
In Christianity, ablution is a prescribed washing of part or all of the body or possessions, such as clothing or ceremonial objects, with the intent of purification or dedication. In Christianity, both baptism and footwashing are forms of ablution. Prior to praying the canonical hours at seven fixed prayer times, Oriental Orthodox Christians wash their hands and face. In liturgical churches, ablution can refer to purifying fingers or vessels related to the Eucharist. In the New Testament, washing also occurs in reference to rites of Judaism part of the action of a healing by Jesus, the preparation of a body for burial, the washing of nets by fishermen, a person's personal washing of the face to appear in public, the cleansing of an injured person's wounds, Pontius Pilate's washing of his hands as a symbolic claim of innocence and foot washing, which is a rite within the Christian Churches. According to the Gospel of Matthew, Pontius Pilate declared himself innocent of the blood of Jesus by washing his hands. This act of Pilate may not, however, have been borrowed from the custom of the Jews. The same practice was common among the Greeks and Romans.
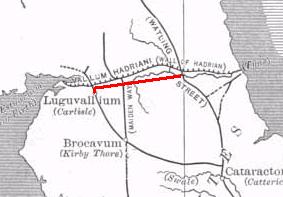
The Stanegate was an important Roman road built in what is now northern England. It linked many forts including two that guarded important river crossings: Corstopitum (Corbridge) on the River Tyne in the east, and situated on Dere Street, and Luguvalium (Carlisle) on the River Eden in the west. The Stanegate ran through the natural gap formed by the valleys of the River Tyne in Northumberland and the River Irthing in Cumbria. It predated Hadrian's Wall by several decades; the Wall would later follow a similar route, albeit slightly to the north.

Maundy, or Washing of the Saints' Feet, Washing of the Feet, or Pedelavium or Pedilavium, is a religious rite observed by various Christian denominations. The word mandatum is the first word of the Latin Biblical quotation sung at the ceremony of the washing of the feet: "Mandatum novum do vobis ut diligatis invicem sicut dilexi vos", from the text of John 13:34 in the Vulgate. The ceremony commemorates the commandment of Christ that his disciples should emulate his loving humility in the washing of the feet. The medieval Latin term mandatum, came to apply to the rite of foot-washing on the Thursday preceding Easter Sunday, known in English as "Maundy Thursday" since at least 1530.

Callosa d'en Sarrià (Valencian:[kaˈʎozaðensariˈa] is a Valencian town and municipality located in the comarca of Marina Baixa, in the province of Alicante, Spain, lying in the valley of the river Guadalest, 50 km from the city of Alicante. Callosa d'en Sarrià has an area of 24.8 km2 and according to the 2003 census, a total population of 8,060 inhabitants. The economy of Callosa is chiefly based on tourism and agriculture: it is the main producer of loquat in Spain. The most important monuments in the town are the Catholic archipresbyteral church of Sant Joan Baptista, built in the 18th century, and the Fortress of Bèrnia, built in the 17th century at the top of a nearby mountain to defend the city from pirates and Moriscos.

The Dolaucothi Gold Mines, also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are ancient Roman surface and underground mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales. The gold mines are located within the Dolaucothi Estate, which is owned by the National Trust.

Pumsaint is a village in Carmarthenshire, Wales, halfway between Llanwrda and Lampeter on the A482 in the valley of the Afon Cothi. It forms part of the extensive estate of Dolaucothi, which is owned by the National Trust.

Whickham is a village in Tyne and Wear, North East England. It is in the Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead. The village is on high ground overlooking the River Tyne and 5 miles (8 km) south-west of Newcastle upon Tyne. It was formerly governed under the historic county of County of Durham.

Segedunum was a Roman fort at modern-day Wallsend, North Tyneside in North East England. The fort lay at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall near the banks of the River Tyne, forming the easternmost portion of the wall. It was in use as a garrison for approximately 300 years, from around 122 AD, almost up to 400 AD. Today, Segedunum is the most thoroughly excavated fort along Hadrian's Wall, and is operated as Segedunum Roman Fort, Baths and Museum. It forms part of the Hadrian's Wall UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Incense Route – Desert Cities in the Negev is a World Heritage-designated area near the end of the Incense Route in the Negev, southern Israel, which connected Arabia to the Mediterranean in the Hellenistic-Roman period, proclaimed as being of outstanding universal value by UNESCO in 2005. The trade led to the development of ancient towns, forts and caravanserai en route, apart from agricultural development.
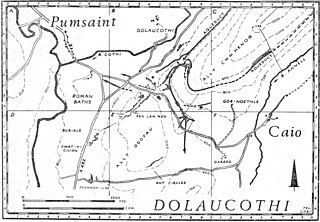
Luentinum or Loventium refers to the Roman fort at Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire. The 1.9 hectares site lies either side of the A482 in Pumsaint and was in use from the mid 70s AD to around 120 AD. It may have had particular functions associated with the adjacent Dolaucothi Gold Mines. It formed part of a network of at least 30 forts across Wales, such as Llandovery, Bremia/Llanio near Llanddewi Brefi, and the fort at Llandeilo. The Roman road Sarn Helen, which runs past the Llanio and Llandovery forts was nearby.

Bremetennacum,, or Bremetennacum Veteranorum, was a Roman fort on the site of the present day village of Ribchester in Lancashire, England. The site is a Scheduled Monument.

Vindomora was an auxiliary fort on Dere Street, in the province of Lower Britain. Its ruins, now known as Ebchester Roman Fort, are situated at Ebchester in the English county of Durham, to the north of Consett and 12 miles (19 km) west-south-west from Newcastle upon Tyne.

Uxelodunum was a Roman fort. It was the largest fort on Hadrian's Wall, and is now buried beneath the suburb of Stanwix, in Carlisle, Cumbria, England.

Maia, or Mais, in Cumbria, England was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, and was the last fort at the western end of the Wall, overlooking the Solway Firth.

Fort Sinquefield is the historic site of a wooden stockade fortification in Clarke County, Alabama, near the modern town of Grove Hill. It was built by early Clarke County pioneers as protection during the Creek War and was attacked in 1813 by Creek warriors.

Caesar's Camp is an Iron Age hill fort around 2,400 years old. It is located just in Crowthorne civil parish to the south of Bracknell in the English county of Berkshire. It falls within the Windsor Forest and is well wooded, although parts of the fort have now been cleared of some trees. The area is managed by the Forestry Commission but owned by Crown Estate, and is open and accessible to the public. The hill fort covers an area of about 17.2 acres and is surrounded by a mile-long ditch, making it one of the largest in southern England.

Avchitgad is a fort located in the Sahyadri ranges of Maharashtra. The fort is situated near Roha in the Raigad district. At the base of this fort is a village called Medha and Padam - Kharapti.

Mynydd Mallaen is an expansive plateau to the northwest of Cilycwm in northeast Carmarthenshire, Wales. It forms part of the Cambrian Mountains massif, and is north-west of the Black Mountain (range) in the Brecon Beacons. It takes the form of an undulating plateau with steep slopes dropping away to the Towy valley to the east and those of the Gwenffrwd, Nant Melyn and Afon Cothi to the north and west. Its highest point of 1516 feet or 462m at OS grid reference SN 723455 is surmounted by two Bronze Age cairns known as Crugiau Merched. Caeo Forest covers much of the southern flanks of the hill and smaller forests also cover its eastern slopes. Much of the native woodland consists of sessile oak groves, especially on the valley sides. The human population is very low, being restricted to hill farms engaged in sheep farming, and some holiday cottages.
Rainwater harvesting in the United Kingdom is a practice of growing importance. Rainwater harvesting in the UK is both a traditional and reviving technique for collecting water for domestic uses and is generally used for non-hygienic purposes like watering gardens, flushing toilets, and washing clothes. In commercial premises like supermarkets it is used for things like toilet flushing where larger tank systems can be used collecting between 1000 and 7500 litres of water. It is claimed that in the South East of England there is less water available per person than in many Mediterranean countries.





















