| Location | Algeria |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 36°54′0″N4°25′0″E / 36.90000°N 4.41667°E |
Rusazus [1] was a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman town located near Cape Corbelin, Algeria. Its ruins are near the town of Azeffoun. [1]
| Location | Algeria |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 36°54′0″N4°25′0″E / 36.90000°N 4.41667°E |
Rusazus [1] was a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman town located near Cape Corbelin, Algeria. Its ruins are near the town of Azeffoun. [1]
RŠZ (Phoenician : 𐤓𐤔𐤆) was the Phoenician and Punic name of Cape Corbelin and meant "Cape of the Strong One" [2] or "Cape of the Fort". [1] It was hellenized as Rhousazoûs (Ancient Greek : Ῥουσαζοῦς) [3] and Latinized variously as Rusazus, [4] Rusazu, [5] Rusazis, [6] Ruseius, [7] and Rusadum. [8]
As to which "Strong One" might have been meant, Lipiński offers that Azeffoun's name itself might be a Berber memory of a Punic toponym honoring Baal Zephon, [2] who was reckoned a patron of maritime trade. He allows, though, that pending the discovery of such an inscription, mere assonance is also possible. [2]
Rusazus was established as a colony along the trade route between the Strait of Gibraltar and Phoenicia. It consisted of a small fortress south of Cape Corbelin. [1] It eventually fell under Carthaginian control, probably during the 6th century BC.
Under the Romans, it was established as a Roman colony under Augustus. [4] It was part of Mauretania Caesariensis after AD 44.
In late antiquity, it was part of the Vandal Kingdom prior to the Byzantine reconquest of Africa. It was overrun by the Umayyad Caliphate in the 7th century.
The site includes a necropolis and the ruins of baths, temples, and Roman-era embankments.
The Roman town had a Christian bishopric (Latin: Dioecesis Rusaditana). [9] [8] It was revived in the 20th century as a Roman Catholic titular see.

Utica was an ancient Phoenician and Carthaginian city located near the outflow of the Medjerda River into the Mediterranean, between Carthage in the south and Hippo Diarrhytus in the north. It is traditionally considered to be the first colony to have been founded by the Phoenicians in North Africa. After Carthage's loss to Rome in the Punic Wars, Utica was an important Roman colony for seven centuries.

Cherchell is a town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast, 89 kilometers (55 mi) west of Algiers. It is the seat of Cherchell District in Tipaza Province. Under the names Iol and Caesarea, it was formerly a Roman colony and the capital of the kingdoms of Numidia and Mauretania.
Ruspina was a Phoenician, Carthaginian and Roman town located in Monastir, Tunisia, situated in Roman times in Africa propria, and mentioned by Pliny the Elder and Ptolemy.

The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians, were a Semitic people who migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term Punic, the Latin equivalent of the Greek-derived term Phoenician, is exclusively used to refer to Phoenicians in the western Mediterranean, following the line of the Greek East and Latin West. The largest Punic settlement was Ancient Carthage, but there were 300 other settlements along the North African coast from Leptis Magna in modern Libya to Mogador in southern Morocco, as well as western Sicily, southern Sardinia, the southern and eastern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, Malta, and Ibiza. Their language, Punic, was a variety of Phoenician, one of the Northwest Semitic languages originating in the Levant.
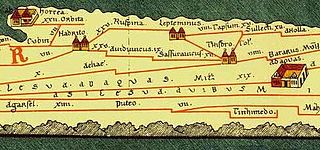
Leptis or Lepcis Parva was a Phoenician colony and Carthaginian and Roman port on Africa's Mediterranean coast, corresponding to the modern town Lemta, just south of Monastir, Tunisia. In antiquity, it was one of the wealthiest cities in the region.

Icosium was a Phoenician and Punic settlement in modern-day Algeria. It was part of Numidia and later became an important Roman colony and an early medieval bishopric in the casbah area of modern Algiers.

Tamentfoust, the classical Rusguniae and colonial La Pérouse, is a site in the Dar El Beïda District of Algiers in Algeria.

Rusadir was an ancient Punic and Roman town at what is now Melilla, Spain, in northwest Africa. Under the Roman Empire, it was a colony in the province of Mauretania Tingitana.

Phoenicia under Roman rule describes the Phoenician city states ruled by Rome from 64 BCE to the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The area around Berytus was the only Latin speaking and Romanized part of Aramaic-speaking Phoenicia.

Ancient Carthage was an ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest metropoleis in the world. It was the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power led by the Punic people who dominated the ancient western and central Mediterranean Sea. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt the city lavishly.
Naraggara was an ancient city in Africa Proconsularis located 33 kilometer northwest of modern-day El Kef, Tunisia. It is considered to be the modern-day town of Sakiet Sidi Youssef, also located in Tunisia. The name Naraggara, a Libyan inscription, suggests a pre-Roman origin for the city, along with the name being bilingual in Latin and Neo-Punic.

Djinet, the classical Cissi, is a port town and commune in the Bordj Menaïel District of Boumerdès Province, Algeria, east of the mouth of the Isser River and around Cape Djinet. As of 2008, the population of the municipality is 21,966.

Azeffoun, the classical Rusazus and colonial Port Gueydon, is a town and commune in Tizi Ouzou Province in northern Algeria, located on Cape Corbelin 64 km (40 mi) north-east of Tizi Ouzou. The economy of the town of Azeffoun is based on tourism, fishing, and agriculture.
Igilgili was a Berber town and a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman colony in located in present-day Jijel, Algeria.

Cartennae or Cartenna was an ancient Carthaginian and Roman port at present-day Ténès, Algeria. Under the Romans, it was part of the province of Mauretania Caesariensis.

Bithia or Bitia was a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman town located near Chia in the extreme south of Sardinia, Italy. Most of the ruins have been submerged underwater.
Rusippisir was a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast at the site of present-day Taksebt.

Ounga, also known as Younga and Jounga, is an archaeological site on the Mediterranean coast of Tunisia, located 45 km (28 mi) south of Sfax along the Mediterranean coast. The area is also known for its oil fields.

Cape Farina is a headland in Bizerte Governorate, Tunisia. It forms the northwestern end of the Gulf of Tunis. The Tunisian towns of Ghar el-Melh, Rafraf, Lahmeri, and the beach of Plage Sidi Ali Mekki Est are located along the peninsula.
Rusubbicari was a Phoenician and Carthaginian colony and Roman town. It has been tentatively identified with ruins at Zemmouri El Bahri, Algeria. The Roman town was in the province of Mauretania Caesariensis.