
A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge (MSG), is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil.

A vernier scalever-NEE-er), named after Pierre Vernier, is a visual aid to take an accurate measurement reading between two graduation markings on a linear scale by using mechanical interpolation, thereby increasing resolution and reducing measurement uncertainty by using vernier acuity to reduce human estimation error. It may be found on many types of instrument measuring linear or angular quantities, but in particular on a vernier caliper, which measures lengths.

In the oil and gas industry, the term wireline usually refers to the use of multi-conductor, single conductor or slickline cable, or "wireline", as a conveyance for the acquisition of subsurface petrophysical and geophysical data and the delivery of well construction services such as pipe recovery, perforating, plug setting and well cleaning and fishing. The subsurface geophysical and petrophysical information results in the description and analysis of subsurface geology, reservoir properties and production characteristics.

A nursery is a place where plants are propagated and grown to a desired size. Mostly the plants concerned are for gardening, forestry, or conservation biology, rather than agriculture. They include retail nurseries, which sell to the general public; wholesale nurseries, which sell only to businesses such as other nurseries and commercial gardeners; and private nurseries, which supply the needs of institutions or private estates. Some will also work in plant breeding.

The wheel size for a motor vehicle or similar wheel has a number of parameters.

In agriculture and gardening, transplanting or replanting is the technique of moving a plant from one location to another. Most often this takes the form of starting a plant from seed in optimal conditions, such as in a greenhouse or protected nursery bed, then replanting it in another, usually outdoor, growing location. The agricultural machine that does this is called a transplanter. This is common in market gardening and truck farming, where setting out or planting out are synonymous with transplanting. In the horticulture of some ornamental plants, transplants are used infrequently and carefully because they carry with them a significant risk of killing the plant.

Caliper(s) or calliper(s) are an instrument used to measure the linear dimensions of an object or hole; namely, the length, width, thickness, diameter or depth of an object or hole. The word "caliper" comes from a corrupt form of caliber.
A bore gauge is a collective term for the tools that are unique to the process of accurately measuring holes.

Diameter at breast height, or DBH, is a standard method of expressing the diameter of the trunk or bole of a standing tree. DBH is one of the most common dendrometric measurements.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and guide to forestry:
A caliper log is a well logging tool that provides a continuous measurement of the size and shape of a borehole along its depth and is commonly used in hydrocarbon exploration. The measurements that are recorded can be an important indicator of wash-outs, cave ins or shale swelling in the borehole, which can affect the results of other well logs.

Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion while the lower part is called the rootstock. The success of this joining requires that the vascular tissues grow together. The natural equivalent of this process is inosculation. The technique is most commonly used in asexual propagation of commercially grown plants for the horticultural and agricultural trades. The scion is typically joined to the rootstock at the soil line; however, top work grafting may occur far above this line, leaving an understock consisting of the lower part of the trunk and the root system.

A diameter tape (D-tape) is a measuring tape used to estimate the diameter of a cylinder object, typically the stem of a tree or pipe. A diameter tape has either metric or imperial measurements reduced by the value of π. This means the tape measures the diameter of the object. It is assumed that the cylinder object is a perfect circle. The diameter tape provides an approximation of diameter; most commonly used in dendrometry.
Stand density index is a measure of the stocking of a stand of trees based on the number of trees per unit area and diameter at breast height (DBH) of the tree of average basal area, also known as the quadratic mean diameter. It may also be defined as the degree of crowding within stocked areas, using various growing space ratios based on crown length or diameter, tree height or diameter, and spacing. Stand density index is usually well correlated with stand volume and growth, and several variable-density yield tables have been created using it. Basal area, however, is usually satisfactory as a measure of stand density index and because it is easier to calculate it is usually preferred over SDI. Stand density index is also the basis for Stand density management diagrams.

An angle gauge is a tool used by foresters to determine which trees to measure when using a variable radius plot design in forest inventory. Using this tool a forester can quickly measure the trees that are in or out of the plot. An angle gauge is similar to a wedge prism though it must be held a fixed distance from the eye to work properly. Unlike the wedge prism, which is held over the plot center, the surveyor's eye is kept over plot-center when using an angle gauge.
The Biltmore stick is a tool used by foresters to estimate tree trunk diameter at breast height. The tool very often includes a hypsometer scale to estimate height as well. It looks much like an everyday yardstick. With practice a Biltmore stick is considered to be exceptionally accurate, often within half an inch on diameters. Some foresters use the tool regularly, however, many prefer to use more accurate tools such as a diameter tape to measure diameter at breast height (DBH) and a clinometer to measure height. On the other end of the spectrum, some foresters consider the use of a Biltmore stick to be no more accurate than their own visual estimates, and make it practice for their surveys to be largely completed in this manner.
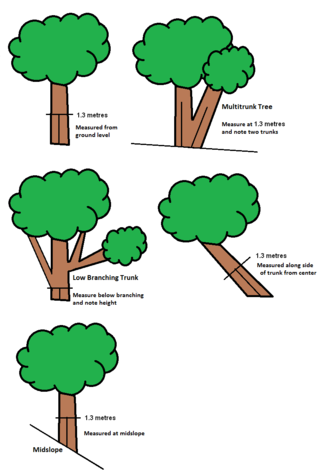
Tree girth is a measurement of the circumference of tree trunk. It is one of the most ancient, quickest, and simplest of foresters' measures of size and records of growth of living and standing trees. The methods and equipment have been standardized differently in different countries. A popular use of this measurement is to compare outstanding individual trees from different locations or of different species.
In forestry, a tree crown measurement is one of the tree measurements taken at the crown of a tree, which consists of the mass of foliage and branches growing outward from the trunk of the tree. The average crown spread is the average horizontal width of the crown, taken from dripline to dripline as one moves around the crown. The dripline is the outer boundary to the area located directly under the outer circumference of the tree branches. When the tree canopy gets wet, any excess water is shed to the ground along this dripline. Some listings will also list the maximum crown spread which represents the greatest width from dripline to dripline across the crown. Other crown measurements that are commonly taken include limb length, crown volume, and foliage density. Canopy mapping surveys the position and size of all of the limbs down to a certain size in the crown of the tree and is commonly used when measuring the overall wood volume of a tree.
Trees have a wide variety of sizes and shapes and growth habits. Specimens may grow as individual trunks, multitrunk masses, coppices, clonal colonies, or even more exotic tree complexes. Most champion tree programs focus finding and measuring the largest single-trunk example of each species. There are three basic parameters commonly measured to characterize the size of a single trunk tree: tree height measurement, tree girth measurement, and tree crown measurement. Foresters also perform tree volume measurements. A detailed guideline to these basic measurements is provided in The Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society by Will Blozan.













