Campobasso is a city and comune in southern Italy, the capital of the region of Molise and of the province of Campobasso. It is located in the high basin of the Biferno river, surrounded by Sannio and Matese mountains.

Molise is a region of Southern Italy. Until 1963, it formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Italy. Covering 4,438 square kilometres (1,714 sq mi), it is the second smallest region in the country, after the Aosta Valley, and has a population of 313,348.
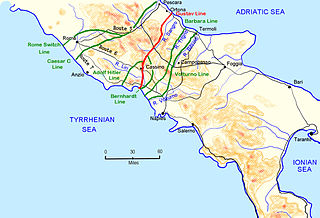
The Volturno Line was a German defensive position in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II.

Pescara is the capital city of the province of Pescara, in the Abruzzo region of Italy. It is the most populated city in Abruzzo, with 118,657 residents. Located on the Adriatic coast at the mouth of the River Aterno-Pescara, the present-day municipality was formed in 1927 joining the municipalities of the old Pescara fortress, the part of the city to the south of the river, and Castellamare Adriatico, the part of the city to the north of the river. The surrounding area was formed into the province of Pescara.

The province of Chieti is a province in the Abruzzo region of Italy. Its provincial capital is the city Chieti, which has a population of 50,770 inhabitants. The province has a total population of 387,649 inhabitants as of 2017 and spans an area of 2,599.58 square kilometres (1,003.70 sq mi). The province contains 104 comuni. Its provincial president is Mario Pupillo.

Ortona is a coastal town and municipality of the Province of Chieti in the Italian region of Abruzzo, with some 23,000 inhabitants.

Larino is a town and comune of approximately 8,100 inhabitants in Molise, province of Campobasso, southern Italy. It is located in the fertile valley of the Biferno River.

The province of Campobasso is a province in the Molise region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Campobasso. It covers an area of c. 2,941 square kilometres (1,136 sq mi) and has a total population of 223,871 (2017). There are 84 comuni in the province.

Shëngjin is a coastal town and a former municipality in Lezhë County, northwestern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality of Lezhë. The population at the 2023 census was 6,963. Shëngjin is a growing tourist destination, well known for its beaches and resort accommodations. Shëngjin is one of many cities within the District of Lezhë and is home to one of Albania's entry ports, Port of Shëngjin.

Campobasso Football Club, commonly referred to as Campobasso, is an Italian football club located in Campobasso, Molise, currently playing in Serie C, the third tier of Italian football.

Pineto is a town and comune in the province of Teramo, Abruzzo, in central Italy. It is a 20th-century seaside resort on the Adriatic coast, with sandy beaches shaded by pine trees that give their name to the town.

Casacalenda is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Campobasso in the Italian region Molise, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) northeast of Campobasso.

Colletorto is a comune (municipality) of approximately 1,786 inhabitants in the province of Campobasso, in the Italian region of Molise, located about 45 kilometres (28 mi) from the capital of the region Campobasso and 40 kilometres (25 mi) from Termoli (CB), sea town with port, railway and highway A14.

Guardialfiera is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Campobasso in the Italian region Molise, located about 30 kilometres (19 mi) northeast of Campobasso. It sits on a hilltop overlooking Lake Guardialfiera, which was created as a result of the damming of the Biferno river.

The trabucco, known in some southern dialects as trabocco or travocc, is an ancient fishing machine typical of the Adriatic shores of Abruzzo — famously dubbed the Costa dei Trabocchi and the Gargano coast, where they are preserved as historical monuments within the Gargano National Park. These distinctive structures are prevalent along the southern Adriatic coastline, particularly in the Italian provinces of Chieti, Campobasso, and Foggia. Trabucchi can also be found on select parts of the southern Tyrrhenian Sea coast.
Operation Devon was the code name of an amphibious landing by British Commandos in 1943 at Termoli, on the Adriatic coast of Italy, during the Italian Campaign of World War II.

Termoli railway station serves the town and comune of Termoli, in the region of Molise, southern Italy. Opened in 1864, it forms part of the Adriatic Railway (Ancona–Lecce) and is also a terminus for the line to Venafro, linking the comuni of Molise with both the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian seas.
Molisan is a group of dialects of the Neapolitan language spoken in Molise, a region of Southern Italy.

The Termoli–Campobasso railway line is a secondary railway line in Molise, Italy. When it first opened in 1883, the line consisted of 15 stations. Today, only 8 are open to passenger service.
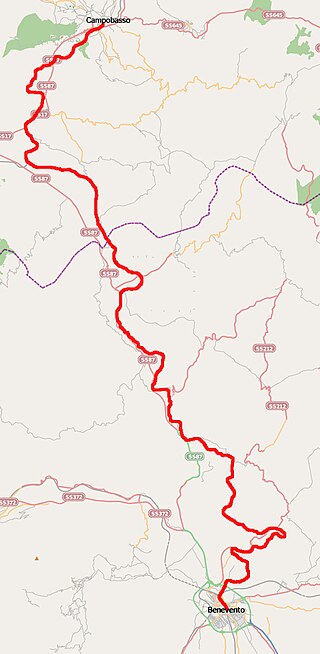
The Benevento–Campobasso railway is a secondary Italian railway line in Campania and Molise connecting Benevento with Campobasso of Samnium. Planned as an alternative to the Naples–Foggia railway to connect the Tyrrhenian Sea to the Adriatic Sea, but later deemed very slow and therefore uncompetitive, it has never been affected by large volumes of traffic.