to the northern Atlantic Ocean and the other species native to the northern Pacific Ocean.

Verasper is a genus of righteye flounders native to the north-western Pacific Ocean.

Euthynnus affinis, the mackerel tuna, little tuna, eastern little tuna, wavyback skipjack tuna, kawakawa, or tongkol komo is a species of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, or mackerel family. It belongs to the tribe Thunnini, better known as the tunas. This is an Indo-Pacific species which is found from the Red Sea to French Polynesia.
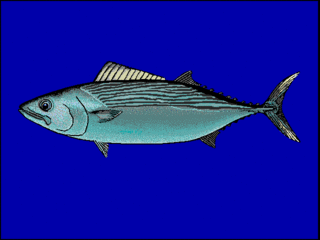
The striped bonito is a species of marine ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae. They have been recorded at lengths of 102 centimetres (40 in), though they are commonly no longer than 55 centimetres (22 in). Distributed through the Indo-Pacific and East Pacific, the striped bonito is known to occur at depths from 1 to 167 metres. They are called mackerel bonito.

Grammatorcynus is a genus of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae. This genus together with Acanthocybium and Scomberomorus are comprised by the tribe Scomberomorini, commonly known as the Spanish mackerels or seerfishes.

The leaping bonito is a species of saltwater finfish from the Scombridae (Mackerel) family. Scombridae includes such tribes as the mackerels, tunas, and bonitos – of the latter of which, the Sardini tribe, this fish is a member. It is the only member of the genus Cybiosarda, which is therefore called a monotypic taxon. Since the bonitos and tunas are close relatives, this fish has variously been referred to by such other common names as Australian tuna, striped bonito, and Watson's bonito.

Rastrelliger is a mackerel genus in the family Scombridae. The three species of Rastrelliger together with the four species of Scomber comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels".
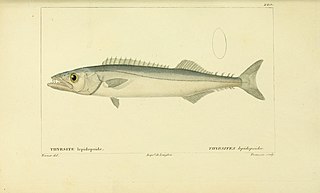
Thyrsitops lepidopoides, the white snake mackerel, is a species of snake mackerel found off the coasts of South America from Brazil on the Atlantic side to Chile on the Pacific side. It can be found at depths of from 30 to 350 metres. This species can reach a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) SL though most do not exceed 25 centimetres (9.8 in) SL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. It is currently the only known member of its genus.

Orcynopsis unicolor, the plain bonito, is a species of ray-finned, bony fish in the bonito tribe of the mackerel family (Scombridae). It occurs in the eastern Atlantic from southern Norway, where it is a vagrant, to Senegal, although it is not found in the seas around the Macaronesian Islands. It is also found in the Mediterranean Sea and extends to the Black Sea.
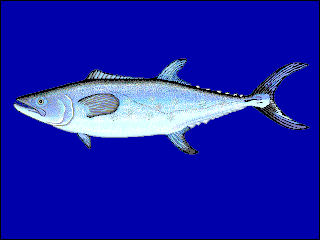
The Chinese mackerel, also known as the Chinese seerfish, is a ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, better known as the mackerel family. More specifically, this fish is a member of the tribe Scomberomorini, the Spanish mackerels. It is a marine species occurring in the Western Pacific Ocean, but it also enters the Mekong River.

The Pacific sierra also known as the Mexican sierra, is a ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, better known as the mackerel family. More specifically, this fish is a member of the tribe Scomberomorini, the Spanish mackerels. It occurs in the eastern Pacific Ocean from southern California to Antofagasta in Chile.

Solea is a genus of soles from the Indo-Pacific and East Atlantic Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea.

Pteraclis is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. They are known commonly as fanfishes. The three species are distributed throughout the oceans of the world.

Scombrini, commonly called the true mackerels, is a tribe of ray-finned bony fishes in the mackerel family, Scombridae – a family it shares with the Spanish mackerel, tuna and bonito tribes, plus the butterfly kingfish.



















