
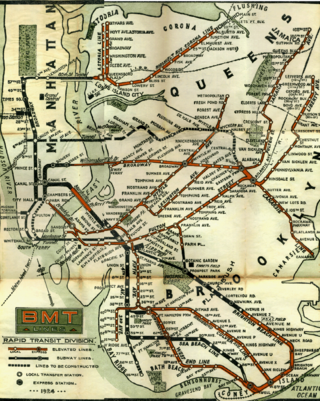
The Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT) was a public transit holding company formed in 1896 to acquire and consolidate railway lines in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States. It was a prominent corporation and industry leader using the single-letter symbol B on the New York Stock Exchange.
The BMT West End Line is a line of the New York City Subway, serving the Brooklyn communities of Sunset Park, Borough Park, New Utrecht, Bensonhurst, Bath Beach and Coney Island. The D train operates local on the entire line at all times. Although there is a center express track and three express stations along the line, there is no regular express service.
The BMT Lexington Avenue Line was the first standard elevated railway in Brooklyn, New York, operated in its later days by the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company, the Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation, and then the City of New York.

The Coney Island–Stillwell Avenue station is a New York City Subway terminal in Coney Island, Brooklyn. It is the railroad-south terminus for the D, F, N, and Q trains at all times and for the <F> train during rush hours in the peak direction.
The BMT Sea Beach Line is a rapid transit line of the BMT division of the New York City Subway, connecting the BMT Fourth Avenue Line at 59th Street via a four-track wide open cut to Coney Island in Brooklyn. It has at times hosted the fastest express service between Manhattan and Coney Island, since there are no express stations along the entire stretch, but now carries only local trains on the N service, which serves the entire line at all times. During rush hours, several W trains serve the line north of 86th Street.
Starting in 1899, the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company and Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation operated rapid transit lines in New York City — at first only elevated railways and later also subways.

The South Brooklyn Railway is a railroad in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. It is owned by the government of New York City and operated by the New York City Transit Authority. Its original main line ran parallel to 38th Street from the Upper New York Bay to McDonald Avenue, and south on McDonald Avenue to the Coney Island Yards, mostly underneath the former Culver Shuttle and the IND Culver Line of the New York City Subway.

Culver Depot, also called Culver Terminal or Culver Plaza, was a railroad and streetcar terminal in Coney Island, Brooklyn, New York City, United States, located on the northern side of Surf Avenue near West 5th Street. It was just north of the boardwalk, near the former Luna Park amusement complex, and across from the current New York Aquarium. Originally built by the Prospect Park and Coney Island Railroad for the Culver surface line, it later became a major terminal for the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT).
The Culver Line, Gravesend Avenue Line, or McDonald Avenue Line was a surface public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running along McDonald Avenue and built by the Prospect Park and Coney Island Railroad. Most of its main line has been essentially replaced by the IND Culver Line of the New York City Subway.

The B54 is a bus route on Myrtle Avenue in Brooklyn, New York City. The line travels between Downtown Brooklyn in the west and Myrtle–Wyckoff Avenues station in the east. The B54 operates from MTA New York City Bus's Fresh Pond Depot in Ridgewood, Queens. The route serves only the section of Myrtle Avenue within Brooklyn; the section within Queens is served by the Q55 bus.

The DeKalb Avenue Line is a public transit line in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, running mostly along DeKalb Avenue, as well as eastbound on Lafayette Avenue, between Downtown Brooklyn and Ridgewood, Queens. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the B38 DeKalb/Lafayette Avenues bus route, operated by the New York City Transit Authority.

The Nassau Electric Railroad was an electric street railway company in the U.S. state of New York. The company operated throughout the borough of Brooklyn, as well as over the Brooklyn Bridge and Williamsburg Bridge into Manhattan.

The B63 is a bus route in Brooklyn, New York City, running mainly along Fifth Avenue and Atlantic Avenue between Fort Hamilton and Cobble Hill. Originally a streetcar line called the Fifth Avenue Line, it is now operated by the New York City Transit Authority as the Fifth/Atlantic Avenues bus.
The Long Island Rail Road is a railroad owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority in the U.S. state of New York. It is the oldest United States railroad still operating under its original name and charter. It consolidated several other companies in the late 19th century. The Pennsylvania Railroad owned the Long Island Rail Road for the majority of the 20th century and sold it to the State in 1966.

The Fifth Avenue Line, also called the Fifth Avenue Elevated or Fifth Avenue–Bay Ridge Line, was an elevated rail line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States. It ran above Hudson Avenue, Flatbush Avenue, Fifth Avenue, 38th Street, and Third Avenue from Downtown Brooklyn south to Bay Ridge. The portion on Third Avenue was called the Third Avenue Elevated to distinguish service from the elevated BMT West End Line; it was separate from the elevated IRT Third Avenue Line in Manhattan and the Bronx.

The B48 bus route constitutes a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, running along Lorimer Street, Franklin Avenue, and Classon Avenue between Flatbush and Greenpoint. Originally the Lorimer Street streetcar line, it is now a bus route operated by MTA New York City Bus.
The Adams Street and Boerum Place Line was a public transit line in Downtown Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running along Boerum Place and Adams Street. It served as access for the Atlantic Avenue Railroad to the City Hall area.

From 1898 to 1950, various companies operated local trolley lines over the Brooklyn Bridge, taking passengers from many points in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States to the Park Row terminal in Lower Manhattan. These lines entered the bridge roadway from Fulton Street or Sands Street in Downtown Brooklyn, some of them using elevated trackage at the Sands Street elevated railway station.
The 86th Street Line or Streetcar Line #31 was a streetcar line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, mostly running along Bath Avenue and other Streets between Coney Island and Sunset Park. Built by the Brooklyn and Queens Transit Corporation as a Streetcar line this route has now been entirely replaced by the B1 and B64 buses.















