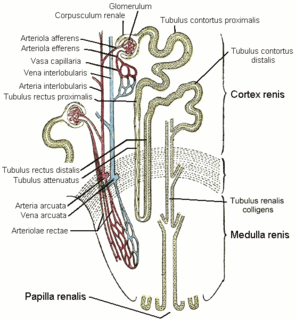
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule.
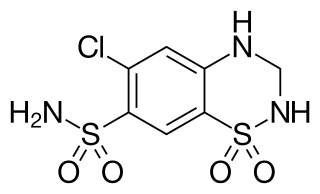
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up. Other uses include diabetes insipidus, renal tubular acidosis, and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. For high blood pressure it is sometimes considered as a first-line treatment, although chlorthalidone is more effective with a similar rate of adverse effects. HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.
ATC code C03Diuretics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the WHO for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C03 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.
ATC code C07Beta blocking agents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the WHO for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C07 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.

Loop diuretics are diuretics that act at the ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or renal insufficiency. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics are more effective in patients with impaired kidney function.

Amiloride, sold under the trade name Midamor among others, is a medication typically used with other medications to treat high blood pressure or swelling due to heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver. Amiloride is often used with a thiazide or other loop diuretic. It is taken by mouth. Onset of action is about two hours and it lasts for about a day.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a diuretic medication used to treat high blood pressure, enlargement of the main pumping chamber of the heart, swelling and fluid retention, Ménière's disease, and inability of an injured kidney to produce concentrated urine. Chlortalidone is also used to prevent calcium oxalate kidney stones and bone fracture due to reduced bone mass. It is a thiazide-like diuretic of the sulfonamide class.

Bendroflumethiazide, formerly bendrofluazide, trade name Aprinox, is a thiazide diuretic used to treat hypertension.
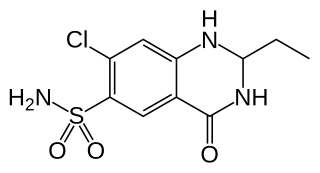
Quinethazone is a thiazide-like diuretic used to treat hypertension. Common side effects include dizziness, dry mouth, nausea, and low potassium levels.
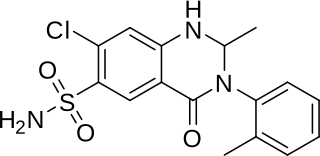
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.

Clopamide is a piperidine diuretic.

Perindopril/indapamide is a combination medication which contains perindopril and indapamide both of which are used for the treatment of essential hypertension.

Xipamide is a sulfonamide diuretic drug marketed by Eli Lilly under the trade names Aquaphor and Aquaphoril. It is used for the treatment of oedema and hypertension.

Cyclopenthiazide is a thiazide diuretic used in the treatment of heart failure and hypertension.

Polythiazide is a thiazide diuretic. A diuretic is any substance that promotes the production of urine.
An ACE inhibitor and thiazide combination is a drug combination used to treat hypertension. They are given by by mouth.
















