
Roanoke is an independent city in the U.S. state of Virginia. At the 2010 census, the population was 97,032. It is located in the Roanoke Valley of the Roanoke Region of Virginia.

The Blue Ridge Parkway is a National Parkway and All-American Road in the United States, noted for its scenic beauty. The parkway, which is America's longest linear park, runs for 469 miles (755 km) through 29 Virginia and North Carolina counties, linking Shenandoah National Park to Great Smoky Mountains National Park. It runs mostly along the spine of the Blue Ridge, a major mountain chain that is part of the Appalachian Mountains. Its southern terminus is at U.S. 441 on the boundary between Great Smoky Mountains National Park and the Cherokee Indian Reservation in North Carolina, from which it travels north to Shenandoah National Park in Virginia. The roadway continues through Shenandoah as Skyline Drive, a similar scenic road which is managed by a different National Park Service unit. Both Skyline Drive and the Virginia portion of the Blue Ridge Parkway are part of Virginia State Route 48, though this designation is not signed.

The Roanoke River is a river in southern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina in the United States, 410 miles (660 km) long. A major river of the southeastern United States, it drains a largely rural area of the coastal plain from the eastern edge of the Appalachian Mountains southeast across the Piedmont to Albemarle Sound. An important river throughout the history of the United States, it was the site of early settlement in the Virginia Colony and the Carolina Colony. An 81-mile (130 km) section of its lower course in Virginia between the Leesville Lake and Kerr Lake is known as the Staunton River, pronounced, as is the Shenandoah Valley city of that name. It is impounded along much of its middle course to form a chain of reservoirs.

Frederick James Kimball was a civil engineer. He was an early president of the Norfolk and Western Railway and helped develop the Pocahontas coalfields in Virginia and West Virginia.
The Roanoke Valley in southwest Virginia is an area adjacent to and including the Roanoke River between the Blue Ridge Mountains to the east and the Appalachian Plateau to the west. The valley includes much of Roanoke County, as well as the two independent cities of Roanoke and Salem.
WHSV-TV, virtual channel 3, is an ABC-affiliated television station licensed to Harrisonburg, Virginia, United States and serving the Shenandoah Valley. Owned by Gray Television, WHSV maintains studios at 50 North Main Street in downtown Harrisonburg, and operates a newsroom in Fishersville, serving Staunton, Waynesboro, and Augusta County. The station's transmitter is located at Elliott Knob west of Staunton.

State Route 419 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Electric Road, the state highway runs 10.54 miles (16.96 km) from U.S. Route 220 and US 220 Business in Roanoke north to SR 311 at Hanging Rock. SR 419 is a major north–south highway in the western part of the Roanoke Valley, connecting Roanoke and Salem with Cave Spring in southwestern Roanoke County.

Poor Mountain is a ridge of high peaks located in Roanoke County, Virginia and Montgomery County, Virginia. At 3,928 feet, Poor Mountain is the tallest mountain in the immediate area.
Fort Lewis Mountain is a mountain which stretches from Ironto in Montgomery County, Virginia to Masons Cove in Roanoke County, Virginia. The rural community of Bradshaw is located in the narrow valley between the south slope of Catawba Mountain and the north slope of Fort Lewis Mountain. The south slope of the mountain faces the western Roanoke Valley and is directly across from Poor Mountain. Fort Lewis Mountain is separated from Brushy Mountain by a narrow gap formed by Masons Creek. Brushy Mountain stretches in the same southwest to northeast direction for several more miles into Botetourt County, Virginia. Another narrow gap separates Fort Lewis Mountain from Little Brushy Mountain, a small 1,926 foot high peak, which is located in Roanoke County just north of Salem, Virginia.
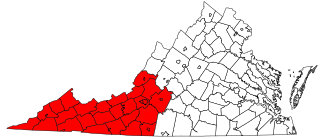
Southwest Virginia, often abbreviated as SWVA, is a mountainous region of Virginia in the westernmost part of the commonwealth. Located within the broader region of western Virginia, Southwest Virginia has been defined alternatively as all Virginia counties on the Appalachian Plateau, all Virginia counties west of the Eastern Continental Divide, or at its greatest expanse, as far east as Blacksburg and Roanoke. Another geographic categorization of the region places it as those counties within the Tennessee River watershed. Regardless of how borders are drawn, Southwest Virginia differs from the rest of the commonwealth in that its culture is more closely associated with Appalachia than the other regions of Virginia. Historically, the region has been and remains rural, but in the 20th century, coal mining became an important part of its economy. With the decline in the number of coal jobs and the decline of tobacco as a cash crop, Southwest Virginia is increasingly turning to tourism as a source of economic development. Collectively, Southwest Virginia's craft, music, agritourism and outdoor recreation are referred to as the region's "creative economy."
Kiwanis Field is a ballpark in Salem, Virginia which was opened in 1932. The ballpark has a capacity of 5,000 people and is primarily used for baseball. Kiwanis Field was the home of a Carolina League team currently known as the Salem Red Sox; at the time, they were the Salem Rebels, Salem Pirates, Salem Redbirds, and Salem Buccaneers. The Salem Avalanche played here briefly in 1995 until they moved to the Salem Memorial Baseball Stadium. The stadium has commanding views of the Blue Ridge Mountains, particularly Twelve O'clock Knob. Until the Salem Football Stadium opened in 1985, Kiwanis Field served as the home football field for Salem High School and its predecessor Andrew Lewis High School. The stadium was known as Salem Municipal Field prior to 1995. Kiwanis Field is currently used for high school, American Legion, and Roanoke College baseball games.

Holston Mountain is a mountain ridge in Upper East Tennessee and southwest Virginia, in the United States. It is in the Blue Ridge Mountains part of the Appalachian Mountains. Holston Mountain is a very prominent ridge-type mountain in Tennessee's Ridge and Valley Region, about 28 miles (45 km) long, running from southwest to northeast, covering about 268 square miles (694 km²). Its highest summit is Holston High Point, on which a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) aircraft navigational beacon is located, at an elevation of 4,280 feet above mean sea level. The second highest point is Rye Patch Knob, at 4,260 feet above mean sea level. The third highest point is Holston High Knob where an old dismantled Cherokee National Forest fire tower marks the elevation at 4,136 feet above mean sea level.
The Roanoke Region is the area of the Commonwealth of Virginia surrounding the city of Roanoke. Its usage may refer to the metropolitan statistical area or the Roanoke Valley, but it sometimes includes areas in the Allegheny Mountains and New River Valley which includes Alleghany county, Montgomery county, Covington, Clifton Forge, Iron Gate, Blacksburg, Christiansburg, and Radford. Rarely, it may include Bedford County and Floyd County.
12 O'clock usually refers the time as shown on a 12-hour clock, either noon - 12 o'clock at daytime - or midnight - 12 o'clock at nighttime.

McAfee Knob is a geological feature with an elevation of 3,197 feet (974 m) above sea level, located on Catawba mountain in Catawba, Virginia, United States. It is named for a Scotch-Irish 18th-century settler. Considered to be the most scenic point along the Appalachian Trail, the vista offers panoramic views of the Catawba Valley, 1,600 feet (490 m) below.

Bent Mountain is an unincorporated community in Roanoke County, Virginia, United States. Bent Mountain is located on U.S. Route 221 13.6 miles (21.9 km) southwest of Roanoke. Bent Mountain has a post office with ZIP code 24059.













