
The president of Slovenia, officially the president of the Republic of Slovenia, is the head of state of the Republic of Slovenia. The position was established on 23 December 1991 when the National Assembly passed a new constitution after the separation of Slovenia from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.

The Constitution of the Republic of Croatia is promulgated by the Croatian Parliament.
The Constitution of the Republic of Slovenia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Slovenia.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Slovenia have significantly evolved over time, and are considered among the most advanced of the former communist countries. Slovenia was the first post-communist country to have legalised same-sex marriage, and anti-discrimination laws regarding sexual orientation and gender identity have existed nationwide since 2016.

The current Constitution of the Republic of Serbia, also known as Mitrovdan Constitution is the supreme and basic law of Serbia. It was adopted in 2006, replacing the previous constitution dating from 1990.

The Socialist Republic of Slovenia, commonly referred to as Socialist Slovenia or simply Slovenia, was one of the six federal republics forming Yugoslavia and the nation state of the Slovenes. It existed under various names from its creation on 29 November 1945 until 25 June 1991.

The Constitutional Court of Slovenia is a special court established by the Slovenian Constitution. Since its inception, the Court has been located in the city of Ljubljana. It is the highest court in the country for reviewing the constitutionality and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, otherwise the highest court in the country is the Supreme Court of the Republic of Slovenia. The constitutional court is not part of any branch of government and is an independent state body.

The Constitution of the Republic of North Macedonia is a codified constitution outlining North Macedonia's system of government and basic human rights. It was adopted in the Parliament of the then-Republic of Macedonia on 17 November 1991.
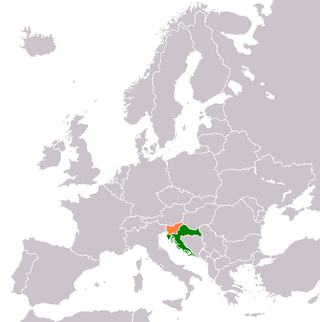
The foreign relations between Croatia and Slovenia are bound together by shared history, neighboring geography and common political ideologies. Both states established diplomatic relations in 1992, following the dissolution of Yugoslavia and the independence of Croatia. Modern relations are warm and friendly. The two states have disputes over their border and sovereign rights over certain nuclear and economic assets. The countries share 670 km (420 mi) of common border. They are perennially each other's largest trading partners on an import-export basis.

The Court of Audit of the Republic of Slovenia is the highest body for supervising state accounts, the state budget and all public spending in Slovenia. The Constitution of Slovenia further provides that the Court of Audit is independent in the performance of its duties and bound by the Constitution and law. The Court of Audit Act also defines that the acts with which Court of Audit exercises its powers of audit cannot be challenged before the courts or other state bodies.
The Government of the Republic of Slovenia exercises executive authority in Slovenia pursuant to the Constitution and the laws of Slovenia. It is also the highest administrative authority in Slovenia.

The judiciary in Slovenia is one of the three constitutional branches of government and is independent of the other two. Judges enjoy a permanent mandate and are appointed by the National Assembly after they have been nominated by the Judicial Council, which itself is not part of the judicial branch of the government.

Róbert Ragnar Spanó is an Icelandic-Italian jurist, judge, and former president of the European Court of Human Rights. He has been a partner at the multinational law firm of Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher since the end of this tenure as president of the court in October 2022. He started his tenure as president of the court on 18 May 2020, succeeding Judge Sicilianos from Greece. Before beginning his service on the court on 1 November 2013, he served provisionally as parliamentary ombudsman of Iceland and dean of the Faculty of Law, University of Iceland. Spano's mandate as a judge and president of the court ended on 31 October 2022 when he was succeeded by Judge Siofra O'Leary.

Miroslav Cerar Jr. is a Slovenian law professor and politician. He was Prime Minister of Slovenia, leading the 12th Government. He served as Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs in the 13th Government. He is a full professor at the Chair of Theory and Sociology of Law at the University of Ljubljana Faculty of Law.
A referendum on a law governing the Divača-Koper rail upgrade was held in Slovenia on 13 May 2018. It followed the annulment of the results of a 2017 referendum on the same subject by the Supreme Court in March 2018. The result saw just 309 more votes cast against the law (50.06%) than in favour (49.94%). Voter turnout was even lower than in 2017, at around 15%, meaning that the requirement of 20% of the electorate casting a "no" vote to validate the referendum outcome was not met. As a result, the law remained in force.

Jurij Toplak is a constitutional scholar, university administrator, election law, and human rights expert. He is professor at University of Maribor and the head of the Cultural Formations research group at the Alma Mater Europaea University, and recurring visiting professor at the Fordham University School of Law in New York. Since 2016, he has served as the provost and vice-president of the Alma Mater Europaea university. The Washington Post, The Guardian, The Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, The New York Times, and The Boston Globe published his legal comments. Toplak is a member of the European Academy of Sciences and Arts and serves as the co-chair of the International Association of Constitutional Law (IACL) Freedom of Expression research group.

Vili Kovačič is a Slovenian impact litigation activist and blogger, who was the first in Europe to successfully challenge a referendum result based on a campaign finance violation. His challenge resulted in the resignation of Prime Minister Miro Cerar and early parliamentary elections in 2018. His successful challenges to elections and referendums resulted in Constitutional Court reforming Slovenian electoral laws and practices.
Slovenian Disability Rights Association is a disability rights organization in Slovenia. Its goals are to enhance the implementation of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and to assist persons with disabilities through awareness raising and impact litigation. Drupis was founded in 2012.

Slavko Vesenjak is a Slovenian lawyer. He is the author of scientific articles and a lecturer. He has represented several high-profile cases before the Supreme Court and the European Court of Human Rights. He was a member of the National Electoral Commission.
In the European continental judicial tradition, the national councils of the judiciary are institutions on judicial administration that ensure the self-management of the judiciary and the effective delivery of justice, which are autonomous or independent of the executive and legislature.
















