
The Frisian languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 400,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and language contact with neighboring languages.
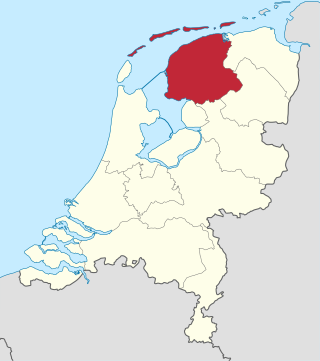
Friesland, historically and traditionally known as Frisia, named after the Frisians, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of Flevoland, northeast of North Holland, and south of the Wadden Sea. As of January 2023, the province had a population of about 660,000, and a total area of 5,753 km2 (2,221 sq mi).
The Frisians are an ethnic group indigenous to the coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark, and during the Early Middle Ages in the north-western coastal zone of Flanders, Belgium. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia.

Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" may include the island of Rem and the other Danish Wadden Sea Islands. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group.
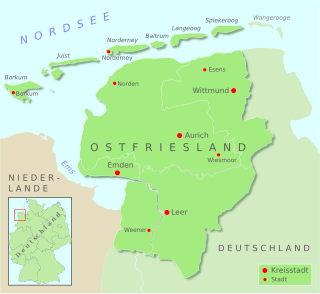
East Frisia or East Friesland is a historic region in modern Lower Saxony, Germany. The modern province is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland but is known to have extended much further inland before modern representations of the territory. Administratively, East Frisia consists of the districts Aurich, Leer and Wittmund and the city of Emden. It has a population of approximately 469,000 people and an area of 3,142 square kilometres (1,213 sq mi).

West Friesland is a contemporary region in the Northwest of the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland.

Burgum is the largest and administrative town of the municipality of Tytsjerksteradiel, in the Dutch province of Friesland. It had a population of 10,058 inhabitants in January 2017.

West Frisia is a term that, when used in an international context, refers to the traditionally Frisian areas that are located west of the Dollart. Along with East Frisia and North Frisia, it is one of the most commonly used subdivisions of Frisia. In its narrowest sense, the term is synonymous with the province of Friesland. Within the Netherlands, however, it is mostly used to refer to the region of West Friesland, located west of Friesland.

Aalsum is a village in the Dutch province of Friesland. It is located in the municipality Noardeast-Fryslân, about 1 km north of Dokkum. It had a population of around 125 in January 2017

Hooge is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.

Ezinge is a village in the Dutch province of Groningen. It is located in the municipality of Westerkwartier, about 15 km northwest of the city of Groningen. Ezinge is the oldest, constantly inhabited village in The Netherlands and is in archeological context referred to as "the Pompeii of the North".
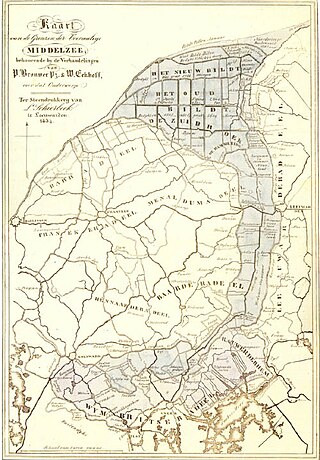
The Middelzee, also called Bordine, was the estuary mouth of the River Boorne now in the Dutch province of Friesland. It ran from as far south as Sneek northward to the Wadden Sea and marked the border between main Frisian regions of Westergoa (Westergo) and Eastergoa (Oostergo). Other historical names for the Middelzee include Bordaa, Borndiep, Boerdiep, and Bordena. The names like Bordine, mean "border".

Wâlterswâld is a village in Dantumadiel municipality, Friesland, the Netherlands. The village had a population of approximately 920 in 2017.

Burdaard is a village in Noardeast-Fryslân in the province of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 1,173 in January 2017. Before 2019, the village was part of the Ferwerderadiel municipality.

Eastrum is a village in Noardeast-Fryslân in the province of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 188 in January 2017. Before 2019, the village was part of the Dongeradeel municipality.

Waaxens is a small village in Noardeast-Fryslân municipality in the province of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of only 35 in January 2017. Before 2019, the village was part of the Dongeradeel municipality.

Sibrandahûs is a small village in the Dantumadiel municipality of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 40 in 2017. It is located just west of Dokkum.

Rinsumageast is a village in the Dantumadiel municipality of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 965 in 2017.

Frisia is a small region in the north of the modern day country known as the Netherlands. In the Iron Age, the ancestors of the modern Frisians first migrated south out of modern day Scandinavia to the south west where they began to settle along the coast. The archeological record goes all the way back to the Neolithic era, however, the first written sources for Frisian history come from Roman records, like Tacitus' account of an unsuccessful Frisian attack on a Roman fort. Frisia would go on to distinguish itself culturally from other Germanic peoples but remained recognizably Germanic nonetheless. In the Early Medieval era, Frisians took the seas with well crafted ships to perform trade and to raid other ports, cities, and towns in other parts of Europe. For most of its modern history, Frisia, or Frysland, has been under the control of the Netherlands but today their language is co-official with Dutch at the provincial level. Frisian is the most closely related language to English aside from Scots.

Niehove is a village in the municipality of Westerkwartier in Groningen, Netherlands. The village was located on the island of Humsterland in the former Lauwerszee from c. 800 until c. 1500. It is a terp village with two ring roads and the church in the middle. The village is a protected site. In 2019, Elsevier Weekblad named Niehove the most beautiful village of the Netherlands.
























