
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

Xandros, Inc. was a software company which sold Xandros Desktop, a Linux distribution. The name Xandros was derived from the X Window System and the Greek island of Andros. Xandros was founded in May 2001 by Linux Global Partners. The company is headquartered in New York City.

Damn Small Linux (DSL) is a computer operating system for the x86 family of personal computers. It is free and open-source software under the terms of the GNU GPL and other free and open source licenses. It was designed to run graphical user interface applications on older PC hardware, for example, machines with 486 and early Pentium microprocessors and very little random-access memory (RAM). DSL is a Live CD with a size of 50 megabytes (MB). What originally began as an experiment to see how much software could fit in 50 MB eventually became a full Linux distribution. It can be installed on storage media with small capacities, like bootable business cards, USB flash drives, various memory cards, and Zip drives.
Slax is a LiveCD Linux distribution developed by Tomáš Matějíček and based on Debian. Packages can be added by apt package manager or can be prepared as modules. The tagline for Slax refers to itself as "your pocket operating system".
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.
The following is a timeline of virtualization development. In computing, virtualization is the use of a computer to simulate another computer. Through virtualization, a host simulates a guest by exposing virtual hardware devices, which may be done through software or by allowing access to a physical device connected to the machine.

Adobe AIR is a cross-platform runtime system currently developed by Harman International for building desktop applications and mobile applications, programmed using Adobe Animate, ActionScript, and optionally Apache Flex. It was originally released in 2008. The runtime supports installable applications on Windows, macOS, and mobile operating systems, including Android, iOS and BlackBerry Tablet OS.
Oracle Secure Global Desktop (SGD) software provides secure access to both published applications and published desktops running on Microsoft Windows, Unix, mainframe and System i systems via a variety of clients ranging from fat PCs to thin clients such as Sun Rays.
Microsoft Application Virtualization is an application virtualization and application streaming solution from Microsoft. It was originally developed by Softricity, a company based in Boston, Massachusetts, acquired by Microsoft on July 17, 2006. App-V represents Microsoft's entry to the application virtualization market, alongside their other virtualization technologies such as Hyper-V, Microsoft User Environment Virtualization (UE-V), Remote Desktop Services, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
This page is a comparison of remote desktop software available for various platforms.

Epesi is an open source, PHP/Ajax framework for rapid development of web based, database driven applications. The framework includes the Epesi CRM multiuser application. It requires PHP 5.x and MySQL or PostgreSQL database server on the server side and can be accessed using any modern browser. Epesi framework and Epesi CRM application are released under MIT license.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier, is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to take control of a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS is Microsoft's implementation of thin client architecture, where Windows software, and the entire desktop of the computer running RDS, are made accessible to any remote client machine that supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). User interfaces are displayed from the server onto the client system and input from the client system is transmitted to the server - where software execution takes place. This is in contrast to application streaming systems, like Microsoft App-V, in which computer programs are streamed to the client on-demand and executed on the client machine.
Turbo is a set of software products and services developed by the Code Systems Corporation for application virtualization, portable application creation, and digital distribution. Code Systems Corporation is an American corporation headquartered in Seattle, Washington, and is best known for its Turbo products that include Browser Sandbox, Turbo Studio, TurboServer, and Turbo.
Opsi is a software distribution and management system for Microsoft Windows clients, based on GNU/Linux servers. Opsi is developed and maintained by uib GmbH from Mainz, Germany. The main parts of Opsi are open-source licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License.
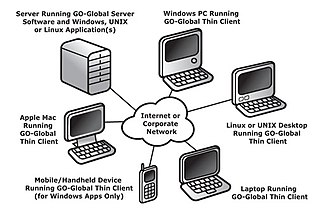
GraphOn GO-Global is a multi-user remote access application publishing solution for Microsoft Windows.

Salix OS is a multi-purpose Linux distribution based on Slackware.
ConnectWise Control is a self-hosted remote desktop software application owned by Connectwise Inc., a software developer based in Tampa, Florida, United States. It was originally developed by Elsinore Technologies in 2008 under the name ScreenConnect.

Ulteo is a software company which provides free and open source (FOSS) virtual desktop solutions. The company is based in Caen, Calvados département, France, and has a research and development center in Colombelles.











