
The spotted handfish is a rare Australian fish in the handfish family, Brachionichthyidae, classified as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List 2020. It has a highly restricted range, being found only in the estuary of Derwent River, Tasmania, and nearby areas, with the main threat to its existence being an invasive species, the Northern Pacific seastar.

Handfish are marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, a group which comprises five genera and 14 extant species and which is classified within the suborder Antennarioidei in the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. These benthic marine fish are unusual in the way they propel themselves by walking on the sea floor rather than swimming.

Brachionichythys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. These fishes are confined to the southeastern Indian Ocean and southwestern Pacific Ocean off Australia.

The starry handfish, starry seabat or minipizza batfish, is species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep-sea batfishes or seabats. This fish is found on the continental shelves of the Indo-Pacific oceans at depths of between 50 and 400 m. They are up to 30 cm long.

Glauert's anglerfish is species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. This species is the only species in the monospecific genus Allenichthys. This species is endemic to southern Australia.
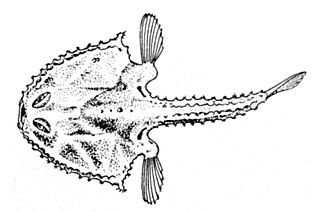
Halieutaea is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. These fishes are found in the Indian and Western Pacific Oceans.
Brachiopsilus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. The fishes in this genus are endemic to Australia.
Pezichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. The fishes in this genus are endemic to southern Australia. These fishes are all extremely localised in distribution and are rare.

Sympterichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. These fishes are endemic to Australia.

Antennarius is a genus of anglerfish belonging to the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. The fishes in this genus are found in warmer parts of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Echinophryne is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. The fishes in this genus are endemic to the waters off Australia.
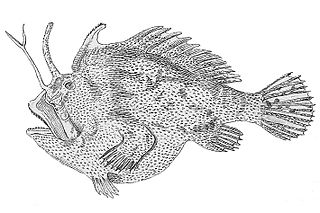
Kuiterichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. These fishes are endemic to Australia.

Phyllophryne is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. The only species in the genus is Phyllophryne scortea, the white-spotted anglerfish, smooth anglerfish or smooth frogfish, which is endemic to southern Australia.

Rhycherus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. The fishes in this genus are endemic to the waters off Australia. This genus is classified in the monogeneric family Rhycheridae, the Balrog frogfishes, by some authorities.

The red handfish is a species of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. Like all members of the handfish family this fish is endemic to Australia. The IUCN classify the red handfish as Critically Endangered.
Ziebell's handfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. This species is endemic to eastern and southern Tasmania. It is a very rare species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature classifies it as Critically Endangered.
Moulton's handfish is species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to th efamily Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. This species is endangered and is endemic to the waters off southeastern Australia.

Echinophryne mitchellii, the long-spined frogfish, bristly frogfish, Mitchell's anglerfish, Mitchell's frogfish, prickly angler fish or spinycoat anglerfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. These fishes are endemic to the temperate waters of southern Australia.

Lophiocharon trisignatus, the spot-tail anglerfish, rough anglerfish or three-spot frogfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Histiophryninae in the family Antennariidae, the frogfishes. This fish is found in the Indo-Pacific region.
The Australian spotted handfish, also known as the Australian handfish or common handfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Brachionichthyidae, the handfishes. This species is endemic to eastern and southern Australia.













