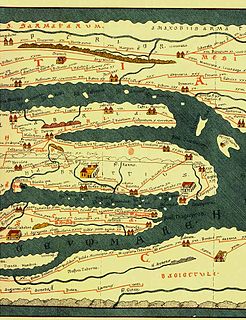
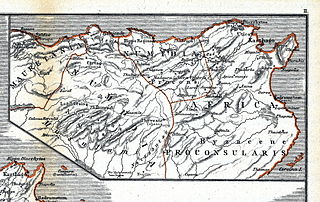
Siga was a Berber and Roman port located near what is now Aïn Témouchent, Algeria. Under the Roman Empire, it was part of western Mauretania Caesariensis, bordering Mauretania Tingitana.

Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars, Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by a "confederation of free Roman cities" such as Tiddis, Cuicul, and Milevum. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4th century and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor Justinian I reconquered and improved the Roman city. It declined in importance after the Muslim invasions, but a small community continued at the site for several centuries. Its ruins are now an archaeological site.

Tabarka is a coastal town located in north-western Tunisia, close to the border with Algeria. Tabarka's history is a colorful mosaic of Berber, Punic, Hellenistic, Roman, and Islamic, and Turkish culture. The town is dominated by an offshore rock on which is remains a Genoese castle. Nationalist leader Habib Bourguiba, later president of post-independence Tunisia, was exiled here by the French colonial authorities in 1952.. Tourist attractions include its coral fishing, the Coralis Festival of underwater photography, and its annual jazz festival.

Zaraï was a Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman town at the site of present-day Aïn Oulmene, Algeria. Under the Romans, it formed part of the province of Numidia.

Bulla Regia was a Berber, Punic, and Roman town near present-day Jendouba, Tunisia. Its surviving ruins and archaeological site are noted for their Hadrianic-era semi-subterranean housing, a protection from the fierce heat and effects of the sun. Many of the mosaic floors have been left in place; others may be seen at the Bardo Museum in Tunis. There is also a small museum connected with the site.

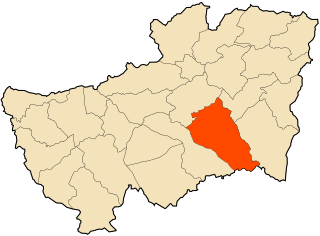
Khamissa, ancient Thubursicum Numidarum or Thubursicum, is an Ancient Roman and Byzantine archeological site, in Souk Ahras Province of northeastern Algeria.
Saint Crispina was a martyr of Africa who suffered during the Diocletian persecution. She was born at Thagara in North Africa. She died by beheading at Theveste, in Numidia.

Souk Ahras is a municipality in Algeria. It is the capital of Souk Ahras Province. The Numidian city of Thagaste, on whose ruins Souk Ahras was built, was the birthplace of Augustine of Hippo and a center of Berber culture. It was a city of great culture, described as the very hub of civilization.

Collo was an ancient Roman–Berber city in the northern Skikda Province, Algeria. It was the capital and one of three municipalities of Collo District, and a Catholic titular episcopal see under its Roman name Chullu. In 1998, it had a population of 27,800.

Tubunae was a Roman-Berber city in Algeria. It is believed to have been in either ancient Mauretania Caesariensis and/or Numidia.

Calama was a colonia in the Roman province of Numidia situated where Guelma in Algeria now stands.
Musti in Numidia], also called Musti Numidiae, was an ancient city and bishopric, and is presently a Catholic titular see, in modern Algeria.

The Church of Carthage was a local church established in the Roman province of Africa Proconsulare, with its ecclesiastical seat in ancient Carthage. It is in the Romanesque architectural style. The cathedral dissolved following the spread of Islam in the region.
Macomades was a Carthaginian and Roman city in North Africa. It was located near present-day Merkeb-Talha, Algeria.
Vegesela was an Ancient city and former bishopric in Roman North Africa and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Timici was a Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman town located in present-day Sidi Bu Sayb, Algeria.
Tipasa, distinguished as Tipasa in Numidia, was a town in the Roman province of Numidia in North Africa. Its ruins are located 957 meters (3,140 ft) above sea level near present-day Tifesh in Constantine Province, Algeria, 88 kilometers (55 mi) south of Annaba.