 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Actigall, Urso, others |
| Other names | Ursodiol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a699047 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.437 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
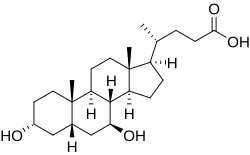
| Formula | C24H40O4 |
| Molar mass | 392.580 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 203 °C (397 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid, produced in humans and most other species from metabolism by intestinal bacteria. It is synthesized in the liver in some species, and was first identified in bile of bears of genus Ursus , from which its name derived. [8] In purified form, it has been used to treat or prevent several diseases of the liver or bile ducts.
Contents
- Medical uses
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- Cholestasis
- Other conditions
- Adverse effects
- Mechanisms of action
- Choleretic effects
- Immunomodulating effects
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Chemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Industrial production
- Society and culture
- Names
- History
- References
It is available as a generic medication. [9] [10]
