
Kollikodon is an extinct species of mammal, considered to be an early monotreme. It is known only from an opalised dentary fragment, with one premolar and two molars in situ, as well as a referred maxillary fragment containing the last premolar and all four molars. The fossils were found in the Griman Creek Formation at Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, Australia. Kollikodon lived in the Late Cretaceous period, during the Cenomanian age. Several other monotremes are known from the Griman Creek Formation, including Dharragarra, Opalios, Parvopalus, Steropodon, and Stirtodon.

Orthoceras is a genus of extinct nautiloid cephalopod restricted to Middle Ordovician-aged marine limestones of the Baltic States and Sweden. This genus is sometimes called Orthoceratites. Note it is sometimes misspelled as Orthocera, Orthocerus or Orthoceros.

Horntail or wood wasp are any of the 150 non-social species of the hymenopteran family Siricidae, a type of wood-eating sawfly. The common name "horntail" derives from the stout, spine-like structure at the end of the adult's abdomen which is present in both sexes. The ovipositor in females is typically longer and also projects posteriorly, but it is not the source of the name. Though they are not wasps, they are sometimes called wood wasps as the appearance of some species resembles one due to mimicry. A typical adult horntail is brown, blue, or black with yellow or red parts, and may often reach up to 4 cm (1.6 in) long. The pigeon horntail can grow up to 5 cm (2.0 in) long, among the longest of all Hymenoptera.

Inoceramus is an extinct genus of fossil marine pteriomorphian bivalves that superficially resembled the related winged pearly oysters of the extant genus Pteria. They lived from the Early Jurassic to latest Cretaceous.

Rhabdodontidae is a family of herbivorous iguanodontian ornithopod dinosaurs whose earliest stem members appeared in the middle of the Lower Cretaceous. The oldest dated fossils of these stem members were found in the Barremian Castrillo de la Reina Formation of Spain, dating to approximately 129.4 to 125.0 million years ago. With their deep skulls and jaws, Rhabdodontids were similar to large, robust iguanodonts. The family was first proposed by David B. Weishampel and colleagues in 2003. Rhabdodontid fossils have been mainly found in Europe in formations dating to the Late Cretaceous.

Polyptychoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, Europe, and North and South America. It was first named by Hisakatsu Yabe in 1927.
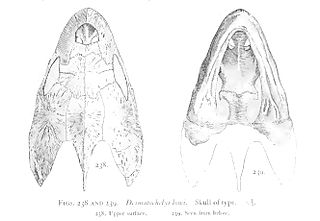
Desmatochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. This genus contains two known species, D. lowii and D. padillai. D. lowii was first discovered in 1895, followed by D. padillai in 2015. Having been estimated at over 120 million years old, D. padillai is currently the oldest known species of sea turtle.

Juliidae, common name the bivalved gastropods, is a family of minute sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the superfamily Oxynooidea, an opisthobranch group.

Archaeomarasmius is an extinct genus of gilled fungus in the Agaricales family Tricholomataceae, containing the single species Archaeomarasmius leggetti. It is known from two fruit bodies recovered from amber, one consisting of a complete cap with a broken stem, the other consisting of a fragment of a cap. The cap has a diameter ranging from 3.2 to 6 mm, while the stem is 0.5 mm (0.02 in) thick. Spores were also recovered from the amber, and are broadly ellipsoid to egg-shaped, measuring roughly 7.3 by 4.7 μm. The species, which resembles the extant genera Marasmius and Marasmiellus, is inferred to have been saprobic on plant litter or other forest debris.
Margaretbarromyces is an extinct monotypic genus of pleosporale fungus of uncertain family placement. At present it contains the single species Margaretbarromyces dictyosporus.
Appianoporites is an extinct monotypic genus of fungus in the Agaricomycetes family Hymenochaetaceae. At present it contains the single species Appianoporites vancouverensis.
Pseudoperna is a genus of extinct very small oysters. Pseudoperna lived in tight groups. This small oyster is commonly found attached in groups to the shell of large species such as Inoceramus. Pycnodonte and Pseudoperna are preserved mostly as calcitic valves and are also found attached to Mytiloides.

Patagotitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Cerro Barcino Formation in Chubut Province, Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species known from at least six young adult individuals, Patagotitan mayorum, which was first announced in 2014 and then named in 2017 by José Carballido and colleagues. Preliminary studies and press releases suggested that Patagotitan was the largest known titanosaur and land animal overall, with an estimated length of 37 m (121 ft) and an estimated weight of 69 tonnes. Later research revised the length estimate down to 31 m (102 ft) and weight estimates down to approximately 50–57 tonnes, suggesting that Patagotitan was of a similar size to, if not smaller than, its closest relatives Argentinosaurus and Puertasaurus. Still, Patagotitan is one of the most-known titanosaurs, and so its interrelationships with other titanosaurs have been relatively consistent in phylogenetic analyses. This led to its use in a re-definition of the group Colossosauria by Carballido and colleagues in 2022.
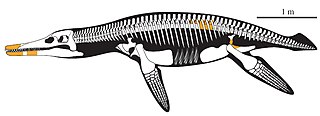
Makhaira rossica is an extinct genus and species of a marine reptile belonging to the family Pliosauridae. It lived during the early Cretaceous period, and its fossils have been found in Russia.
Suciacarpa is an extinct genus of asterid flowering plants in the order Cornales. It is known from the fossil species Suciacarpa starrii and Suciacarpa xiangae, both found in Western North America.

Matheronodon is a genus of rhabdodontid ornithopod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Grès à Reptiles Formation in France. The genus contains a single species, M. provincialis, which is known from a single maxilla and associated teeth. It was named by Pascal Godefroit and colleagues in 2017. The teeth of Matheronodon are large but few in number. The teeth are also in an unusual arrangement, emerging alternatingly from one of a pair of fused tooth sockets in its mouth. In life, the teeth would have functioned like a pair of scissors, allowing Matheronodon to feed on the tough leaves of monocot plants.

Imperobator is a genus of probable unenlagiid paravian theropod dinosaurs, that lived during the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous in what is now James Ross Island in Antarctica. Imperobator is one of only two non-avian theropods known from Antarctica, crossing over to the landmass when it was part of Gondwana. The only described specimen was found in 2003 by an expedition launched by the University of California Museum of Paleontology and initially described as a dromaeosaur in 2007. The fossil was formally described as a new genus in 2019, and later searches reported more fossils from the site including teeth and skull bones.
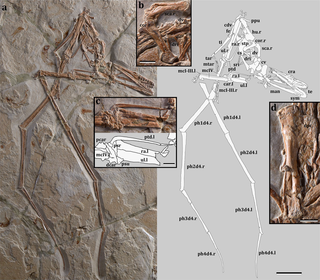
Mimodactylus is a genus of istiodactyliform pterosaur that lived in what is now Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous, 95 million years ago. The only known specimen was discovered in a limestone quarry near the town of Hjoula, belonging to the Sannine Formation. The owner of the quarry allowed the specimen to be prepared and scientifically described by an international team of researchers, and when it was eventually sold, the buyer donated it to the MIM Museum in Beirut. In 2019, the researchers named the new genus and species Mimodactylus libanensis; the generic name refers to the MIM Museum, combined with the Greek word daktylos for "digit", and the specific name refers to Lebanon. The well-preserved holotype specimen is the first complete pterosaur from the Afro-Arabian continent, and the third pterosaur fossil known from Lebanon.
Yuanjiawaornis is an extinct genus of large enantiornithean bird known from the early Cretaceous of present-day China. It is monotypic, with only type species Y. virisosus known.

Rastellum is an genus of extinct molluscs, which lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous.














