
Corymbia, commonly known as bloodwoods, is a genus of about one hundred species of tree that, along with Eucalyptus, Angophora and several smaller groups, are referred to as eucalypts. Until 1990, corymbias were included in the genus Eucalyptus and there is still considerable disagreement among botanists as to whether separating them is valid. As of January 2020, Corymbia is an accepted name at the Australian Plant Census.

Kookaburras are terrestrial tree kingfishers of the genus Dacelo native to Australia and New Guinea, which grow to between 28 and 47 cm in length and weigh around 300 g (11 oz). The name is a loanword from Wiradjuri guuguubarra, onomatopoeic of its call. The loud, distinctive call of the laughing kookaburra is widely used as a stock sound effect in situations that involve an Australian bush setting or tropical jungle, especially in older movies.

Laridae is a family of seabirds in the order Charadriiformes that includes the gulls, terns, noddies, skimmers, and kittiwakes. It includes around 100 species arranged into 22 genera. They are an adaptable group of mostly aerial birds found worldwide.

Thylacinidae is an extinct family of carnivorous marsupials from the order Dasyuromorphia. The only species to survive into modern times was the thylacine, which became extinct in 1936.

Desidae is a family of spiders, some of which are known as intertidal spiders. The family is named for the genus Desis, members of which live in a very unusual location — between the tides. The family has been reevaluated in recent years and now includes inland genera and species as well, such as Badumna and Phryganoporus. In 2017, the family Amphinectidae was merged into Desidae. The family Toxopidae has been separated off. Those intertidal spiders that are truly marine commonly live in barnacle shells, which they seal up with silk; this allows them to maintain an air bubble during high tide. They emerge at night to feed on various small arthropods that live in the intertidal zone.

The genus Helichrysum consists of an estimated 600 species of flowering plants in the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The type species is Helichrysum orientale. They often go by the names everlasting, immortelle, and strawflower. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ἥλιος and χρῡσός.

Dudgeonea is a small genus of moths and the only genus of its family, the Dudgeoneidae. It includes six species distributed sparsely across the Old World from Africa and Madagascar to Australia and New Guinea.

Myrmecia is a genus of ants first established by Danish zoologist Johan Christian Fabricius in 1804. The genus is a member of the subfamily Myrmeciinae of the family Formicidae. Myrmecia is a large genus of ants, comprising at least 93 species that are found throughout Australia and its coastal islands, while a single species is only known from New Caledonia. One species has been introduced out of its natural distribution and was found in New Zealand in 1940, but the ant was last seen in 1981. These ants are commonly known as bull ants, bulldog ants or jack jumper ants, and are also associated with many other common names. They are characterized by their extreme aggressiveness, ferocity, and painful stings. Some species are known for the jumping behavior they exhibit when agitated.

Lophocoronoidea is a superfamily of insects in the order Lepidoptera. There is a single extant genus, Lophocorona, in the family Lophocoronidae. These are small, primitive nocturnal moths restricted to Australia whose biology is largely unknown.

Rainbowfishes are small, colourful freshwater fishes belonging to the family Melanotaeniidae, found in northern and eastern Australia, New Guinea, Sulawesi and Madagascar.

Acacia, commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about 1084 species of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America and Australasia, but is now reserved for species mainly from Australia, with others from New Guinea, Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean. The genus name is Neo-Latin, borrowed from the Greek ἀκακία, a term used by Dioscorides for a preparation extracted from the leaves and fruit pods of Vachellia nilotica, the original type of the genus. In his Pinax (1623), Gaspard Bauhin mentioned the Greek ἀκακία from Dioscorides as the origin of the Latin name.

Copromorphidae, the "tropical fruitworm moths", is a family of insects in the lepidopteran order. These moths have broad, rounded forewings, and well-camouflaged scale patterns. Unlike Carposinidae the mouthparts include "labial palps" with the second rather than third segment the longest. With other unusual structural characteristics of the caterpillar and adult, it could represent the sister lineage of all other extant members of this superfamily. The genus Sisyroxena from Madagascar is also notable for its unusual venation and wing scale sockets.

Superfamily Tabanoidea are insects in the order Diptera.

Hyalochlamys is a genus of Australian flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.

Pogonolepis is a genus of Australian plants in the tribe Gnaphalieae within the family Asteraceae.
Pinkfloydia is a genus of small Australian long-jawed orb-weavers, reaching a maximum lengths of about 4.5 millimetres (0.18 in). It was first described by D. Dimitrov & G. Hormiga in 2011, and contains two species, found in New South Wales and Western Australia: P. harveyi and P. rixi. They have a unique rounded, cone-shaped head structure with one pair of large eyes and three pairs of smaller eyes. The genus is named after British rock band Pink Floyd.

Haegiela is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae described as a genus in 1990. There is only one known species, Haegiela tatei, native to South Australia, and Victoria.
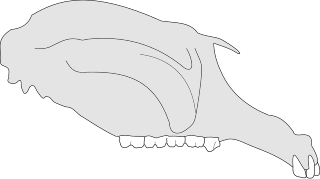
Propalorchestes is a fossil genus of palorchestid marsupial that existed in Australia during the Miocene epoch.

Blennospora phlegmatocarpa is a herb species in the family Asteraceae. It is found in Western Australia.
Valeseguyidae is a family of flies, belonging to Scatopsoidea. It contains only one known extant species, Valeseguya rieki, known from a single male specimen found in Victoria, Australia, described in 1990. It was initially classified as a member of the wood gnat family Mycetobiidae, but was later given its own family in 2006. Two fossil species are known, including another species of Valeseguya, V. disjuncta, which is known from Miocene aged Dominican amber from the Caribbean, and Cretoseguya, containing the single species C. burmitica, which is known from the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber of Myanmar, dating to around 100 million years ago.

















