
In anatomy, the scapula, also known as the shoulder bone, shoulder blade, wing bone or blade bone, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The levator scapulae is a skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle on the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

The teres minor is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.

The suprascapular nerve is a nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of two of the muscles that originate from the scapula, namely the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles.

The supraspinatus is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine.
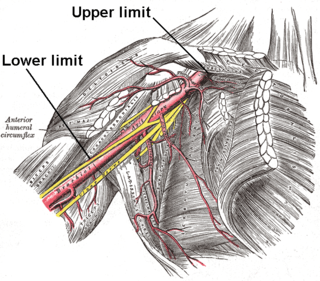
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball and socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves articulation between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus.
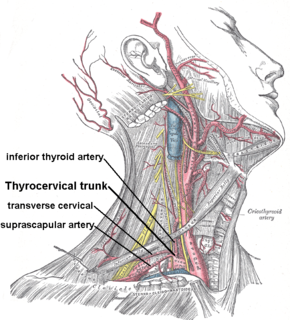
The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.

The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck.

The infraspinatous fossa of the scapula is much larger than the supraspinatous fossa; toward its vertebral margin a shallow concavity is seen at its upper part; its center presents a prominent convexity, while near the axillary border is a deep groove which runs from the upper toward the lower part.

The suprascapular notch is a notch in the superior border of the scapula, just medial to the base of the coracoid process.

The great scapular notch is a notch which serves to connect the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa. It lies immediately medial to the attachment of the acromion to the lateral angle of the scapular spine.
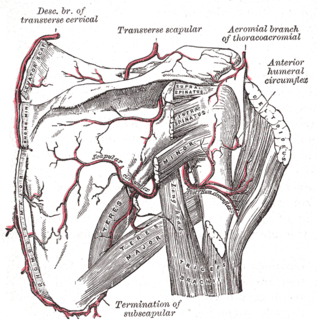
The scapular anastomosis is a system connecting certain subclavian artery and their corresponding axillary artery, forming a circulatory anastomosis around the scapula. It allows blood to flow past the joint in case of occlusion, damage, or pinching of the following scapular arteries:

The spine of the scapula or scapular spine is a prominent plate of bone, which crosses obliquely the medial four-fifths of the scapula at its upper part, and separates the supra- from the infraspinatous fossa.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:






















