
The Chapultepec Peace Accords were a set of peace agreements signed on January 16, 1992, the day in which the Salvadoran Civil War ended. The treaty established peace between the Salvadoran government and the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN). It was signed in Chapultepec Castle, Mexico.

United Nations Security Council resolution 783, adopted unanimously on 13 October 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991), 718 (1991), 728 (1992), 745 (1992) and 766 (1992) and noting a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali, the council welcomed the progress the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) had made in Cambodia in accordance with the Paris Agreements, however it recognised various security and economic concerns facing UNTAC.
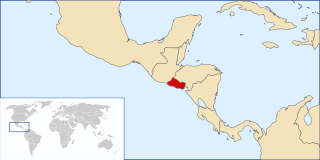
United Nations Security Council resolution 784, adopted unanimously on 30 October 1992, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991) and 729 (1992), the council approved a decision by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a further month until 30 November 1992.

United Nations Security Council resolution 791, adopted unanimously on 30 November 1992, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992) and 784 (1992), the Council approved a decision by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a further six months until 31 May 1993.

United Nations Security Council resolution 818, adopted unanimously on 14 April 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 782 (1992) and 797 (1992) on the situation in Mozambique, the Council stressed its concern regarding the delays and difficulties affecting the implementation of the peace process envisaged in the Rome General Peace Accords during the Mozambican Civil War.

United Nations Security Council resolution 832, adopted unanimously on 27 May 1993, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992) and 791 (1992), the council noted a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali and enlarged the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) to include the observation of the electoral process.

United Nations Security Council resolution 850, adopted unanimously on 9 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 782 (1992), 797 (1992) and 818 (1993) on the situation in Mozambique, the Council discussed the implementation of the Rome General Peace Accords and the formation of a new armed forces in the country.
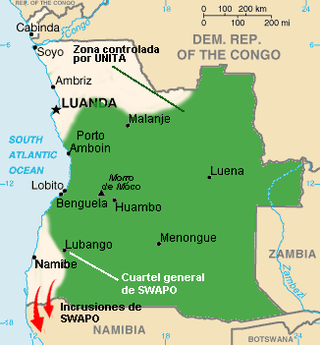
United Nations Security Council resolution 851, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993) and 834 (1993), the Council noted the continuing deterioration of the situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 15 September 1993, discussing further the peace process in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 863, adopted unanimously on 13 September 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 782 (1992), 797 (1992), 818 (1993) and 850 (1993) on the situation in Mozambique, the council discussed the implementation of the Rome General Peace Accords.

United Nations Security Council resolution 872, adopted unanimously on 5 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 812 (1993) and 846 (1993) on the situation in Rwanda and Resolution 868 (1993) on the security of United Nations operations, the council stressed the need for an international force in the country and therefore established the United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda (UNAMIR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 882, adopted unanimously on 5 November 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 782 (1992) and subsequent resolutions on Mozambique, the council noted, in addition to positive developments in the country, that some aspects of the Rome General Peace Accords had not been implemented.

United Nations Security Council resolution 898, adopted unanimously on 23 February 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 782 (1992) and all subsequent resolutions on Mozambique, the Council discussed the implementation of the Rome General Peace Accords and established a 1,144 strong police component of the United Nations Operation in Mozambique (ONUMOZ).

United Nations Security Council resolution 912, adopted unanimously on 21 April 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Rwanda, particularly resolutions 872 (1993) and 909 (1994), the council expressed its alarm and condemnation of the large-scale violence in the country which resulted in the death of thousands of innocent civilians, and proposed a revised mandate of the United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda (UNAMIR).
United Nations Security Council resolution 916, adopted unanimously on 5 May 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 782 (1992) and all subsequent resolutions on Mozambique, the council decided to renew the mandate of the United Nations Operation in Mozambique (ONUMOZ) for a final period ending 15 November 1994, and discussed the implementation of the Rome General Peace Accords.
United Nations Security Council resolution 920, adopted unanimously on 26 May 1994, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992), 832 (1993), 888 (1993), the council discussed the implementation of peace agreements in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) until 30 November 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 961 was adopted unanimously on 23 November 1994, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992), 832 (1993), 888 (1993) and 920 (1994), the council discussed the implementation of peace agreements in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a final time until 30 April 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 966, adopted unanimously on 8 December 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 868 (1993) and all resolutions on Angola, the Council discussed the monitoring of a ceasefire in the country and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 8 February 1995.
United Nations Security Council resolution 991, adopted unanimously on 28 April 1995, after recalling all resolutions and statements on the situation in El Salvador, the Council terminated the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1400, adopted unanimously on 28 March 2002, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sierra Leone, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL) for a further six months until 30 September 2002 in the run up to the May 2002 general elections.

The Truth Commission for El Salvador was a restorative justice truth commission approved by the United Nations to investigate the grave wrongdoings that occurred throughout the country's twelve year civil war. It is estimated that 1.4 percent of the Salvadoran population was killed during the war. The commission operated from July 1992 until March 1993, when its findings were published in the final report, From Madness to Hope. The eight-month period heard from over 2,000 witness testimonies and compiled information from an additional 20,000 witness statements.

















