
Thyme is a culinary herb consisting of the dried aerial parts of some members of the genus Thymus of flowering plants in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are native to Eurasia and north Africa. Thymes have culinary, medicinal, and ornamental uses. The species most commonly cultivated and used for culinary purposes is Thymus vulgaris, native to Southeast Europe.
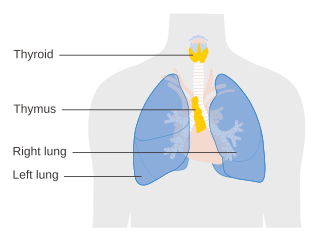
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.

Coleus amboinicus, synonym Plectranthus amboinicus, is a semi-succulent perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae with a pungent oregano-like flavor and odor. Coleus amboinicus is considered to be native to parts of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and India, although it is widely cultivated and naturalized elsewhere in the tropics where it is used as a spice and ornamental plant. Common names in English include Indian borage, country borage, French thyme, Indian mint, Mexican mint, Cuban oregano, broad leaf thyme, soup mint, Spanish thyme. The species epithet, amboinicus refers to Ambon Island, in Indonesia, where it was apparently encountered and described by João de Loureiro (1717–1791).
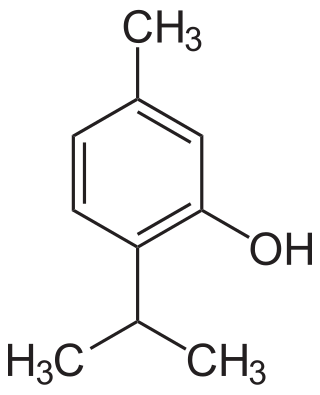
Thymol, C10H14O, is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of p-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris, ajwain, and various other plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties. Thymol also provides the distinctive, strong flavor of the culinary herb thyme, also produced from T. vulgaris. Thymol is only slightly soluble in water at neutral pH, but it is extremely soluble in alcohols and other organic solvents. It is also soluble in strongly alkaline aqueous solutions due to deprotonation of the phenol. Its dissociation constant (pKa) is 10.59±0.10. Thymol absorbs maximum UV radiation at 274 nm.

The genus Thymus contains about 350 species of aromatic perennial herbaceous plants and subshrubs in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to the Old World.

Thymus serpyllum, known by the common names of Breckland thyme, Breckland wild thyme, wild thyme, creeping thyme, or elfin thyme, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, native to most of Europe and North Africa. It is a low, usually prostrate subshrub growing to 2 cm (1 in) tall with creeping stems up to 10 cm (4 in) long. The oval evergreen leaves are 3–8 mm long. The strongly scented flowers are either lilac, pink-purple, magenta, or a rare white, all 4–6 mm long and produced in clusters. The hardy plant tolerates some pedestrian traffic and produces odors ranging from heavily herbal to lightly lemon, depending on the variety.

Za'atar is a Levantine culinary herb or family of herbs. It is also the name of a spice mixture that includes the herb along with toasted sesame seeds, dried sumac, often salt, and other spices. As a family of related Levantine herbs, it contains plants from the genera Origanum (oregano), Calamintha, Thymus, and Satureja (savory) plants. The name za'atar alone most properly applies to Origanum syriacum, considered in biblical scholarship to be the ezov of the Hebrew Bible, often translated as hyssop but distinct from modern Hyssopus officinalis.

Thymus herba-barona is a species of thyme native to Corsica, Sardinia, and Majorca. It is also sometimes known by the common name caraway thyme, as it has a strong scent similar to caraway, for which it can be used as a substitute in any recipe. It can be used in cuisine or as an evergreen ground cover plant for the garden.

Thymus citriodorus, the lemon thyme or citrus thyme, is a lemon-scented evergreen mat-forming perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae. There has been a great amount of confusion over the plant's correct name and origin. Recent DNA analysis suggests that it is not a hybrid or cross, but a distinct species as it was first described in 1811., yet an analysis in a different study clustered Thymus citriodorus together with Thymus vulgaris, which is considered as one of its parent species.

Ezov is the Classical Hebrew name of a plant mentioned in the Hebrew Bible in the context of religious rituals. In some English-language Bibles, the word is transliterated as ezob.

Origanum syriacum; syn. Majorana syriaca, bible hyssop, Biblical-hyssop, Lebanese oregano or Syrian oregano, is an aromatic perennial herb in the mint family, Lamiaceae.

Cuscuta epithymum is a parasitic plant assigned to the family Cuscutaceae or Convolvulaceae, depending on the taxonomy. It is red-pigmented, not being photosynthetically active. It has a filiform habit, like a group of yarns. Its leaves are very small, like flakes. Its flowers, disposed in little glomerules, have a white corolla, with the androecium welded to the corolla.

Hyssopus officinalis or hyssop is a shrub in the Lamiaceae or mint family native to Southern Europe, the Middle East, and the region surrounding the Caspian Sea. Due to its purported properties as an antiseptic, cough reliever, and expectorant, it has been used in traditional herbal medicine.

Melaleuca thymifolia, commonly known as thyme honey-myrtle, is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae and is native to eastern Australia. It is often noticed in spring, with its attractive, purple flowers and is one of the most commonly cultivated melaleucas. A fragrant shrub, it usually grows to about 1.0 m (3 ft) tall, has corky bark and slender, wiry stems.

Pyropteron muscaeforme, the thrift clearwing, is a moth of the family Sesiidae that lives in most of Europe.

Thymus pulegioides, common names broad-leaved thyme or lemon thyme, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to Europe. Growing to 5–25 cm (2–10 in) tall by 25 cm (10 in) wide, it is a small spreading subshrub with strongly aromatic leaves, and lilac pink flowers in early summer. The specific epithet pulegioides highlights its similarity to another species within Lamiaceae, Mentha pulegium (pennyroyal).

Thymus zygis is a type of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae native to the Iberian Peninsula and northern Morocco.

Satureja thymbra, commonly known as savory of Crete, whorled savory, pink savory, and Roman hyssop, is a perennial-green dwarf shrub of the family Lamiaceae, having strongly scented leaves, native to Libya, southeastern Europe from Sardinia to Turkey; Cyprus, Lebanon, Israel and the Palestinian Authority. The plant is noted for its dark-green leaves which grow on numerous, closely compacted branches, reaching a height of 20–50 cm. The plant bears pink to purple flowers that blossom between March and June.

Anchusa strigosa is a non-succulent species of herbaceous plants in the Boraginaceae family endemic to the Eastern Mediterranean regions, particularly Greece, Turkey, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, and Iran. It is known widely by its common names of strigose bugloss and prickly alkanet.

Echium judaeum, commonly known as the Judean viper's bugloss, is an annual plant endemic to southern Lebanon, southern Syria and Israel, of the Boraginaceae family, and which, like other herbaceous flowering plants of the same genus, derives its name from the style's resemblance to the forked-tongue of a serpent during the flower's pistillate-stage of development.




















