In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own, defense, and interactions with other organisms.
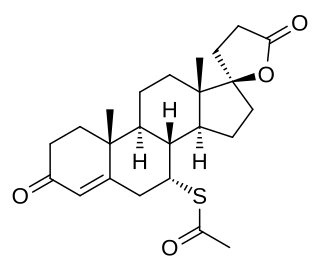
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood pressure, low blood potassium that does not improve with supplementation, early puberty in boys, acne and excessive hair growth in women, and as a part of transgender hormone therapy in transfeminine people. Spironolactone is taken by mouth.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling including that due to heart failure, liver failure, and nephrotic syndrome, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is reliably effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.
An osmotic diuretic is a type of diuretic that inhibits reabsorption of water and sodium (Na). They are pharmacologically inert substances that are given intravenously. They increase the osmolarity of blood and renal filtrate.

Cocaethylene (ethylbenzoylecgonine) is the ethyl ester of benzoylecgonine. It is structurally similar to cocaine, which is the methyl ester of benzoylecgonine. Cocaethylene is formed by the liver when cocaine and ethanol coexist in the blood. In 1885, cocaethylene was first synthesized, and in 1979, cocaethylene's side effects were discovered.

Tienilic acid or ticrynafen (USAN) is a loop diuretic drug with uric acid-lowering (uricosuric) action, formerly marketed for the treatment of hypertension. It was approved by FDA on May 2, 1979, and withdrawn in 1982, after case reports in the United States indicated a link between the use of ticrynafen and hepatitis.

Quazepam, sold under brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines. Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture.

Pinazepam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.
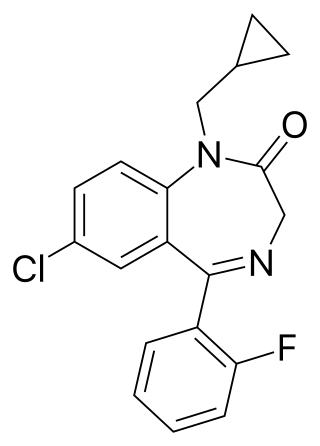
Flutoprazepam (Restas) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine. It was patented in Japan by Sumitomo in 1972 and its medical use remains mostly confined to that country. Its muscle relaxant properties are approximately equivalent to those of diazepam - however, it has more powerful sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects and is around four times more potent by weight compared to diazepam. It is longer acting than diazepam due to its long-acting active metabolites, which contribute significantly to its effects. Its principal active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam.

Metaclazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is a relatively selective anxiolytic with less sedative or muscle relaxant properties than other benzodiazepines such as diazepam or bromazepam. It has an active metabolite N-desmethylmetaclazepam, which is the main metabolite of metaclazepam. There is no significant difference in metabolism between younger and older individuals.

Norcocaine is a minor metabolite of cocaine. It is the only confirmed pharmacologically active metabolite of cocaine, although salicylmethylecgonine is also speculated to be an active metabolite. The local anesthetic potential of norcocaine has been shown to be higher than that of cocaine, however cocaine continues to be more widely used. Norcocaine used for research purposes is typically synthesized from cocaine. Several methods for the synthesis have been described.

Meclonazepam ((S)-3-methylclonazepam) was discovered by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s and is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative similar in structure to clonazepam. It has sedative and anxiolytic actions like those of other benzodiazepines, and also has anti-parasitic effects against the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni.

Trichlormethiazide is a diuretic with properties similar to those of hydrochlorothiazide. It is usually administered for the treatment of oedema and hypertension. In veterinary medicine, trichlormethiazide can be combined with dexamethasone to be used on horses with mild swelling of distal limbs and general bruising.

Muzolimine is a High-ceiling loop diuretic. It is a pyrazole diuretic which was used for treatment of hypertension but was withdrawn worldwide because of severe neurological side effects.
The eudysmic ratio represents the difference in pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers of a drug. In most cases where a chiral compound is biologically active, one enantiomer is more active than the other. The eudysmic ratio is the ratio of activity between the two. A eudysmic ratio significantly differing from 1 means that they are statistically different in activity. Eudisimic ratio (ER) reflects the degree of enantioselectivity of the biological systems. For example, (S)-propranolol meaning that (S)-propranolol is 130 times more active as its (R)-enantiomer.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.

Lirequinil (Ro41-3696) is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drug which binds to benzodiazepine sites on the GABAA receptor. In human clinical trials, lirequinil was found to have similar efficacy to zolpidem, with less side effects such as clumsiness and memory impairment. However it was also much slower acting than zolpidem, with peak plasma concentrations not reached until 2.5 hours after oral administration, and its O-desethyl metabolite Ro41-3290 is also active with a half-life of 8 hours. This meant that while effective as a hypnotic, lirequinil failed to prove superior to zolpidem due to producing more next-day sedation, and it has not been adopted for clinical use. It was developed by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1990s.
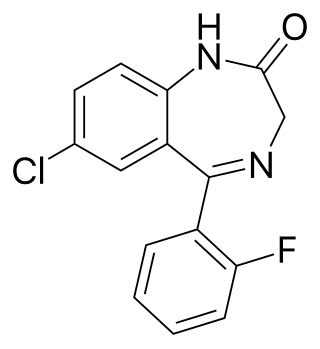
N-Desalkylflurazepam is a benzodiazepine analog and an active metabolite of several other benzodiazepine drugs including flurazepam, flutoprazepam, fludiazepam, midazolam, flutazolam, quazepam, and ethyl loflazepate. It is long-acting, prone to accumulation, and binds unselectively to the various benzodiazepine receptor subtypes. It has been sold as a designer drug from 2016 onward.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.


















