
The United Nations Protection Force was the first United Nations peacekeeping force in Croatia and in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Yugoslav Wars. The force was formed in February 1992 and its mandate ended in March 1995, with the peacekeeping mission restructuring into three other forces.

The United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia, commonly abbreviated UNCRO, was a United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission in Croatia. It was established under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter and approved by the UN Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 981 on 31 March 1995. UNCRO inherited personnel and infrastructure from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR). Its command was located in Zagreb; the peacekeeping troops were deployed in four sectors named North, South, East, and West. Twenty different countries contributed troops to the mission.

United Nations Security Council resolution 758, adopted unanimously on 8 June 1992, after reaffirming resolutions 713 (1991), 721 (1991), 724 (1991), 727 (1992), 740 (1992) 743 (1992), 749 (1992), 752 (1992) and 757 (1992), the council, in accordance with a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali, decided to enlarge the mandate and strength of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) in former Yugoslavia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 769, adopted unanimously on 7 August 1992, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and all subsequent resolutions relating to the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council authorised enlargements in the strength and mandate of UNPROFOR to "enable the Force to control the entry of civilians into the United Nations Protected Areas", in addition to performing immigration and customs functions.

United Nations Security Council resolution 779, adopted unanimously on 6 October 1992, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions and noting a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali submitted pursuant to resolutions 743 and 762 (1992), the Council authorised the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) to assume responsibility for monitoring the complete withdrawal of the Yugoslav People's Army from Croatia, demilitarization of the Prevlaka peninsula and the removal of heavy weapons from neighbouring areas of Croatia and Montenegro in co-operation with the European Community Monitoring Mission.

United Nations Security Council resolution 802, adopted unanimously on 25 January 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent relevant resolutions and expressing its concern at offensives by the Croatian Army in the United Nations Protected Areas, the council demanded the immediate cessation of hostilities and the withdrawal of Croatian forces from the areas.

United Nations Security Council resolution 807, adopted unanimously on 19 February 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and all subsequent relevant resolutions concerning the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council determined that the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia continued to constitute a threat to international peace and security and therefore extended the mandate of UNPROFOR for an interim period ending 31 March 1993.
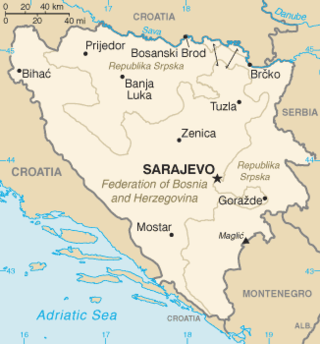
United Nations Security Council resolution 824, adopted unanimously on 6 May 1993, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali pursuant to Resolution 819 (1993), the council discussed the treatment of certain towns and surroundings as "safe areas" in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council resolution 836 was adopted on 4 June 1993. After reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the Council expressed its alarm at the continuing situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina and decided to expand the mandate of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) by allowing it to use force to protect the "safe areas".

United Nations Security Council resolution 847, adopted unanimously on 30 June 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions relating to the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the council condemned military attacks in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina and extended the mandate of UNPROFOR until 30 September 1993.
United Nations Security Council resolution 869, adopted unanimously on 30 September 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions relating to the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council extended its mandate for a further 24 hours until 1 October 1993.

United Nations Security Council resolution 870, adopted unanimously on 1 October 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions relating to the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, extended UNPROFOR's mandate for additional period terminating 5 October 1993.
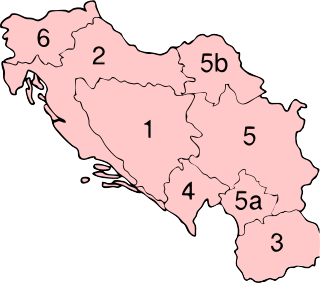
United Nations Security Council resolution 871, adopted unanimously on 4 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 713 (1992) and 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions relating to the situation in the former Yugoslavia and United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council expressed concern that United Nations peacekeeping plan for Croatia, in particular Resolution 769 (1992), had not been implemented and went on to discuss the peace plan and extend UNPROFOR's mandate until 31 March 1994.
United Nations Security Council resolution 908, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia and in particular Resolution 871 (1993), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) until 30 September 1994 and declared its intention to increase the number of personnel in the peacekeeping force.

United Nations Security Council resolution 947, adopted unanimously on 30 September 1994, after recalling all resolutions on the situation on the former Yugoslavia including Resolution 908 (1994), the Council discussed the situation in Croatia and extended the mandate of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) until 31 March 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 958, adopted unanimously on 19 November 1994, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia including Resolution 836 (1993), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, determined that the situation in the former Yugoslavia continued to constitute a threat to international peace and security and in its support of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), authorised the use of air strikes in Croatia in addition to Bosnia and Herzegovina by member states, in order for UNPROFOR to carry out its mandate. UNPROFOR was authorised to use air force independently, via direct member states support or via regional organizations. Subsequent air force interventions in Udbina airfield and other locations in Croatia and Bosnia, were conducted with NATO support.

United Nations Security Council resolution 981, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the council established the United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia (UNCRO) for a period terminating 30 November 1995.
United Nations Security Council resolution 982, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia in particular Resolution 947 (1994) concerning the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council extended the mandate of UNPROFOR for additional period terminating 30 November 1995 and discussed operations in Croatia.
United Nations Security Council resolution 987, adopted unanimously on 19 April 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, in particular Resolution 982 (1994), the Council called for measures to ensure the safety, security and freedom of movement of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) in Bosnia and Herzegovina following attacks on it.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1031, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1995, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, discussed the transfer of authority from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) to the multinational Implementation Force (IFOR).
















