
Northern storm petrels are seabirds in the genus Hydrobates in the family Hydrobatidae, part of the order Procellariiformes. The family was once lumped with the similar austral storm petrels in the combined storm petrels, but have been split, as they were not closely related. These smallest of seabirds feed on planktonic crustaceans and small fish picked from the surface, typically while hovering. Their flight is fluttering and sometimes bat-like.

The European storm petrel, also known as British storm petrel, or just storm petrel, is a species of seabird in the northern storm petrel family, Hydrobatidae. The small, square-tailed bird is entirely black except for a broad, white rump and a white band on the under wings, and it has a fluttering, bat-like flight. The large majority of the population breeds on islands off the northern coasts of Europe, with the greatest numbers in the Faroe Islands, United Kingdom, Ireland, and Iceland. The Mediterranean population is a separate subspecies whose strongholds are Filfla Island (Malta), Sicily, and the Balearic Islands. This subspecies is indiscernible at sea from its Atlantic relatives.

Leach's storm petrel or Leach's petrel is a small seabird of the tubenose order. It is named after the British zoologist William Elford Leach. The scientific name is derived from Ancient Greek. Hydrobates is from hydōr "water", and batēs "walker", and leucorhous is from leukos, "white" and orrhos, "rump". It was formerly defined in the genus Oceanodroma before that genus was synonymized with Hydrobates.

Zino's petrel or the freira, is a species of small seabird in the gadfly petrel genus, endemic to the island of Madeira. This long-winged petrel has a grey back and wings, with a dark "W" marking across the wings, and a grey upper tail. The undersides of the wings are blackish apart from a triangle of white at the front edge near the body, and the belly is white with grey flanks. It is very similar in appearance to the slightly larger Fea's petrel, and separating these two Macaronesian species at sea is very challenging. It was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the soft-plumaged petrel, P. mollis, but they are not closely related, and Zino's was raised to the status of a species because of differences in morphology, calls, breeding behaviour and mitochondrial DNA. It is one of Europe's most endangered seabirds, with breeding areas restricted to a few ledges high in the central mountains of Madeira.

Wilson's storm petrel, also known as Wilson's petrel, is a small seabird of the austral storm petrel family Oceanitidae. It is one of the most abundant bird species in the world and has a circumpolar distribution mainly in the seas of the southern hemisphere but extending northwards during the summer of the northern hemisphere. The world population was estimated in 2022 as stable at 8 to 20 million birds. In 2010 it had been estimated at 12-30 million. A 1998 book had estimated more than 50 million pairs. The name commemorates the Scottish-American ornithologist Alexander Wilson. The genus name Oceanites refers to the mythical Oceanids, the three thousand daughters of Tethys. The species name is from Latin oceanus, "ocean".

The white-faced storm petrel, also known as white-faced petrel or frigate petrel is a small seabird of the austral storm petrel family Oceanitidae. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Pelagodroma. It is widely distributed across the northern and southern hemisphere, especially around the coastal and open ocean waters of southern Australia, New Zealand, Tristan da Cunha, Cabo Verde, the Canary islands and the Selvagens islands.

The band-rumped storm petrel, Madeiran storm petrel, or Harcourt's storm petrel is of the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae.

The Cape Verde shearwater, or cagarra locally, is a medium-large shearwater, a seabird in the petrel family Procellariidae. It is endemic to the Cape Verde archipelago of Macaronesia in the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of West Africa.

The ashy storm petrel is a small, scarce seabird of the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae. It breeds colonially on islands off the coasts of California and Mexico, and is one of six species of storm petrel that live and feed in the rich California Current system.

The ringed storm petrel, also known as Hornby's storm petrel, is a seabird that ranges in the Humboldt Current off the coasts of South America. The species is a very distinctive member of the storm petrel family, with a dark cap, white face and underparts, forked tail and a black band across the chest. It is relatively common in the seas off Peru, Chile and Ecuador. The species is named after Admiral Sir Phipps Hornby.

The black storm petrel is a small seabird of the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae. It is 23 cm in length, with a wingspan of 46–51 cm.

The least storm petrel is a small seabird of the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae. It is 13–15 cm in length, with a wingspan of 32 cm. It is the smallest member of the order Procellariiformes. It was formerly defined in the genus Oceanodroma before that genus was synonymized with Hydrobates.

The fork-tailed storm petrel is a small seabird of the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae. It is the second-most abundant and widespread storm petrel and is the only bird in its family that is bluish-grey in colour.

Markham's storm petrel is a seabird native to the Pacific Ocean around Peru, Chile, and Ecuador. The species is named after British explorer Albert Hastings Markham, who collected the specimen on which the scientific description was based. It is a large and slender storm petrel, with a wingspan between 49 and 54 cm. Its plumage is black to sooty brown with a grayish bar that runs diagonally across the upper side of the wings. A member of the family Hydrobatidae, the northern storm petrels, the species is similar to the black storm petrel, from which it can be hard to distinguish.

Matsudaira's storm petrel is a species of seabird in the family Hydrobatidae.

Tristram's storm petrel or ʻakihikeʻehiʻale is a species of seabird in the storm petrel family Hydrobatidae. The species' common and scientific name is derived from the English clergyman Henry Baker Tristram; the species can also be known as the sooty storm petrel. Tristram's storm petrel has a distribution across the north Pacific Ocean, predominantly in tropical seas.

Austral storm petrels, or southern storm petrels, are seabirds in the family Oceanitidae, part of the order Procellariiformes. These smallest of seabirds feed on planktonic crustaceans and small fish picked from the surface, typically while hovering. Their flight is fluttering and sometimes bat-like.

Monteiro's storm petrel is a seabird species from the storm petrel family, Hydrobatidae. The cryptic species was once considered to be conspecific with the band-rumped storm petrel. The species is endemic to the Azores.
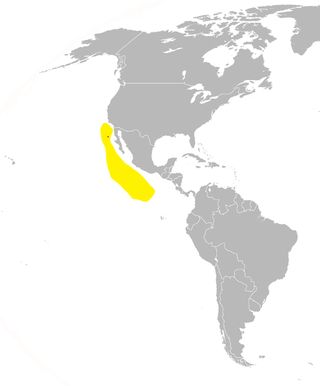
Townsend's storm petrel is a species of seabird in the family Hydrobatidae. It breeds in the summer on rocks and islets of Guadalupe Island off the western coast of Mexico. It ranges in the Eastern Pacific Ocean north to southern California in the United States and south to 10°N latitude. It used to be considered a subspecies of the Leach's storm petrel. It was formerly defined in the genus Oceanodroma before that genus was synonymized with Hydrobates.

Ainley's storm petrel is a species of seabird in the family Hydrobatidae. It breeds in the winter on Guadalupe Island off the western coast of Mexico. It ranges south to the Galápagos Islands. It is considered by some authorities to be a subspecies of Leach's storm petrel.





















